Abstract
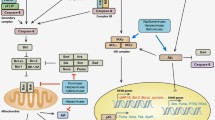
A large proportion of global population is infected with lymphotropic herpesviruses—cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). The products of CMV and EBV gene expression influence various elements of the apoptosis signaling pathways in infected cells and result in successful virus persistence. Some specific features in the interaction of CMV and EBV proteins and RNA transcripts with cellular proteins of apoptosis signaling pathways are considered. The review focuses on the structural and functional elements of the apoptosis-associated signaling pathways that are affected by these viruses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, B. and Sinzger, C., Endothelial cells in human cytomegalovirus infection: one host cell out of many or a crucial target for virus spread? Thromb. Haemostasis, 2009, vol. 102, no. 6, pp. 1057–1063.
Amundson, S.A., Myers, T.G., and Fornace, A.J., Jr., Roles for p53 in growth arrest and apoptosis: putting on the brakes after genotoxic stress, Oncogene, 1998, vol. 17, pp. 3287–3299.
Anderton, E., Yee, J., Smith, P., et al., Two Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) oncoproteins cooperate to repress expression of the proapoptotic tumor-suppressor Bim: clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma, Oncogene, 2008, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 421–433.
Bellows, D.S., Howell, M., Pearson, C., et al., Epstein–Barr virus BALF1 is a BCL-2-like antagonist of the herpesvirus antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins, J. Virol., 2002, vol. 76, no. 5, pp. 2469–2479.
Blokhin, D.Yu., Sokolovskaya, A.A., Mikhailov, A.D., et al., CD95-induced apoptosis and multiresistant phenotype of human lymphoblastoid T-cells, Ross. Bioter. Zh., 2003, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 37–46.
Bonin, L.R. and McDougall, J.K., Human cytomegalovirus IE2 86-kilodalton protein binds p53 but does not abrogate G1 checkpoint function, J. Virol., 1997, vol. 71, pp. 5861–5870.
Brune, W., Inhibition of programmed cell death by cytomegaloviruses, Virus Res., 2011, vol. 157, pp. 144–150.
Cai, X., Schafer, A., Lu, S., et al., Epstein–Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differen tially expressed, PLoS Pathog., 2006, vol. 2, no. 3, p. e23.
Carmilleri-Broet, B.S., Davi, F., Feuillard, J., et al., High expression of latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein–Barr virus and Bcl-2 oncoprotein in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related primary brain lymphomas, Blood, 1995, vol. 86, no. 2, pp. 432–435.
Chakrabarti, A., Chen, A.W., and Varner, J.D., A review of the mammalian unfolded protein response, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2011, vol. 108, pp. 2777–2793.
Chen, C., Li, D., and Guo, N., Regulation of cellular and viral protein expression by the Epstein–Barr virus transcriptional regulator Zta: implications for therapy of EBV associated tumors, Cancer Biol. Ther., 2009, vol. 8, no. 11, pp. 987–995.
Chiou, S.H., Yang, Y.P., Lin, J.C., et al., The immediate early 2 protein of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) mediates the apoptotic control in HCMV retinitis through up-regulation of the cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein expression, J. Immunol., 2006, vol. 177, pp. 6199–6206.
Choy, E.Y., Siu, K.L., Kok, K.H., et al., An Epstein–Barr virusencoded microRNA targets Puma to promote host cell survival, J. Exp. Med., 2008, vol. 205, no. 11, pp. 2551–2560.
Cohen, J.I. and Lekstrom, K., Epstein–Barr virus BARF1 protein is dispensable for B-cell transformation and inhibits alpha interferon secretion from mononuclear cells, J. Virol., 1999, vol. 73, no. 9, pp. 7627–7632.
Cross, J.R., Postigo, A., Blight, K., and Downward, J., Viral pro-survival proteins block separate stages in Bax activation but changes in mitochondrial ultrastructure still occur, Cell Death Diff., 2008, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 997–1008.
