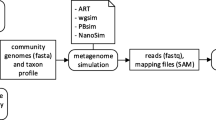
Abstract
Bacterial communities are closely interrelated systems consisting of numerous species making it challenging to analyze their structure and relations. At present, there are several experimental techniques providing heterogeneous data, concerning various aspects of this research object. The recent avalanche of available metagenomic data challenges not only biostatisticians but also biomodelers, since these data are essential for improving the modeling quality, while simulation methods are useful for understanding the evolution of microbial communities and their function in the ecosystem. An outlook on the existing modeling and simulation approaches based on different types of experimental data in the field of microbial ecology and environmental microbiology is presented. A number of approaches focused on the description of microbial community aspects such as trophic structure, metabolic and population dynamics, genetic diversity, as well as spatial heterogeneity and expansion dynamics, are considered. We also propose a classification of the existing software designed for the simulation of microbial communities. It has been shown that, in spite of the prevailing trend for using multiscale/hybrid models, the integration between models concerning different levels of biological organization of communities still remains a problem to be solved. The multiaspect nature of integration approaches used for modeling microbial communities is based on the necessity of taking into account the heterogeneous data obtained from various sources by applying high-throughput genome investigation methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, J., Chemotaxis in bacteria, J. Supramol. Struct., 1976, vol. 4, pp. 305–317. doi 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013
Beardmore, R.E., Gudelj, I., Lipson, D.A., and Hurst, L.D., Metabolic trade-offs and the maintenance of the fittest and the flattest, Nature, 2011, vol. 472, pp. 342–346. doi 10.1038/nature09905
Beslon, G., Parsons, D.P., Sanchez-Dehesa, Y., and Knibbe, C., Scaling laws in bacterial genomes: A side-effect of selection of mutational robustness?, Biosystems, 2010, vol. 102, pp. 32–40. doi 10.1016/j.biosystems.2010.07.009
Chernavskii, D.S. and Ierusalimskii, N.D., On the question of the defining link in the system of enzymatic reactions, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol., 1965, vol. 5, pp. 665–672.
Chewapreecha, C., Your gut microbiota are what you eat, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 12, p. 8. doi 10.1038/nrmicro3186
Comolli, L.R., Intra-and inter-species interactions in microbial communities, Front. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 5, pp. 1–3. doi 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00629
Covert, M.W., Schilling, C.H., Famili, I., Edwards, J.S., Goryanin, I.I., Selkov, E., and Palsson, B.O., Metabolic modeling of microbial strains in silico, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2001, vol. 26, pp. 179–186. doi 10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01754-0
De Jong, H., Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: A literature review, J. Comput. Biol., 2002, vol. 9, pp. 67–103. doi 10.1089/10665270252833208
De Roy, K., Marzorati, M., Van den Abbeele, P., Van de Wiele T., and Boon, N., Synthetic microbial ecosystems: An exciting tool to understand and apply microbial communities, Environ. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 16, pp. 1472–1481. doi 10.1111/1462-2920.12343
DeAngelis, D.L. and Mooij, W.M., Individual-based modeling of ecological and evolutionary processes 1, Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst., 2005, vol. 36, pp. 147–168. doi 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.36.102003.152644
Durot, M., Bourguignon, P.-Y., and Schachter, V., Genome-scale models of bacterial metabolism: Reconstruction and applications, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2009, vol. 33, pp. 164–190. doi 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00146.x
Emonet, T., Macal, C.M., North, M.J., Wickersham, C.E., and Cluzel, P., Agent-Cell: A digital single-cell assay for bacterial chemotaxis, Bioinformatics, 2005, vol. 21, pp. 2714–2721. doi 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti391
Esteban, P.G. and Rodríguez-Patón, A., Simulating a rockscissors-paper bacterial game with a discrete cellular automaton, in New Challenges on Bioinspired Applications, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Ferràndez, J.M., Àlvarez Sànchez, J.R., de la Paz, F., and Toledo, F.J., Eds., Berlin–Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011. doi 10.1007/978-3-642-21326-7
Faust, K. and Raes, J., Microbial interactions: From networks to models, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 10, pp. 538–550. doi 10.1038/nrmicro2832
Frey, E., Evolutionary game theory: Theoretical concepts and applications to microbial communities, Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl., 2010, vol. 389, pp. 4265–4298. doi 10.1016/j.physa.2010.02.047
Fuhrman, J.A., Microbial community structure and its functional implications, Nature, 2009, vol. 459, pp. 193–199. doi 10.1038/nature08058
Gimel’farb, A.A., Ginzburg, L.R., Poluektov, R.A., Pykh, Yu.A., and Ratner, V.A., Dinamicheskaya teoriya biologicheskikh populyatsii (Dynamic Theory of Biological Populations), Nauka, 1974.
