Abstract
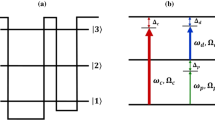
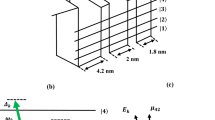
The characteristics of an electromagnetically induced grating (EIG) created in symmetric multiple quantum wells in the regime of electromagnetically induced transparency have been presented. The EIG is created due to absorption and phase modulation under the electromagnetically induced transparency. The increasing value of the Rabi frequency of control standing wave enhances transmission through the EIG. In addition, it is found that the diffraction efficiency of the grating and the intensity of the first-order diffraction can be controlled by controlling the Rabi frequency of the standing wave control field and the interaction length in the quantum well. Optical nonlinearities can improve the diffraction intensity of significant orders, particularly zeroth and first order. The improvement is largest in case only the Kerr is the dominant nonlinearity and moderate under quintic nonlinearity. Present results may be useful in communication and signal processing.
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The manuscript has no associated data, or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.]
References
S.E. Harris, Electromagn. Induc. Transpar. Phys. Today 50, 36–42 (1997)
J.P. Marangos, Electromagnetically induced transparency. J. Mod. Opt. 45, 471–503 (1998)
M. Fleischhauer, A. Imamoglu, J.P. Marangos, Electromagnetically induced transparency: optics in coherent media. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 633 (2005)
J.F. Dynes, M.D. Frogley, J. Rodger, C.C. Philips, Optically mediated coherent population trapping in asymmetric semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 72, 085323–327 (2005)
M.D. Frogley, J.F. Dynes, M. Beck, J. Faist, C.C. Philips, Gain without inversion in semiconductor nanostructures. Nat. Mater. 5, 175–178 (2006)
Y. Niu, S. Gong, R. Li, Z. Xu, X. Liang, Giant kerr nonlinearity induced by interacting dark resonances. Opt. Lett. 30, 3371–3373 (2005)
H. Schmidt, A. Imamoglu, Giant Kerr nonlinearities obtained by electromagnetically induced transparency. Opt. Lett. 21, 1936–1938 (1996)
N. Borgohain, M. Belic, S. Konar, Giant parabolic nonlinearities at infrared in \(\Lambda \)-type three level multiple quantum wells. Annl. Phys. 361, 107 (2015)
C. Zhu, G. Huang, Giant Kerr nonlinearity controlled entangled photons and polarization phase gates in coupled quantum-well structures. Opt. Express 19, 23364–23376 (2011)
E. Paspalakis, P.L. Knight, Phase control of spontaneous emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 293 (1998)
Y. Niu, S. Gong, Enhancing Kerr nonlinearity via spontaneously generated coherence. Phys. Rev. A 73, 053811 (2006)
Z.J. Simmons, N.A. Proite, J. Miles, D.E. Sikes, D.D. Yavuz, Refractive index enhancement with vanishing absorption in short, high-density vapor cells. Phys. Rev. A 85, 053810 (2012)
J.E. Field, K.H. Hahn, S.E. Harris, Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency in collisionally broadened lead vapor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 3062 (1991)
L.V. Hau, S.E. Harris, Z. Dutton, C.H. Behroozi, Light speed reduction to 17 metres per second in an ultracold atomic gas. Nature 397, 594–598 (1999)
C. Liu, Z. Dutton, C.H. Behroozi, L.V. Hau, Observation of coherent optical information storage in an atomic medium using halted light pulses. Nature 409, 490–493 (2001)
J. Clarke, H. Chen, A.V. Wijngaarden, Electromagnetically induced transparency and optical switching in a rubidium cascade system. Appl. Opt. 40, 2047–2051 (2001)
M.D. Lukin, A. Imamoglu, Controlling photons using electromagnetically induced transparency. Nature 413, 273–276 (2001)
A. Joshi, M. Xiao, Optical bistability in a three-level semiconductor quantum-well system. Appl. Phys. B 79, 65–69 (2004)