Dempsey, P.W., Doyle, S.E., He, J.Q., et al., The signaling adaptors and pathways activated by TNF superfamily, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 2003, vol. 14, pp. 193–209.
Desbien, A.L., Kappler, J.W., and Marrack, P., The Epstein–Barr virus Bcl-2 homolog, BHRF1, blocks apoptosis by binding to a limited amount of Bim, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2009, vol. 106, no. 14, pp. 5663–5668.
Dewson, G., Kratina, T., Sim, H.W., et al., To trigger apoptosis, Bak exposes its BH3 domain and homodimerizes via BH3: groove interactions, Mol. Cell, 2008, vol. 30, pp. 369–380.
Dreyfus, D.H., Nagasawa, M., Pratt, J.C., et al., Inactivation of NF-kB by EBV BZLF-1-encoded ZEBRA protein in human T cells, J. Immunol., 1999, vol. 163, no. 11, pp. 6261–6268.
Electronic epidemiological atlas of the Volga Federal District. http://epidatlas.nniiem.ru. Accessed January 20, 2017.
Filatova, E.N. and Utkin, O.V., Modern approaches to the modeling of herpesvirus infection, Medial’, 2014, vol. 2, no. 12, pp. 172–197.
Finke, J., Fritzen, R., Ternes, P., et al., Expression of bcl-2 in Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines: induction by latent Epstein–Barr virus genes, Blood, 1992, vol. 80, no. 2, pp. 459–469.
Fliss, P.M. and Brune, W., Prevention of cellular suicide by cytomegaloviruses, Viruses, 2012, vol. 4, pp. 1928–1949.
Floettmann, J.E. and Rowe, M., Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) C-terminus activation region 2 (CTAR2) maps to the far C-terminus and requires oligomerisation for NF-?B activation, Oncogene, 1997, vol. 15, pp. 1851–1858.
Fu, Q., He, C., and Mao, Z.R., Epstein–Barr virus interactions with the Bcl-2 protein family and apoptosis in human tumor cells, J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. Biomed. Biotech., 2013, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 8–24.
Gerna, G., Zipeto, D., Percivalle, E., et al., Human cytomegalovirus infection of the major leukocyte subpopulations and evidence for initial viral replication in polymorphonuclear leukocytes from viremic patients, J. Infect. Dis., 1992, vol. 166, no. 6, pp. 1236–1244.
Gires, O., Zimber-Strobl, U., Gonnella, R., et al., Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein–Barr virus mimics a constitutively active receptor molecule, EMBO J., 1997, vol. 16, pp. 6131–6140.
Goldmacher, V.S., Bartle, L.M., Skaletskaya, A., et al., A cytomegalovirus-encoded mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis structurally unrelated to Bcl-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1999, vol. 96, pp. 12536–12541.
Golks, A., Brenner, D., Fritsch, C., et al., c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis, J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, no. 15, pp. 14507–14513.
Green, D.R. and Reed, J.C., Mitochondria and apoptosis, Science, 1998, vol. 281, pp. 1309–1312.
Grefte, A., Blom, N., van der Giessen, M., et al., Ultrastructural analysis of circulating cytomegalic cells in patients with active cytomegalovirus infection: evidence for virus production and endothelial origin, J. Infect. Dis., 1993, vol. 168, no. 5, pp. 1110–1118.
Hayward, S.D., Viral interactions with the Notch pathway, Semin. Cancer Biol., 2004, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 387–396.
Hehlgans, T. and Pfeffer, K., The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games, J. Immunol., 2005, vol. 115, pp. 1–20.
Hickish, T., Robertson, D., Clarke, P., et al., Ultrastructural localization of BHRF1: an Epstein–Barr virus gene product which has homology with bcl-2, Cancer Res., 1994, vol. 54, pp. 2808–2811.
