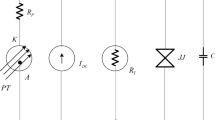
Abstract
The transmission and encoding of information in the brain has been the subject of much research. The aim is to improve biophysical functions and to design reliable artificial synapses for the connection of several biological neurons. In this manuscript, it is coupled through a hybrid synapse two FitzHugh–Nagumo neural circuits driven simultaneously by a phototube and a thermistor. The hybrid synapse is based on an ideal Josephson Junction in parallel with a linear resistance. This configuration allows the evaluation of the external magnetic field in the neural circuit. Using the standard scale transformation on the physical variables and parameters, we obtain the mathematical model of the coupled neurons. A bifurcation analysis on the intrinsic parameters of the coupling channel is carried out to demonstrate the complete synchronization and phase synchronization. It can be seen a synchronization stability when the parameters of the coupling channel are well defined. To practically confirm these results, an electronic circuit is designed using discrete electronic components and multipliers. Thanks to the simulations in the PSpice software, we see that this circuit can well and well be used to estimate the effect of the external magnetic field on a coupled neural circuit and predict a stable synchronization.
Graphical abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All the information’s were given in the paper to generate the results in the paper; there is no need of the deposited data.]
References
Z. Aram, S. Jafari, J. Ma, J.C. Sprott, S. Zendehrouh, V.T. Pham, Using chaotic artificial neural networks to model memory in the brain. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 44, 449–59 (2017)
C. Borgers, An Introduction to Modeling Neuronal Dynamics, vol. 17 (Springer, Berlin, 2017)
A. Mondal, R. KumarUpadhyay, J. Ma, B.K. Yadav, S.K. Sharma, Bifurcation analysis and diverse firing activities of a modified excitable neuron model. Cogn. Neurodyn. 13, 393–407 (2017)
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. Lond. 117, 500 (1952)
J.L. Hindmarsh, R.M. Rose, A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296, 162–164 (1982)
J.L. Hindmarsh, R.M. Rose, A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 221, 87–102 (1984)
R. Fitzhugh, Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J . 1, 445–466 (1961)
C. Morris, H. Lecar, Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J . 35, 193–213 (1981)
T.R. Chay, Chaos in a three-variable model of an excitable cell. Phys. D. 16, 233–242 (1985)
J.J. Hopfield, Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of 2-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 3088–3092 (1984)
H.G. Gu, B.B. Pan, G.R. Chen, L.X. Duan, Biological experimental demonstration of bifurcations from bursting to spiking predicted by theoretical models. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 391–407 (2014)
J. Ma, X. Song, J. Tang et al., Wave emitting and propagation induced by autapse in a forward feedback neuronal network. Neurocomputing 167, 378–389 (2015)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, H. Wang et al., Spiking activities in chain neural network driven by channel noise with field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3237–3247 (2019)
L. Lu, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda et al., Effects of noise and synaptic weight on propagation of subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic current signal in a feed-forward neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1673–1686 (2019)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, Y. Xu et al., Wave propagation and synchronization induced by chemical autapse in chain Hindmarsh-Rose neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 352, 136–145 (2019)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda et al., Propagation of firing rate by synchronization in a feed-forward multilayer Hindmarsh-Rose neural network. Neurocomputing 320, 60–68 (2018)
J. Tang, J. Zhang, J. Ma et al., Noise and delay sustained chimera state in small world neuronal network. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62, 1134–1140 (2019)
H. Zhang, Q. Wang, M. Perc et al., Synaptic plasticity induced transition of spike propagation in neuronal networks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18, 601–615 (2013)
M. Dipoppa, A. Ranson, M. Krumin et al., Vision and locomotion shape the interactions between neuron types in mouse visual cortex. Neuron 98(3), 602–615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.037
F. Gabbiani, H.G. Krapp, C. Koch et al., Multiplicative computation in a visual neuron sensitive to looming. Nature 420(6913), 320–324 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01190
S. Peron, F. Gabbiani, Spike frequency adaptation mediates looming stimulus selectivity in a collision-detecting neuron. Nat. Neurosci. 12(3), 318–326 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2259
P. Heil, First-spike latency of auditory neurons revisited. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14(4), 461–467 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2004.07.002
C.K. Machens, H. Schütze, A. Franz et al., Single auditory neurons rapidly discriminate conspecific communication signals. Nat. Neurosci. 6(4), 341–342 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1036
P. Zhou, Z. Yao, J. Ma et al., A piezoelectric sensing neuron and resonance synchronization between auditory neurons under stimulus. Chaos Solitons Fract. 145, 110751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110751