Ginovart, M., Löpez, D., and Valls, J., INDISIM, an individual-based discrete simulation model to study bacterial cultures, J. Theor. Biol., 2002, vol. 214, pp. 305–319. doi 10.1006/jtbi.2001.2466
Grimm, V., Berger, U., Bastiansen, F., Eliassen, S., Ginot, V., Giske, J., Goss-Custard, J., Grand, T., Heinz, S.K., Huse, G., Huth, A., Jepsen, J.U., Jørgensen, C., Mooij, W.M., Müller, B., et al., A standard protocol for describing individual-based and agent-based models, Ecol. Modell., 2006, vol. 198, pp. 115–126. doi 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.04.023
Halfen, L.N. and Castenholz, R.W., Gliding Motility in the Blue-Green Alga Oscillatoria Princeps, 1971.
Hecker, M., Lambeck, S., Toepfer, S., van Someren, E., and Guthke, R., Gene regulatory network inference: Data integration in dynamic models–A review, Biosystems, 2009, vol. 96, pp. 86–103. doi 10.1016/j.biosystems.2008.12.004
Henrichsen, J., Bacterial surface translocation: A survey and a classification, Bacteriol. Rev., 1972, vol. 36, pp. 478–503.
Henson, M.A. and Hanly, T.J., Dynamic flux balance analysis for synthetic microbial communities, IET Syst. Biol., 2014, vol. 8, pp. 214–229. doi 10.1049/iet-syb.2013.0021
Ishii, N., Robert, M., Nakayama, Y., Kanai, A., and Tomita, M., Toward large-scale modeling of the microbial cell for computer simulation, J. Biotechnol., 2004, vol. 113, pp. 281–294. doi 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.04.038
Karr, J.R., Sanghvi, J.C., MacKlin, D.N., Gutschow, M.V., Jacobs, J.M., Bolival, B., Assad-Garcia, N., Glass, J.I., and Covert, M.W., A whole-cell computational model predicts phenotype from genotype, Cell, 2012, vol. 150, pp. 389–401. doi 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.044
Karunakaran, E., Mukherjee, J., Ramalingam, B., and Biggs, C.A., “Biofilmology:” A multidisciplinary review of the study of microbial biofilms, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 90, pp. 1869–1881. doi 10.1007/s00253-011-3293-4
Klimenko, A.I., Matushkin, Y.G., Kolchanov, N.A., and Lashin, S.A., Modeling evolution of spatially distributed bacterial communities: A simulation with the haploid evolutionary constructor, BMC Evol. Biol., 2015, vol. 15, p. S3. doi 10.1186/1471-2148-15-S1-S3
Klitgord, N. and Segre, D., Environments that induce synthetic microbial ecosystems, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2010, vol. 101, pp. 1435–1439. doi 10.1371/Citation
Knibbe, C., Fayard, J.-M., and Beslon, G., The topology of the protein network influences the dynamics of gene order: From systems biology to a systemic understanding of evolution, Artif. Life, 2008, vol. 14, pp. 149–156. doi 10.1162/artl.2008.14.1.149
Kolmakova, O.V., Modern methods for determining speciesspecific biogeochemical functions of bacterioplankton, Zh. Sib. Fed. Univ., Ser. Biol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 73–95.