Howe, J.G. and Steitz, J.A., Localization of Epstein–Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1986, vol. 83, pp. 9006–9010.
Isler, J.A., Skalet, A.H., and Alwine, J.C., Human cytomegalovirus infection activates and regulates the unfolded protein response, J. Virol., 2005, vol. 79, pp. 6890–6899.
Kalla, M., Schmeinck, A., Bergbauer, M., et al., AP-1 homolog BZLF1 of Epstein–Barr virus has two essential functions dependent on the epigenetic state of the viral genome, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, no. 2, pp. 850–855.
Keating, S., Prince, S., Jones, M., and Rowe, M., The lytic cycle of Epstein–Barr virus is associated with decreased expression of cell surface major histocompatibility complex class I and class II molecules, J. Virol., 2002, vol. 76, no. 16, pp. 8179–8188.
Kelly, G.L., Long, H.M., and Stylianou, J., An Epstein–Barr virus anti-apoptotic protein constitutively expressed in transformed cells and implicated in Burkitt’s lymphomagenesis: the WP/BHRF1 link, PLoS Pathog., 2009, vol. 5, no. 3, p. e1000341.
Kenney, J.L., Guinness, M.E., Curiel, T., and Lacy, J., Antisense to the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) suppresses LMP-1 and bcl-2 expression and promotes apoptosis in EBVimmortalized B cells, Blood, 1998, vol. 92, no. 5, pp. 1721–1727.
Kieff, E. and Rickinson, A.B., Epstein–Barr virus and its replication, in Fields Virology, Knipe, D.M. and Howley, P.M., Eds., Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2007, pp. 2603–2654.
Kiener, P.A., Davis, P.M., Staring, G.C., et al., Differential induction of apoptosis by Fas–Fas-ligand interactions in human monocytes and macrophages, J. Exp. Med., 1997, vol. 185, pp. 1511–1516.
Kim, S., Yu, S.S., and Kim, V.N., Essential role of NF-kB in transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the human cytomegalovirus 1E1 protein, J. Gen. Virol., 1996, vol. 77, pp. 83–91.
Ko, L.J. and Prives, C., p53: puzzle and paradigm, Genes Dev., 1996, vol. 10, pp. 1054–1072.
Kohlhof, H., Hampel, F., Hoffmann, R., et al., Notch1, Notch2, and Epstein–Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 signaling differentially affects proliferation and survival of Epstein–Barr virus-infected B cells, Blood, 2009, vol. 113, no. 22, pp. 5506–5515.
Komano, J., Maruo, S., Kurozumi, K., et al., Oncogenic role of Epstein–Barr virus-encoded RNAs in Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line akata, J. Virol., 1999, vol. 73, no. 12, pp. 9827–9831.
Kuskova, T.K. and Belova, E.G., Modern herpesvirus family, Lech. Vrach, 2004, no. 5, pp. 64–69.
Kuwana, T., Bouchier-Hayes, L., Chipuk, J.E., et al., BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Baxmediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly, Mol. Cell, 2005, vol. 17, pp. 525–535.
Kvansakul, M., Wei, A.H., Fletcher, J.I., et al., Structural basis for apoptosis inhibition by Epstein–Barr virus BHRF1, PLoS Pathog., 2010, vol. 6, no. 12, pp. 1–10.
Le Clorennec, C., Youlyouz-Marfak, I., Adriaenssens, E., et al., EBV latency III immortalization program sensitizes B cells to induction of CD95-mediated apoptosis via LMP1: role of NF-?B, STAT1, and p53, Blood, 2006, vol. 107, pp. 2070–2078.
Le Clorennec, C., Ouk, T.S., Youlyouz-Marfak, I., et al., Molecular basis of cytotoxicity of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) in EBV latency III b cells: LMP1 induces type II ligand-independent autoactivation of CD95/Fas with caspase 8- mediated apoptosis, J. Virol., 2008, vol. 82, no. 13, pp. 6721–6733.
