Abstract
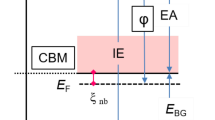
A model of the chemisorption passivity of metals based on the consideration of equality of the electrochemical potentials of the metal ion at the interfaces between the bulk of a metal, the monoatomic surface layer (SL) of a metal, and the surface metal oxide has been proposed. Thereby, unlike the Vetter model, this approach takes into account the occurrence of the Galvani potential of the metal atoms (ions) in the SL in the form of the surface Gibbs energy ΔG S(hkl) of a particular crystal face. On this basis, a formula of the Flade potential E F(S) of a metal has been derived; this formula, along with the chemical Gibbs energy of formation of oxides, makes allowance for the ΔG S(hkl) value (of a low-index face of the metal). Normal potential E 0F(S) (a pH of 0) has been calculated using the data of the first-principle calculation of the surface energy of metals. The calculated E 0F(S) values of 0.46 and−0.19 V for Ni and Cr, respectively, are in good agreement with the literature data. The calculated E F(S) values and the critical points in the anodic curves of passivation and activation of nickel in a 0.5 M H2SO4 solution and in the presence of KSCN additives have been compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vetter, K., Electrochemical Kinetics: Theoretical and Experimental Aspects, New York: Academic, 1967.
Flade, F., Z. Phys. Chem., 1911, vol. 76, p. 513.
Kolotyrkin, Ya.M., Z. Elektroch., 1958, Bd. 62, S. 664.
Shvabe, K., Electrochim. Acta, 1960, vol. 3, p. 186.
Uhlig, H.H., Corrosion and Corrosion Control, New York: Wiley, 1962.
Kabanov, B.N., Elektrokhimiya metallov i adsorbtsiya (Electrochemistry of Metals and Adsorption), Moscow: Nauka, 1966.
Erlikh, B.V., Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1942, vol. 37, p. 258.
Andreev, Yu.Ya., Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2012, vol. 48, no. 1, p. 42.
Andreev, Yu.Ya., Elektrokhimiya metallov i splavov (Electrochemistry of Metals and Alloys), Moscow: Vysshee Obraz. i Nauka., 2015.
Vitos, L., Ruban, A.V., Skriver, H.L., and Kollar, J., Surf. Sci., 1998, vol. 411, p. 186.
Andreev, Y.Y., Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2009, vol. 45, no. 6, p. 669-674.
Andreev, Y.Y., Bobkov, T.V., Dub, A.V., and Podgornyi, D.A., Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2013, vol. 49, no. 4, p. 444.
Kaesche, H., Die Korrosion der Metalle. PhysikalischChemische Prinzipien und Aktuelle Probleme, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1966.
Skapski, A.S., J. Chem. Phys., 1948, vol. 16, p. 386.
Roberts, M.W. and McKee, C.S., Chemistry of the Metal-Gas Interface, Oxford: Clarendon, 1978.
Andreev, Yu.Ya., Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 1998, vol. 72, no. 3, p. 447.
Andreev, Yu.Ya., Electrochim. Acta, 1998, vol. 43, p. 2627.
Andreev, Yu.Ya. and Kiselev, D.A., Phil. Mag., 2013, vol. 93, p. 2401.
Andreev, Yu.Ya., Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2005, vol. 79, no. 2, p. 179.
Thomas, J.M. and Thomas, W.J., Principles and Practice of Heterogeneous Catalysis, Weinheim: VCH, 1997.
Conway, B.E., in Electrochemistry–The Past Thirty Years and the Next Thirty Years, Bloom, H. and Gutmann, F., Eds., New York: Plenum, 1977.
Wickes, C.E. and Block, F.E., Thermodynamic Properties of 65 Elements–Their Oxides, Halides, Carbides, and Nitrides, Bureau Mines Bull. 605, Washington: US Gov. Print. Off., 1963.
Hoppe, H.-W. and Strehblow, H.-H., Surf. Interface Anal., 1989, vol. 14, p. 121.
Haupt, S. and Strehblow, H.-H., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1987, vol. 228, p. 365.
Sury, P., Corros. Sci., 1976, vol. 16, p. 879.
Kesten, M. and Feller, H.G., Electrochim. Acta, 1971, vol. 16, p. 763.
Marshakov, I.K., Zotova, E.E., and Protasova, I.V., Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2004, vol. 40, no. 3, p. 220–225.
Sato, N. and Okamoto, G., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1963, vol. 110, p. 605.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Yu.Ya. Andreev, T.V. Bobkov, 2015, published in Fizikokhimiya Poverkhnosti i Zashchita Materialov, 2015, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 456–465.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreev, Y.Y., Bobkov, T.V. Chemisorption model of electrochemical passivity of metals and thermodynamic calculation of the flade potential of metals Ni and Cr taking into account their surface Gibbs energy. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 51, 730–739 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205115050032
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205115050032