J. Li, R. Yu, J. Liu, P. Huang, X. Yang, Voltage-controlled optical bistability of a tunable three-level system in a quantum- dot molecule. Physica E 41, 70–73 (2008)
Y. Zhang, A.W. Brown, M. Xiao, Opening four-wave mixing and six-wave mixing channels via dual electromagnetically induced transparency windows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 123603 (2007)
G.X. Huang, C. Hang, L. Deng, Gain-assisted superluminal optical solitons at very low light intensity. Phys. Rev. A 77, 011803(R) (2008)
S. Shwetanshumala, S. Konar, A. Biswas, Ultraslow solitons due to large quintic nonlinearity in coupled quantum well structures driven by two control laser beams. Appl. Phys. B 111, 53–64 (2013)
M. Sahrai, H. Tajalli, K.T. Kapale, M.S. Zubairy, Tunable phase control for subluminal to superluminal light propagation. Phys. Rev. A 70, 023813 (2004)
A. Andre, M.D. Lukin, Manipulating light pulses via dynamically controlled photonic band gap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 143602 (2002)
M. Artoni, G.C. La Rocca, Optically tunable photonic stop bands in homogeneous absorbing media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 073905 (2006)
H.Y. Ling, Y.Q. Li, M. Xiao, Electromagnetically induced grating: homogeneously broadened medium. Phys. Rev. A 57, 1338 (1998)
G.C. Cardoso, J.W.R. Tabosa, Electromagnetically induced gratings in a degenerate open two-level system. Phys. Rev. A 65, 033803 (2002)
M. Mitsunaga, N. Imoto, Observation of an electromagnetically induced grating in cold sodium atoms. Phys. Rev. A 59, 4773–4776 (1999)
L.E.E. de Araujo, Electromagnetically induced phase grating. Opt. Lett. 35, 977–979 (2010)
R.G. Wan, J. Kou, L. Jiang, Y. Jiang, J.Y. Gao, Electromagnetically induced grating via enhanced nonlinear modulation by spontaneously generated coherence. Phys. Rev. A 83, 033824 (2011)
A.W. Brown, M. Xiao, All-optical switching and routing based on an electromagnetically induced absorption grating. Opt. Lett. 30, 699–701 (2005)
Y. Zhang, Z. Wu, M.R. Belic, H. Zheng, Z. Wang, M. Xiao, Y. Zhang, Photonic Floquet topological insulators in atomic ensembles. Laser Photon. Rev. 9, 331–338 (2015)
J.W.R. Tabosa, A. Lezama, G. Cardoso, Transient Bragg diffraction by a transferred population grating: application for cold atoms velocimetry. Opt. Commun. 165, 59 (1999)
B.K. Dutta, P.K. Mahapatra, Electromagnetically induced grating in a three-level \(\Xi \)-type system driven by a strong standing wave pump and weak probe fields. J. Phys. B 39, 1145 (2006)
Z.H. Xiao, S.G. Shin, K. Kim, An electromagnetically induced grating by microwave modulation. J. Phys. B 43, 161004 (2010)
B. Xie, X. Cai, Z.-H. Xiao, Electromagnetically induced phase grating controlled by spontaneous emission. Opt. Commun. 285, 133–135 (2012)
S.H. Asadpour, A. Panahpour, M. Jafari, Phase-dependent electromagnetically induced grating in a four-level quantum system near a plasmonic nanostructure. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133, 411 (2018)
S.H. Asadpour, M. Jafari, Plasmon-induced phase grating via nonlinear modulation. Opt. Commun. 421, 125–133 (2018)
T. Shui, L. Li, X. Wang, W.-X. Yang, One- and two-dimensional electromagnetically induced gratings in an \({Er}^{3+}\) doped yttrium aluminum garnet crystal. Sci. Rep. 10, 4019 (2020)
F. Zhou, Y. Qi, H. Sun, D. Chen, J. Wang, Y. Niu, S. Gong, Electromagnetically induced grating in asymmetric quantum wells via Fano interference. Opt. Express 21, 12249 (2013)
H. Kang, G. Hemandez, Y. Zhu, Slow-Light six-wave mixing at low light intensities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 073601 (2004)
C. Hang, Y. Li, L. Ma, G. Huang, Three-way entanglement and three-qubit phase gate based on a coherent six-level atomic system. Phys. Rev. A 74, 012319 (2006)