Le, V.T., Trilling, M., and Hengel, H., The cytomegaloviral protein pUL138 acts as potentiator of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 surface density to enhance ULb-encoded modulation of TNF-signaling, J. Virol., 2011, vol. 85, no. 24, pp. 13260–13270.
Lei, K. and Davis, R.J., JNK phosphorylation of Bimrelated members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 2432–2437.
Li, X. and Bhaduri-McIntosh, S., A central role for STAT3 in gammaherpesvirus-life cycle and -diseases, Front. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 7, art. 1052.
Marshall, W.L., Yim, C., Gustafson, E., et al., Epstein–Barr virus encodes a novel homolog of the bcl-2 oncogene that inhibits apoptosis and associates with Bax and Bak, J. Virol., 1999, vol. 73, no. 6, pp. 5181–5185.
McCormick, A.L., Skaletskaya, A., Barry, P.A., et al., Differential function and expression of the viral inhibitor of caspase 8-induced apoptosis (vICA) and the viral mitochondria- localized inhibitor of apoptosis (vMIA) cell death suppressors conserved in primate and rodent cytomegaloviruses, Virology, 2003, vol. 316, pp. 221–233.
McCormick, A.L., Roback, L., Livingston-Rosanoff, D., and St. Clair, C., The human cytomegalovirus UL36 gene controls caspase-dependent and -independent cell death programs activated by infection of monocytes differentiating to macrophages, J. Virol., 2010, vol. 84, pp. 5108–5123.
Morrison, T.E. and Kenney, S.C., BZLF1, an Epstein–Barr virus immediate-early protein, induces p65 nuclear translocation while inhibiting p65 transcriptional function, Virology, 2004, vol. 328, no. 2, pp. 219–232.
Niedobitek, G., Young, L.S., and Herbst, H., Epstein–Barr virus infection and the pathogenesis of malignant lymphomas, Cancer Surv., 1997, vol. 30, pp. 143–162.
O’Brien, V. Viruses and apoptosis, J. Gen. Virol., 1998, vol. 79, pp. 1833–1845.
Oldstone, M.B., How viruses escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes: molecular parameters and players, Virology, 1997, vol. 234, no. 2, pp. 179–185.
Paschos, K., Smith, P., Anderton, E., et al., Epstein–Barr virus latency in B cells leads to epigenetic repression and CpG methylation of the tumor suppressor gene bim, PLoS Pathog., 2009, vol. 5, no. 6, p. e1000492.
Paschos, K., Parker, G.A., Watanatanasup, E., et al., BIM promoter directly targeted by EBNA3C in polycombmediated repression by EBV, Nucleic Acids Res., 2012, vol. 40, no. 15, pp. 7233–7246.
Pauleau, A.L., Larochette, N., Giordanetto, F., et al., Structurefunction analysis of the interaction between Bax and the cytomegalovirus-encoded protein vMIA, Oncogene, 2007, vol. 26, pp. 7067–7080.
Paulus, C. and Nevels, M., The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins as antagonists of intrinsic and innate antiviral host responses, Viruses, 2009, vol. 1, pp. 760–779.
Plachter, B., Sinzger, C., and Jahn, G., Cell types involved in replication and distribution of human cytomegalovirus, Adv. Virus Res., 1996, vol. 46, pp. 195–261.
Portis, T. and Longnecker, R., Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/AKT pathway, Oncogene, 2004, vol. 23, no. 53, pp. 8619–8628.
Powers, C., De Filippis, V., Malouli, D., and Fruh, K., Cytomegalovirus immune evasion, Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol., 2008, vol. 325, pp. 333–359.
Pratt, Z.L., Zhang, J., and Sugden, B., Simultaneously induce and inhibit oncogene of Epstein–Barr virus can the latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) apoptosis in B cells, J. Virol., 2012, vol. 86, no. 8, pp. 4380–4393.
