Abstract
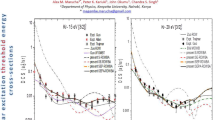
Data on excitation of rare gases is mainly important in the study of lighting, plasma displays and lasers. From literature, cross sections data on electron impact excitation of low-lying resonance states of xenon atoms with both relativistic and non-relativistic computations often differ with available experimental data mostly at low and intermediate impact energies and at intermediate scattering angles. With this in view, we have applied relativistic effects in a fully relativistic distorted-wave born approximation approach to excitation of the lowest lying resonance states of a xenon target atom in a complex potential in order to solve the Dirac equations to obtain the free electron wavefunctions and corresponding excitation cross sections. Present differential cross sections (DCS) results from this study predict that absorption effects in the distortion potential generally have minimal effect on cross sections at impact energies below 50 eV, but then significantly improve these results in comparison with experiments as kinetic energy of the incident electron increases. Furthermore, it is evident that the energy dependent dynamic polarization potential adopted plays a major role in improving shapes of cross sections at low and near threshold impact energies, where other distorted-wave methods fail to give satisfactory results.
Graphical abstract
We have applied a fully relativistic distorted-wave (RDW) approach to inelastic excitation of the lowest J = 1 states of xenon in which a complex potential (SEPA = static (S), + exchange (SE), + polarization (SEP) and + absorption (SEPA)) is used to solve the Dirac equations to obtain electron initial and final wave functions \(\chi_{a}^{ + }\) and \(\chi_{b}^{ + }\) respectively). The transition matrix \(T_{a \to b}^{RDW} = \left\langle {\chi_{b}^{ - } \left| {V - U} \right|A\chi_{a}^{ + } } \right\rangle\) is then used to obtain the differential cross sections. Theoretical studies on excitation of xenon J = 1 states [1,2,3] have not yet applied this approach. Experimental (Expt.) results are in bullets while calculations are in full and dotted lines. Present DCS results predict that the polarization potential plays a major role of improving cross sections at low and near excitation threshold while absorption does this above 50 eV.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: Data analyzed and presented in this article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.]
References
N. Andreas, D. Michael, S. Hermann, P. Heinzwerner, J. Chem. Phys. 102, 8 (1995)
K. Bartschat, D.H. Madison, J. Phys. B 20, 5839 (1987)
C.J. Bostock, C.J. Fontes, D.V. Fursa, H.L. Zhang, I. Bray, Phys. Rev. A. 88, 012711 (2013)
C.F. Fischer, G. Gaigalas, P. Jonsson, J. Bieron. Comput. Phys. Commun. 237, 184 (2019)
D. Filipovic, B. Marinkovic, V. Pejcev, L. Vuscovic, Phys. Rev. A 37, 356 (1988)
C.J. Fontes, H.L. Zhang, Phys. Rev. A 76, 040703 (2007)
J.B. Furness, I.E. McCarthy, J. Phys. B 6, 2280 (1973)
I.P. Grant, Adv. Phys. 19, 747 (1970)
Y. Itikawa, Phys. Rep. 143, 2 (1986)
S. Kaur, R. Srivastava, R.P. McEachran, A.D. Stauffer, J. Phys. B 31, 157 (1998)
S.P. Khare, K. Ashok, Vijayshri, J. Phys. B. 18, 1827 (1985)
M. Khakoo, S. Trajmar, L.R. LeClair, I. Kanik, G. Csanak, C.J. Fontes, J. Phys. B 29, 3455 (1996)
M. Khakoo, P. Vandeventer, J.G. Childers, I. Kanik, C.J. Fontes, K. Bartschat, V. Zeman, D.H. Madison, S. Saxena, R. Srivastava, A.D. Stauffer, J. Phys. B 37, 247 (2004)
D.H. Madison, C.M. Maloney, J.B. Wang, J. Phys. B 31, 873 (1998)
A.M. Marucha, P.K. Kariuki, J. Okumu, C.S. Singh, J. Phys. Commun. 5, 075011 (2021)
A.M. Marucha, P.K. Kariuki, J. Okumu, C.S. Singh, Eur. Phys. J. D 75, 225 (2021)
R.P. McEachran, A.D. Stauffer, J. Phys. B 19, 3523 (1986)
S. Nakazaki, K.A. Berrington, W. Eissner, Y. Itikawa, J. Phys. B 30, 5805 (1997)
H. Nishimura, A. Danjo and T. Matsuda. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Physics of Electronic and Atomic Collisions ( ed Coggiola, M. J. Huestic, D. L. and Saxon, R. P. (Amsterdam: North-Holland) Abstracts p 108 (1985)
W.F. Perger, Z. Halabuka, D. Trautmann, Comput. Phys. Commun. 76, 250 (1993)
K. Sharma, Acta. Phys. Pol. A 126, 3 (2014)
G. Staszewska, W. Schwenke, G. Truhlar, Phys. Rev. A 29, 3078 (1984)
T. Zuo, R.P. McEachran, A.D. Stauffer, J. Phys. B 24, 2853 (1991)
T. Zuo, R.P. McEachran, A.D. Stauffer, J. Phys. B 25, 3393 (1992)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Kenyatta University for partly supporting this research through the African Development Bank funds which were released in the year 2017 to various departments of the School of Pure and Applied Sciences. Furthermore we thank the National Research Fund Kenya for funding this research by giving funds for purchase of equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Alex M. Marucha, Peter K. Kariuki, John Okumu, and Chandra S. Singh contributed equally toward the design and implementation of the research, to the analysis of the results and to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marucha, A.M., Kariuki, P.K., Okumu, J. et al. The role of dynamic absorption and polarization potentials in relativistic excitation of xenon. Eur. Phys. J. D 76, 80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00396-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00396-5