Kutalik, Z., Razaz, M., and Baranyi, J., Connection between stochastic and deterministic modelling of microbial growth, J. Theor. Biol., 2005, vol. 232, pp. 285–299. doi 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.08.013
Larsen, P., Hamada, Y., and Gilbert, J., Modeling microbial communities: Current, developing, and future technologies for predicting microbial community interaction, J. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 160, pp. 17–24. doi 10.1016/j.jbiotec. 2012.03.009
Laspidou, C.S. and Rittmann, B.E., Evaluating trends in biofilm density using the UMCCA model, Water Res., 2004, vol. 38, pp. 3362–33672. doi 10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.051
Lencstre Fernandes, R., Nierychlo, M., Lundin, L., Pedersen, A.E., Puentes Tellez, P.E., Dutta, A., Carlquist, M., Bolic, A., Schäpper, D., Brunetti, A.C., Helmark, S., Heins, A.L., Jensen, A.D., Nopens, I., Rottwitt, K., et al., Experimental methods and modeling techniques for description of cell population heterogeneity, Biotechnol. Adv., 2011, vol. 29, pp. 575–599. doi 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.03.007
Leslie, P.H., On the use of matrices in certain population mathematics, Biometrika, 1945. doi 10.2307/2332297
Likhoshvai, V.A. and Ratushny, A.V., Generalized Hill function method for modeling molecular processes, J. Bioinf. Comput. Biol., 2007, vol. 05, pp. 521–531. doi 10.1142/S0219720007002837
Likhoshvai, V.A., Khlebodarova, T.M., Ratushnyi, A.V., Lashin, S.A., Turnaev, I.I., Podkolodnaya, O.A., Anan’ko, E.A., Smirnova, O.G., Ibragimova, S.S., and Kolchanov, N.A., Computer genetic designer: Mathematical modeling of genetic and metabolic subsystems of E. coli, in The Role of Microorganisms in Functioning of Living Systems: Fundamental Problems and Bioengineering Applications, Vlasov, V.V., Degermendzhi, A.G., Kolchanov, N.A., Parmon, V.N., and Repin, E.A., Eds., Novosibirsk: Izd. SO RAN, 2010.
Logofet, D.O. and Belova, I.N., Nonnegative matrices as a tool to model population dynamics: Classical models and contemporary expansions, Fundam. Prikl. Mat., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 145–164.
Mahadevan, R. and Henson, M.A., Genome-based modeling and design of metabolic interactions in microbial communities, Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J., 2012, vol. 3, pp. 1–7. doi 10.5936/csbj.201210008
Mburu, N., Rousseau, D.P.L., Stein, O.R., and Lens, P.N.L., Simulation of batch-operated experimental wetland mesocosms in AQUASIM biofilm reactor compartment, J. Environ. Manage., 2014, vol. 134, pp. 100–108. doi 10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.005
Monod, J., La technique de culture continue. Theorie et applications, Ann. Inst. Pasteur, 1950, vol. 79, pp. 391–410.
Netrusov, A.I. and Kotova, I.B., Mikrobiologiya (Microbiology), Moscow: Akademiya, 2007.
Niu, B., Wang, H., Duan, Q., and Li, L., Biomimicry of quorum sensing using bacterial lifecycle model, BMC Bioinf., 2013, vol. 14, no. 8, p. S8. doi 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S8-S8
O’Donnell, A.G., Young, I.M., Rushton, S.P., Shirley, M.D., and Crawford, J.W., Visualization, modelling and prediction in soil microbiology, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 5, pp. 689–699. doi 10.1038/nrmicro1714
Oberhardt, M.A. and Palsson, B.Ø, Papin, J.A., Applications of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions, Mol. Syst. Biol., 2009, vol. 5. doi 10.1038/msb.2009.77
Pfeiffer, T. and Schuster, S., Game-theoretical approaches to studying the evolution of biochemical systems, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2005, vol. 30, pp. 20–25. doi 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.006
Price, N.D., Reed, J.L., and Palsson, B.Ö, Genome-scale models of microbial cells: Evaluating the consequences of constraints, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 2, pp. 886–897. doi 10.1038/nrmicro1023
Ramkrishna, D., Population Balances: Theory and Applications to Particulate Systems in Engineering, Chemical Engineering, 2000.
Riznichenko, G.Yu., Matematicheskie modeli v biofizike i ekologii (Mathematical Models in Biophysics and Ecology), Moscow, Izhevsk: Inst. Komp’yut. Issled., 2003.
Riznichenko, G.Yu. and Rubin, A.B., Matematicheskie modeli biologicheskikh produktsionnykh protsessov (Mathematical Models of Biological Production Processes), Moscow: Izd. MGU, 1993.