Putcha, G.V., Le, S., Frank, S., et al., JNK-mediated BIM phosphorylation potentiates BAX-dependent apoptosis, Neuron, 2003, vol. 38, pp. 899–914.
Reed, J.C., Doctor, K.S., and Goldzik, A., The domain of apoptosis: a genomic perspective, Sci. Signaling, 2004, vol. 239, pp. 1–29.
Reeves, M.B., Davies, A.A., McSharry, B.P., et al., Complex I binding by a virally encoded RNA regulates mitochondria- induced cell death, Science, 2007, vol. 316, no. 5829, pp. 1345–1348.
Reinke, P., Fietze, E., Ode-Hakim, S., et al., Late-acute renal allograft rejection and symptomless cytomegalovirus infection, Lancet, 1994, vol. 344, nos. 8939–8940, pp. 1737–1738.
Schneider, F., Neugebauer, J., Griese, J., et al., The viral oncoprotein LMP1 exploits TRADD for signaling by masking its apoptotic activity, PLoS Biol., 2008, vol. 6, no. 1, p. e8.
Schulze-Osthoff, K., Ferrari, D., Los, M., et al., Apoptosis signaling by death receptors, Eur. J. Biochem., 1998, vol. 254, pp. 439–459.
Schütze, S., Tchikov, V., and Schneider-Brachert, W., Regulation of TNFR1 and CD95 signalling by receptor compartmentalization, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2008, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 655–662.
Seto, E., Moosmann, A., Gromminger, S., et al., Micro RNAs of Epstein–Barr virus promote cell cycle progression and prevent apoptosis of primary human B cells, PLoS Pathog., 2010, vol. 6, p. e1001063.
Sheng, W., Decaussin, G., Sumner, S., and Ooka, T., N-terminal domain of BARF1 gene encoded by Epstein–Barr virus is essential for malignant transformation of rodent fibroblasts and activation of BCL-2, Oncogene, 2001, vol. 20, no. 10, pp. 1176–1185.
Sinzger, C., Plachter, B., Grefte, A., et al., Tissue macrophages are infected by human cytomegalovirus in vivo, J. Infect. Dis., 1996, vol. 173, no. 1, pp. 240–245.
Sinzger, C., Digel, M., and Jahn, G., Cytomegalovirus cell tropism, Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol., 2008, vol. 325, pp. 63–83.
Skaletskaya, A., Bartle, L.M., Chittenden, T., et al., A cytomegalovirus- encoded inhibitor of apoptosis that suppresses caspase-8 activation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2001, vol. 98, pp. 7829–7834.
Somova, L.M., Besednova, N.N., and Plekhova, N.G., Apoptosis and infectious diseases, Infekts. Immun., 2014, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 303–318.
Speir, E., Modali, R., Huang, E.S., et al., Potential role of human cytomegalovirus and p53 interaction in coronary restenosis, Science, 1994, vol. 265, pp. 391–394.
Steelman, L.S., Pohnert, S.C., Shelton, J.G., et al., JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and BCRABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis, Leukemia, 2004, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 189–218.
Strockbine, L.D., Cohen, J.I., Farrah, T., et al., The Epstein–Barr virus BARF1 gene encodes a novel, soluble colonystimulating factor-1 receptor, J. Virol., 1998, vol. 72, no. 5, pp. 4015–4021.
Szegezdi, E., Logue, S.E., Gorman, A.M., and Samali, A., Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis, EMBO Rep., 2006, vol. 7, pp. 880–885.
Terhune, S., Torigoi, E., Moorman, N., et al., Human cytomegalovirus UL38 protein blocks apoptosis, J. Virol., 2007, vol. 81, pp. 3109–3123.
Thome, M., Schneider, P., Hofmann, K., et al., Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors, Nature, 1997, vol. 386, no. 6624, pp. 517–521.