T. Nakayama, Thermosensitive neurons in the brain. Jpn. J. Physiol. 35(3), 375–389 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2170/jjphysiol.35.375
M. Ruchty, F. Roces, C.J. Kleineidam, Detection of minute temperature transients by thermosensitive neurons in ants. J. Neurophysiol. 104(3), 1249–1256 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00390.2010
Y. Xu, M.H. Liu, Z.G. Zhu et al., Dynamics and coherence resonance in a thermosensitive neuron driven by photocurrent. Chin. Phys. B 29(9), 098704 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab9dee
Y. Xu, Y.Y. Guo, G.D. Ren et al., Dynamics and stochastic resonance in a thermosensitive neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 385, 125427 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2020.125427
L. Zhang, S. Jones, K. Brody et al., Thermosensitive transient receptor potential channels in vagal afferent neurons of the mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liv. Physiol. 286(6), G983–G991 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00441.2003
L. Yong, X. Wan-jiang, M. Jun, A. Faris, H. Aatef, A new photosensitive neuron model and its dynamics. Inform. Technol. Electron. Eng, Front. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1900606
T.J. Fossi, H.C. Edima, T.Z. Njitacke, K.F. Feudjio, N.R. Mballa, J. Atangana, Bifurcations analysis and experimental study of the dynamics of a thermosensitive neuron conducted simultaneously by photocurrent and thermistance. Phys. J. Spec. Top. Eur. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00311-w
C. Grebogi, E. Ott, J.A. Yoke, Crises, sudden changes in chaotic attractors and transient chaos. Phys. D 7, 181–200 (1983)
A. Pikovsky, G. Osipov, M. Rosenblum, M. Zaks, J. Kurths, Attractor-repeller collision and eyelet intermittency at the transition to phase synchronization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(1), 47–50 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.79.47
M. Desroches, B. Krauskopf, H.M. Osinga, Mixed-mode oscillations and slow manifolds in the self-coupled FitzHugh–Nagumo system. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 18(1), 015107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2799471
M. Abdelouahab, R. Lozi, L.O. Chua et al., Int. J. Bifur. Chaos 24, 1430023 (2014)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, Y. Xu, L. Yang, Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 515–23 (2017)
Lv. Mi, C. Wang, G. Ren, J. Ma, X. Song, Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–90 (2016)
S. Mostaghimi, F. Nazarimehr, S. Jafari, J. Ma, Chemical and electrical synapse modulated dynamical properties of coupled neurons under magnetic flow. Appl. Math. Comput. 348, 42–56 (2019)
G. Ren, Y. Xu, C. Wang, Synchronization behavior of coupled neuron circuits composed of memristors. Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 893–901 (2017)
C.N. Takembo, A. Mvogo, H. Ekobena, H.P. Fouda, T.C. Kofane, Localized modulated wave solution of diffusive FitzHugh-Nagumo cardiac networks under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(2), 1079–98 (2018)
C.N. Takembo, A. Mvogo, H. Ekobena, H.P. Fouda, N. Kofane, Effect of electromagnetic radiation on the dynamics of spatiotemporal patterns in memristor based neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1067 (2019)
K. Usha, P.A. Subha, Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with memristors. Biosystems 178, 1–9 (2019)
K.M. Wouapi, H. Fotsin, F.P. Louodop, K.F. Feudjio, T.Z. Njitacke, T.H. Djeudjo, Various firing activities and finite-time synchronization of an improved Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model under electric field effect. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09570-0
Y. Zhao, X. Sun, Y. Liu, J. Kurths, Phase synchronization dynamics of coupled neurons with coupling phase in the electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(3), 1315–1324 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4261-7
Z. Yao, J. Ma, Y. Yao et al., Synchronization realization between two nonlinear circuits via an induction coil coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 205–217 (2019)
S.C. Lesher-Pérez, C. Zhang, S. Takayama, Capacitive coupling synchronizes autonomous microfluidic oscillators. Electrophoresis 39(8), 1096–1103 (2018)
Z. Liu, J. Ma, G. Zhang et al., Synchronization control between two Chua s circuits via capacitive coupling. Appl. Math. Comput. 360, 94–106 (2019)
Y. Xu, Z. Yao, A. Hobiny et al., Differential coupling contributes to synchronization via a capacitor connection between chaotic circuits. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 20(4), 571–583 (2019)
Y. Leng, D. Yu, Y. Hu et al., Dynamic behaviors of hyperbolic-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network considering synaptic crosstalk. Chaos 30(3), 33108 (2020)
Z. Wang, F. Parastesh, K. Rajagopal et al., Delay induced synchronization in two coupled chaotic memristive Hopfield neural networks. Chaos Soliton Fract. 134, 109702 (2020)
B. Bao, Q. Yang, D. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Q. Xu, M. Chen, Initial-induced coexisting and synchronous firing activities in memristor synapse-coupled Morris-Lecar bi-neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2339–2354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05395-7
H. Bao, Y. Zhang, W. Liu et al., Memristor synapse coupled memristive neuron network: synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 937–950 (2020)
