Abstract
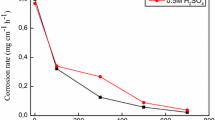
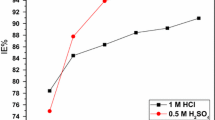
The inhibitory potential of an acid extract of Eichhornia crassipes constituents on corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution was the basis of this study. Acid extract of the root was employed to create the same type of environment for acidic cleaning and pickling. The roots of Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth) were sun-dried and pulverized into powdered form. Acid extraction was carried out by weighing 10 g of the pulverized roots into a beaker containing 1000 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4, placed in water bath at 90°C for 6 h and filtered the second day. The mild steel with a known weight was immersed inside the respective concentration of the blank and inhibitors (2–10% vol/vol) solutions at room temperature, after which it was retrieved and weighed at 1-day interval progressively for 12 days. A collection of compositional data was from AAS, FTIR. Polarization resistant, current density (I corr), and corrosion potentials (E corr) obtained from Methro Ohms Potentiostat. Phytochemical screening of the corrosion product was carried out using Spectrophotometer. Polarization calculation shows that the root acid extracts on mild steel have corrosion resistance potentials even after preserving it for 60 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amitha Rani, B.E. and Bharathi, B.J., Int. J. Corros., 2012, vol. 2012, p. 1.
Ebenso, E.E., Bull. Electrochem., 2003, vol. 19, p. 209.
El Ashry, H.E., El Nemr, A., Esawy, S.A., et al., Electrochim. Acta, 2006, vol. 51, p. 3957.
Wang, H., Wang, X., Wang, L., et al., J. Mol. Model., 2007, vol. 13, p. 147.
Zucchi, F. and Omar, I.H., Surf. Technol., 1985, vol. 24, p. 391.
Eddy, N.O. and Ebenso, E.E., Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem., 2008, vol. 2, p. 1.
Eddy, N.O. and Odoemelam, S.A., Adv. Nat. Appl. Sci., 2009, vol. 2, p. 225.
Abiola, O.K., Oforka, N.C., Ebenso, E.E., et al., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2007, vol. 54, p. 219.
Alaneme, K.K. and Olusegun, S.J., Leonardo J. Sci., 2012, vol. 20, p. 59.
Oguzie, E.E., Pigm. Resin Technol., 2006, vol. 35, p. 334.
Oloruntoba, D.T., Abbas, J.A., and Olusegun, S.J., Proc. 4th West Africa Built Environment Research (WABER) Conf., Abuja, July 24–26, 2012, p. 1129.
Oloruntoba, D.T., Caspian J. Appl. Sci. Res., 2013, vol. 2, p. 6.
Oloruntoba, D.T., Talabi, H.K., and Ajibola, O.O., Acta Tech. Corviniensis, 2015, vol. 8, p. 95.
Makkar, H.P., Blummel, M., Borowy, N.K., et al., J. Sci. Food Agric., 1993, vol. 61, p. 161.
Brunner, J.H., Anal. Chem., 1994, vol. 34, p. 1314.
Sofowora, A., Medicinal Plants and Traditional Medicine in Africa, Ibadan: Spectrum Books, 1995.
Bao, J.Y., Cai, M., Sun, G., et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2005, vol. 53, p. 2327.
Vinod, K.P., Narayanan, M.S., and Rexin, T.G., Port. Electrochim. Acta, 2012, vol. 28, p. 373.
Mulu, B.D., J. Thermodyn., 2013, vol. 20, p. 6.
Olasehinde, E.F., Olusegun, S.J., Adesina, A.S., et al., Nat. Sci., 2013, vol. 11, p. 83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oloruntoba, D.T., Popoola, A.P.I., Lawal, O.O. et al. Acid-acid function of Eichhornia crassipes roots as inhibitor for mild steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 53, 150–158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117010142
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205117010142