Thorley-Lawson, D.A. and Babcock, J.G., A model for persistent infection with Epstein–Barr virus: the stealth virus of human B cells, Life Sci., 1999, vol. 65, no. 14, pp. 1433–1453.
Tomkinson, B., Robertson, E., and Kieff, E., Epstein–Barr virus nuclear proteins EBNA-3A and EBNA-3C are essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation, J. Virol., 1993, vol. 67, no. 4, pp. 2014–2025.
Urano, F., Wang, X., Bertolotti, A., et al., Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1, Science, 2000, vol. 287, pp. 664–666.
Uren, R.T., Dewson, G., Chen, L., et al., Mitochondrial permeabilization relies on BH3 ligands engaging multiple prosurvival Bcl-2 relatives, not Bak, J. Cell Biol., 2007, vol. 177, pp. 277–287.
Utkin, O.V. and Novikov, V.V., Regulation of apoptosis by alternative splicing of matrix RNA, Ross. Bioter. Zh., 2007, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 13–20.
Utkin, O.V. and Novikov, V.V., Role of receptors of death in apoptosis modulation, Usp. Sovrem. Biol., 2012, vol. 132, no. 4, pp. 381–390.
Wang, S., Rowe, M., and Lundgren, E., Expression of the Epstein–Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 causes a rapid and transient stimulation of the Bcl-2 homologue Mcl-1 levels in B-cell lines, Cancer Res., 1996, vol. 56, pp. 4610–4613.
Westphal, D., Dewson, G., Czabotar, P.E., and Kluck, R.M., Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2011, vol. 1813, pp. 521–531.
Williams, E.J., Embleton, N.D., Clark, J.E., et al., Viral infections: contributions to late fetal death, stillbirth, and infant death, J. Pediatr., 2013, vol. 163, no. 2, pp. 424–428.
Womack, J. and Jimenez, M., Common questions about infectious mononucleosis, Am. Fam. Physician, 2015, vol. 91, no. 6, pp. 372–376.
Wong, H.L., Wang, X., Chang, R.C., et al., Stable expression of EBERs in immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial cells confers resistance to apoptotic stress, Mol. Carcinog., 2005, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 92–101.
Xuan, B., Qian, Z., Torigoi, E., and Yu, D., Human cytomegalovirus protein pUL38 induces ATF4 expression, inhibits persistent JNK phosphorylation, and suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death, J. Virol., 2009, vol. 83, pp. 3463–3474.
Zhao, J., Sinclair, J., Houghton, J., et al., Cytomegalovirus 2.7 RNA transcript protects endothelial cells against apoptosis during ischemia/reperfusion injury, J. Heart Lung Transplant., 2010, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 342–345.
Zhu, H., Shen, Y., and Shenk, T., Human cytomegalovirus IE1 and IE2 proteins block apoptosis, J. Virol., 1995, vol. 69, pp. 7960–7970.
Zimber-Strobl, U. and Strobl, L.J., EBNA2 and Notch signaling in Epstein–Barr virus mediated immortalization of B lymphocytes, Semin. Cancer Biol., 2001, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 423–434.
Zuo, J., Thomas, W.A., Haigh, T.A., et al., Epstein–Barr virus evades CD4+ T cell responses in lytic cycle through BZLF1-mediated down-regulation of CD74 and the cooperation of vBcl-2, PLoS Pathog., 2011, vol. 7, no. 12, p. e1002455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.A. Sakharnov, O.V. Utkin, D.I. Knyazev, E.N. Filatova, V.D. Tsvetkova, 2017, published in Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii, 2017, Vol. 137, No. 4, pp. 387–397.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakharnov, N.A., Utkin, O.V., Knyazev, D.I. et al. Specific Features of Apoptotic Signaling Regulation in Cells Infected with Cytomegalovirus and Epstein–Barr Virus. Biol Bull Rev 8, 114–123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S207908641802007X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S207908641802007X