D.K. Giri, P.S. Gupta, Short-time squeezing effects in spontaneous and stimulated six-wave mixing process. Opt. Commun. 221, 135–143 (2003)
Y. Zhang, U. Khadka, B. Anderson, M. Xiao, Temporal and spatial interference between four-wave mixing and six- wave mixing channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 013601 (2009)
A. Vafafard, M. Sahrai, H.R. Hamedi, S.H. Asadpour, Tunneling induced two-dimensional phase grating in a quantum well nanostructure via third and fifth orders of susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 10, 7389 (2020)
A. Vafafard, M. Sahrai, V. Siahpoush, H.R. Hamedi, S.H. Asadpour, Optically induced diffraction gratings based on periodic modulation of linear and nonlinear effects for atom-light coupling quantum systems near plasmonic nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 10, 16684 (2020)
B.K. Dutta, P. Panchadhyayee, I. Bayal, P.K. Mahapatra, N. Das, Multi-wave-mixing-induced nonlinear modulation of diffraction peaks in an opto-atomic grating. Sci. Rep. 10, 16779 (2020)
J. Faist, F. Capasso, C. Sirtori, D.L. Sivco, A.L. Hutchinson, S.N.G. Chu, A.Y. Cho, Measurement of the intersubband scattering rate in semiconductor quantum wells by excited state differential absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 1354 (1993)
M.O. Scully, M.S. Zubairy, Quantum Optics, 1st edn. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001)
W.X. Wang, J.M. Hou, R.K. Lee, Ultraslow bright and dark solitons in semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. A 77, 033838 (2008)
C.R. Lee, Y.C. Li, F.K. Men, C.H. Pao, Y.C. Tsai, J.F. Wang, Model for an inversionless two-color laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 201112 (2005)
E. Paspalakis, M. Tsaousidou, A.F. Terzis, Coherent manipulation of a strongly driven semiconductor quantum well. Phys. Rev. B 73, 125344 (2006)
J.H. Li, Controllable optical bistability in a four-subband semiconductor quantum well system. Phys. Rev. B 75, 155329 (2007)
N. Borgohain, S. Konar, The effects of control field detuning on the modulation instability in a three-level quantum well system. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 213103 (2016)
D. Pushkarov, S. Tanev, Bright and dark solitary wave propagation and bistability in the anomalous dispersion region of optical waveguide with third and fifth order nonlinearities. Opt. Commun. 124, 354–364 (1996)
A.S. Reyna, C.B. de Araújo, Spatial phase modulation due to quintic and septic nonlinearities in metal colloids. Opt. Express. 22, 22456–22469 (2014)
R. Mukherjee, S. Konar, P. Mishra, Phase-sensitive modulation instability in coupled quantum wells. Phys. Rev. A 103, 033517 (2021)
F. Bozorgzadeh, M. Sahrai, Laser-induced diffraction grating in asymmetric double quantum well nanostructure. Laser. Phys. Lett. 16, 036002 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We thank unanimous referees for valuable comments which have been very helpful to improve the quality of the manuscript. One of the authors Rohit Mukherjee would like to thank Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), Government of India, New Delhi, for providing fellowship through the R&D project ERIP/ER/1202225/M/01/1668. The work is financially supported by DRDO; SK would like to thank and acknowledge for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equal contributions in this work.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, R., Konar, S. Effects of giant Kerr and quintic nonlinearities on electromagnetically induced grating in multiple quantum wells. Eur. Phys. J. D 75, 263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00272-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00272-8