Abstract
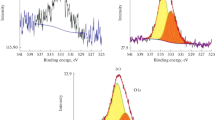
Cathode catalysts for a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell (FC) with proton-conducting (acidic) and anion-conducting (alkaline) electrolytes are synthesized via the pyrolysis of nitrogen-containing iron and cobalt complexes on the surfaces of highly disperse carbon materials. The catalysts are characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and tested under model conditions on a thin-layer disk electrode and as a part of a membrane electrode assembly of hydrogen–oxygen FCs. The properties of the CoFe/C system formed via the pyrolysis of macroheterocyclic cobalt and iron compounds on carbon materials (XC-72 soot and multiwall nanotubes (MNTs)) are described for the first time. According to XPS data, the surface of the CoFe/C catalytic systems is enriched with carbon (95.5 at %) and contains nitrogen (2 at %), oxygen (2 at %), and metals (0.5 at %). According to the results from electrochemical measurements under model conditions, the CoFe/MNT catalytic systems approaches 60% Pt/C (HiSPEC9100) commercial platinum catalyst according to their activity in the oxygen reduction reaction in an alkaline medium (0.5 M KOH). The half-wave potentials are 0.85 and 0.88 V for CoFe/MNT and 60% Pt/C (HiSPEC9100) catalysts, respectively. The maximum specific powers of hydrogen–oxygen FCs with anion-conducting electrolytes are 210 mW/cm2 (60% Pt/C (HiSPEC9100) based cathode) and 180 mW/cm2 (CoFe/MNT based cathode). The characteristics of a membrane electrode assembly with a non-platinum cathode correspond to the best analogs described in the literature. The results of this work show the prospects for further studies on scaling this technology for the synthesis of the proposed non-platinum cathode catalysts and optimizing the architecture of the membrane electrode assembly of FCs based on them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Fuel Cell Industry Review 2013. http://www. fuelcelltoday.com/media/1889744/fct_review_2013.pdf. Cited April 29, 2015.
Fernandes, A.C. and Ticianelli, E.A., J. Power Sources, 2009, vol. 193, no. 2, pp. 547–554.
Peighambardoust, S.J., Rowshanzamir, S., and Amjadi, M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2010, vol. 35, no. 17, pp. 9349–9384.
Nasef, M.M. and Aly, A.A., Desalination, 2012, vol. 287, pp. 238–246.
Merle, G., Wessling, M., and Nijmeijer, K., J. Membr. Sci., 2011, vol. 377, nos. 1–2, pp. 1–35.
Fukuta, K., Electrolyte materials for AMFCs and AMFC performance. http://www1.eere.energy.gov/ hydrogenandfuelcells/pdfs/amfc_050811_fukuta.pdf. Cited April 29, 2015.
Varcoe, J.R., Slade, R.C.T., Wright, G.L., and Chen, Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, vol. 110, no. 42, pp. 21041–21049.
Lu, S., Pan, J., Huang, A., Zhuang, L., and Lu, J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 52, pp. 20611–20614.
Sheng, W., Bivens, A.P., Myint, M., Zhuang, Z., Chen, J.G., and Yan, Y., 224th ECS Meet. Abstr., San Francisco, CA, 2013, abstract 1367.
Hu, Q., Li, G., Pan, J., Tan, L., Lu, J., and Zhuang, L., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, vol. 38, no. 36, pp. 16264–16268.
Ng, J.W.D., Gorlin, Y., Nordlund, D., and Jaramillo, T.F., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, vol. 161, no. 7, pp. D3105–D3112.
Tarasevich, M.R. and Korchagin, O.V., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2013, vol. 49, no. 7, pp. 600–618.
Tarasevich, M.R., Mazin, P.V., and Kapustina, N.A., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2012, vol. 48, no. 11, pp. 1113–1122.
Tarasevich, M.R., Mazin, P.V., and Kapustina, N.A., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2011, vol. 47, no. 8, pp. 923–932.
Bogdanovskaya, V.A., Tarasevich, M.R., and Lozovaya, O.V., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2011, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 846–860.
Bogdanovskaya, V.A., Beketaeva, L.A., Rybalka, K.V., Efremov, B.N., Zagudaeva, N.M., Sakashita, M., Iidzima, T., and Ismagilov, Z.R., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2008, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 293–302.
Yang, Z., Nie, H., Chen, X., Chen, X., and Huang, S., J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 236, pp. 238–249.
Procedures for performing in-plane membrane conductivity testing. http://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/ 2014/03/f10/htmwg_may09_conductivity_testing.pdf. Cited August 14, 2015.
Wang, H. and Turner, J.A., J. Power Sources, 2008, vol. 183, no. 2, pp. 576–580.
Grew, K.N., Ren, X., and Chu, D., Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2011, vol. 14, no. 12, pp. B127–B131.
Davydova, E.S. and Tarasevich, M.R., Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2015, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 240–247.
Finšgar, M., Fassbender, S., Hirth, S., and Milošev, I., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009, vol. 116, no. 1, pp. 198–206.
Pleskov, Yu.V. and Filinovskii, V.Yu., Vrashchayushchiisya diskovyi elektrod (Rotating Disk Electrode), Moscow: Nauka, 1972.
Tsivadze, A.Yu., Tarasevich, M.R., Kuzov, A.V., Kuznetsova, L.N., Lozovaya, O.V., Davydova, E.S., Dokl. Phys. Chem., 2012, vol. 442, no. 2, pp. 45–48.
Tarasevich, M.R. and Korchagin, O.V., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2014, vol. 50, no. 8, pp. 737–750.
Wu, J., Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Wan, Y., and Hou, B., J. Power Sources, 2012, vol. 198, pp. 122–126.
Gunasekara, I., Lee, M., Abbott, D., and Mukerjee, S., ECS Electrochem. Lett., 2012, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. F16–F19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Korchagin, V.A. Bogdanovskaya, M.R. Tarasevich, A.V. Kuzov, G.V. Zhutaeva, M.V. Radina, V.T. Novikov, V.V. Zharikov, 0000, published in Kataliz v Promyshlennosti.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korchagin, O.V., Bogdanovskaya, V.A., Tarasevich, M.R. et al. Characteristics of non-platinum cathode catalysts for a hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell with proton- and anion-conducting electrolytes. Catal. Ind. 8, 265–273 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070050416030053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070050416030053