Rudge, T.J., Steiner, P.J., Phillips, A., and Haseloff, J., Computational modeling of synthetic microbial biofilms, ACS Synth. Biol., 2012, vol. 1, no. 8, pp. 345–352. doi 10.1021/sb300031n
Salli, K.M. and Ouwehand, A.C., The use of in vitro model systems to study dental biofilms associated with caries: A short review, J. Oral Microbiol., 2015, vol. 7. doi 10.3402/jom.v7.26149
Sauer, U., Heinemann, M., and Zamboni, N., GENETICS: Getting closer to the whole picture, Science, 2007, vol. 316, pp. 550–551. doi 10.1126/science.1142502
Scheffer, M., Baveco, J.M., DeAngelis, D.L., Rose, K.A., and van Nes, E.H., Super-individuals a simple solution for modelling large populations on an individual basis, Ecol. Modell., 1995, vol. 80, pp. 161–170. doi 10.1016/0304-3800(94)00055-M
Scheibe, T.D., Mahadevan, R., Fang, Y., Garg, S., Long, P.E., and Lovley, D.R., Coupling a genome-scale metabolic model with a reactive transport model to describe in situ uranium bioremediation, Microb. Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 2, pp. 274–286. doi 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2009.00087.x
Schuster, S., Fell, D.A., and Dandekar, T., A general definition of metabolic pathways useful for systematic organization and analysis of complex metabolic networks, Nat. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 18, pp. 326–332. doi 10.1038/73786
Segrè, D., Vitkup, D., and Church, G.M., Analysis of optimality in natural and perturbed metabolic networks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2002, vol. 99, pp. 15112–15117. doi 10.1073/pnas.232349399
Shrout, J.D., A fantastic voyage for sliding bacteria, Trends Microbiol., 2015, vol. 23, pp. 244–246. doi 10.1016/j.tim.2015.03.001
Song, H.-S., Cannon, W., Beliaev, A., and Konopka, A., Mathematical modeling of microbial community dynamics: a methodological review, Processes, 2014, vol. 2, pp. 711–752. doi 10.3390/pr2040711
Stauffer, D., Kunwar, A., and Chowdhury, D., Evolutionary ecology in silico: Evolving food webs, migrating population and speciation, Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2005, vol. 352, pp. 202–215. doi 10.1016/j.physa.2004.12.036
Tang, Y. and Valocchi, A.J., An improved cellular automaton method to model multispecies biofilms, Water Res., 2013, vol. 47, pp. 5729–5742. doi 10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.055
Tindall, M.J., Maini, P.K., Porter, S.L., and Armitage, J.P., Overview of mathematical approaches used to model bacterial chemotaxis II: Bacterial populations, Bull. Math. Biol., 2008a. doi 10.1007/s11538-008-9322-5
Tindall, M.J., Porter, S.L., Maini, P.K., Gaglia, G., and Armitage, J.P., Overview of mathematical approaches used to model bacterial chemotaxis I: The single cell, Bull. Math. Biol., 2008b. doi 10.1007/s11538-008-9321-6
Tomita, M., Hashimoto, K., Takahashi, K., Shimizu, T., Matsuzaki, Y., Miyoshi, F., Saito, K., Tanida, S., Yugi, K., Venter, J., and Hutchison, C., E-CELL: Software environment for whole-cell simulation, Bioinf., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 72–84. doi 10.1093/bioinformatics/15.1.72
Tomita, M., Whole-cell simulation: A grand challenge of the 21st century, Trends Biotechnol., 2001, vol. 19, pp. 205–210. doi 10.1016/S0167-7799(01)01636-5
Turing, A.M., The chemical theory of morphogenesis, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., 1952, vol. 13, p. 1.
Wanner, O. and Morgenroth, E., Biofilm modeling with AQUASIM, Water Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 49, pp. 137–144.
Wimpenny, J.W.T. and Colasanti, R., A unifying hypothesis for the structure of microbial biofilms based on cellular automaton models, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 1997. doi 10.1016/S0168-6496(96)00078-5
Wimpenny, J., Manz, W., and Szewzyk, U., Heterogeneity in biofilms, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2000. doi 10.1016/S0168-6445(00)00052-8
Wolfe, B.E. and Dutton, R.J., Review fermented foods as experimentally tractable microbial ecosystems, Cell, 2015, vol. 161, pp. 49–55. doi 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.034
Wooley, J.C., Godzik, A., and Friedberg, I., A primer on metagenomics, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2010. doi 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000667
Zomorrodi, A.R. and Maranas, C.D., OptCom: A multilevel optimization framework for the metabolic modeling and analysis of microbial communities, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2012, vol. 8. doi 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002363
Zomorrodi, A.R., Islam, M.M., and Maranas, C.D., D-OptCom: Dynamic multi-level and multi-objective metabolic modeling of microbial communities, ACS Synth. Biol., 2014, vol. 3, pp. 247–257. doi 10.1021/sb4001307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.I. Klimenko, Z.S. Mustafin, A.D. Chekantsev, R.K. Zudin, Yu.G. Matushkin, S.A. Lashin, 2015, published in Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genetiki i Selektsii, 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 745–752.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klimenko, A.I., Mustafin, Z.S., Chekantsev, A.D. et al. A review of simulation and modeling approaches in microbiology. Russ J Genet Appl Res 6, 845–853 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059716070066
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059716070066