Z. Liu, C. Wang, G. Zhang et al., Synchronization between neural circuits connected by hybrid synapse. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 33, 1950170 (2019)
C. Hens, P. Pal, S.K. Dana, Bursting dynamics in a population of oscillatory and excitable Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. E 92, 022915 (2015)
T. Hongray, J. Balakrishnan, S.K. Dana, Bursting behaviour in coupled Josephson junctions. Chaos 25, 123104 (2015)
K. Segall, S. Guo, P. Crotty et al., Phase-flip bifurcation in a coupled Josephson junction neuron system. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 455, 71–75 (2014)
J.M. Shainline, S.M. Buckley, R.P. Mirin et al., Superconducting optoelectronic circuits for neuromorphic computing. Phys. Rev. Appl. 7, 034013 (2017)
R. Cheng, U.S. Goteti, M.C. Hamilton, Spiking neuron circuits using superconducting quantum phase-slip junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 152126 (2018)
P. Crotty, D. Schult, K. Segall, Josephson junction simulation of neurons. Phys. Rev. E 82, 011914 (2010)
M.J.A. Diaz, O. Tequita, F. Naranjo, Neuronal synchronization of electrical activity, using the Hodgkin-Huxley model and RCLSJ circuit. Ingenieria y Ciencia 12, 93–106 (2016)
J.M. Shainline, S.M. Buckley, A.N. McCaughan et al., Circuit designs for superconducting optoelectronic loop neurons. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 152130 (2018)
J.M. Shainline, S.M. Buckley, A.N. McCaughan et al., Superconducting optoelectronic loop neurons. J. Appl. Phys. 126, 044902 (2019)
K. Segall, M. LeGro, S. Kaplan et al., Synchronization dynamics on the picosecond time scale in coupled Josephson junction neurons. Phys. Rev. E 95, 032220 (2017)
Z.T. Njitacke, I.S. Doubla, S. Mabekou, J. Kengne, Hidden electrical activity of two neurons connected with an asymmetric electric coupling subject to electromagnetic induction: coexistence of patterns and its analog implementation, Chaos. Solit. Fract. 137, 109785 (2020)
Z.T. Njitacke, I.S. Doubla, J. Kengne, A. Cheukem, Coexistence of firing patterns and its control in two neurons coupled through an asymmetric electrical synapse. Chaos 30, 023101 (2020)
Z. Yao, P. Zhou, Z. Zhu et al., Phase synchronization between a light-dependent neuron and a thermosensitive neuron. Neurocomputing 423, 518–34 (2021)
X.F. Zhang, Wang C.N., Ma J., et al., Control and synchronization in nonlinear circuits by using a thermistor. Mod. Phys. Lett. B (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021798492050267X In press
Y. Zhang, C.N. Wang, J. Tang et al., Phase coupling synchronization of FHN neurons connected by a Josephson junction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 61, 2328–38 (2020)
A. Pikovsky, M. Rosenblum, J. Kurths, Phase synchronization in regular and chaotic systems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 10(10), 2291–2305 (2000)
S.Y. Ma, Z. Yao, Y. Zhang et al., Phase synchronization and lock between memristive circuits under field coupling. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) 105, 177–185 (2019)
B.C. Bao, H. Qian, J. Wang, Q. Xu, M. Chen, H.G. Wu, Y.J. Yu, Numerical analyses and experimental validations of coexisting multiple attractors in hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(4), 2359–69 (2017)
D.C. Hamill, Learning about chaotic circuits with SPICE. IEEE Trans. Educ. 36, 28–35 (1993)
C.I. Johnson, Analog Computer Techniques (Mc-GrawHill, New York, 1963)
J. Kengne, J.C. Chedjou, G. Kenne, K. Kyamakya, G.H. Kom, Analog circuit implementation and synchronization of a system consisting of a van der pol oscillator linearly coupled to a duffing oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 2163–73 (2012)
P. Louodop, H. Fotsin, M. Kountchou, L.B.M. Ngouonkadi, H.A. Cerdeira, S. Bowong, Finite-time synchronization of tunnel-diode-based chaotic oscillators. Phys. Rev. E 89, 032921 (2014)
K. Michaux, L. Patrick, B. Samuel, F. Hilaire Saïdou, analog circuit design and optimal synchronization of a modified Rayleigh system. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2694-4
M.S. Patel, U. Patel, A. Sen, G.C. Sethia, C. Hens, S.K. Dana, U. Feudel, K. Showalter, C.N. Ngonghala, R.E. Amritkar, Experimental observation of extreme multistability in an electronic system of two coupled Rossler oscillators. Phys. Rev. E 89, 022918 (2014)
V.T. Pham, S. Jafari, S. Vaidyanathan, C.K. Volos, X. Wang, A novel memristive neural network with hidden attractors and its circuitry implementation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59, 358–63 (2016)
J.D. Sitt, J. Aliaga, Versatile biologically inspired electronic. Phys. Rev. E 76, 051919 (2007)
D.H. Sheingold, Nonlinear Circuits Handbook (Analog Devices, Norwood, 1976)
X. Wu, J. Ma, L. Yuan et al., Simulating electric activities of neurons by using PSPICE. Nonlinear Dyn. 75, 113–26 (2014)
Acknowledgements
Jules Fossi Tagne thanks the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Ngaoundéré for its important contribution. Zeric Tabekoueng Njitacke has been supported by the Polish National Science Centre under the Grant OPUS 14 No.2017/27/B/ST8/01330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed equitably in the production and interpretation of the results and then in the writing of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fossi, J.T., Deli, V., Edima, H.C. et al. Phase synchronization between two thermo-photoelectric neurons coupled through a Josephson Junction. Eur. Phys. J. B 95, 66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00324-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-022-00324-x