Abstract
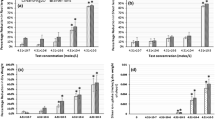
The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in the regulation of Germination and Seedling Parameters of Bitter Vetch (Vicia ervilia L.) Plants under Salinity stress (NaCl). Experimental salinity was controlled in terms of dS/m at levels of 0 (control), 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 dS/m. Different concentrations of AgNPs (0 (control), 5, 10, 15, and 20 ppm) were applied to Bitter Vetch plants at Germination and Seedling stage. Exposure of Salinity stress alone reduced the Germination parameter in the plant. However, the application of AgNPs protects Bitter Vetch plants against Salinity stress and improves the Germination parameter, plant root length, shoot length, root fresh weight, shoot dry weight, root dry weight and shoot fresh weight in 20 ppm AgNPs compared to control. In conclusion, the application of AgNPs may protect Bitter Vetch plants against Salinity stress by improving morphological growth.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
FAO, 2007, FAO Agristat. www.fao.org.
A. Maggio, S. Miyazaki, P. Veronese, et al., “Does proline accumulation play an active role in stress-induced growth reduction?,” Plant J. 2, 699 (2002).
P. H. Graham and C. P. Vance, “Legumes: Importance and constraints to greater use,” Plant Physiol., No. 131, 872–877 (2003).
J. E. Werner and R. R. Finkelstein, “Arabidopsis mutants with reduced response to NaCl and osmotic stress,” Physiol. Plantarum 93, 659 (1995).
M. A. Khan and S. Gulzar, “Germination responses of Sporobolus ioclados: A saline desert grass,” J. Arid Environ. 53, 387–394 (2003).
M. Gorai and M. Neffati, “Germination responses of Reaumuria vermiculata to salinity and temperature,” Ann. Appl. Biol. 151, 53–59 (2007).
I. A. Ungar, “Seed germination and seed-bank ecology of halophytes,” in Seed Dev. Germination, Ed. by J. Kigel and G. Galili (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1995), pp. 599–629.
D. Zohary, M. Hopf, and E. Weiss, Domestication of Plants in the Old World, 3rd ed. (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 2012), p. 264.
Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), GRIN Taxonomy for Plants (U. S. Dep. Agriculture, Agricult. Res. Service, Beltsville Area, 2008).
FAO, 2015. http://faostat3.fao.org/download/Q/QC/E
M. Trnka, J. E. Olesen, K. C. Ker Sebaum, et al., “Agroclimatic conditions in Europe under climate change,” Global Change Biol. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.pp.1365-2486.2011.02396.x
A. Foury, “Les légumineuses fourragères au Maroc (deuxième partie). Les cahiers de la recherche agronomique,” INRA, Rabat 5, 287–658 (1954).
N. Maxted, An Ecogeographical Study of Vicia Subgenus Vicia, Syst. Ecogeogr. Studies Crop Genepools 8 (International Plant Genetic Resources Inst., Rome, Italy, 1995).
A. M. Abd El Moneim, M. C. Saxena, A. El-Saleh, and H. Nakkoul, “The status of breeding Grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.) for improved yield and quality at ICARDA,” in Lathyrus and Lathyrism, a Decade of Progress, Ed. by R. Tekle Haimanat and F. Lambein (Univ. of Ghent, Ghent, Belgium, 1997), pp. 81–83.
V. K. Sharma, R. A. Yngard, and Y. Lin, “Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities,” Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 145, 83–96 (2009).
S. Hojjat and M. Kamyab, “The effect of silver nanoparticle on Fenugreek seed germination under salinity levels,” Russ. Agricult. Sci. 43, 61–65 (2017).
P. Sharma, D. Bhatt, M. G. Zaidi, et al., “Silver naoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea,” Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167, 2225–2233 (2012).
L. Yin, B. P. Coleman, B. M. McGill, et al., “Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on germination and early growth on eleven wetland plants,” PLoS One 7 (10), e47674 (2012).
C. Vannini, G. Domingo, E. Onelli, et al., “Morphological and proteomic responses of Eruca sativa exposed to silver nanoparticles or silver nitrate,” PLoS One 8 (7), e68752 (2013).
H. M. H. Salama, “Effects of silver nanoparticles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (Zea mays L.),” Int. Res. J. Biotechnol. 3, 190–197 (2012).
G. B. A. Shelar and M. Chavan, “Myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Trichoderma harzianum and its impact on germination status of oil seed,” Biolife 3, 109–113 (2015).
R. Barrena, E. Casals, J. Colon, et al., “Evaluation of the ecotoxicity of model nanoparticles,” Chemoshere 75, 850 (2009).
USEPA - United States Environmental Protection Agency, OPPTS 850.4400 Aquatic Plant Toxicity Test Using Lemna spp., Public draft, EPA 712-C-96-156 (1996).
S. Rehman, P. J. C. Harris, W. F. Bourne, and J. Wilkin, “The effect of sodium chloride on germination and the potassium and calcium contents of acacia seeds,” Seed Sci. Technol. 25, 45–57 (1996).
G. Okcu, M. Demir Kaya, and M. Atak, “Effects of salt and drought stresses on germination and seedling growth of pea (Pisum sativum L.),” Turk. J. Agricult. Forestry 9, 237–242 (2005).
G. Kaya, M. D. Kaya, M. Caliskan, and Y. Arslan, “Comparative analysis for germination and seedling growth of wheat with some competitive weeds under salinity,” J. Food. Agric. Environ. 7, 534–536 (2009).
J. D. Maguire, “Speed of germination-aid selection and evaluation for seedling emergence and vigor,” Crop Sci. 2, 176–177 (1962).
J. W. Bradbeer, Seed Dormancy and Germination (Blackie and Son, Glasgow, 1988), p. 146.
K. J. Bradford, “Water relations in seed germination,” Seed Developm. Germinat. 1, 351–396 (1995).
S. Senthilkumar, “Customizing nanoparticles for the maintenance of seed vigour and viability in Blackgram (Vigna mungo) cv. VBN 4,” Magister Sci. (Agric.) Thesis (TNAU, Coimbatore, India, 2010); R. Nair, S. H. Varghese, B. G. Nair, T. Maekawa, Y. Yoshida, and D. S. Kumar, “Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants,” Plant Sci. 179, 154–163 (2011).
F. Torney, B. G. Trewyn, V. S. Y. Lin, and K. Wang, “Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants,” Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 295–300 (2007).
P. K. Gill, A. D. Sharma, P. Singh, and S. S. Bhullar, “Changes in germination, growth and soluble sugar contents of sorghum bicolor L. moench seeds under various abiotic stresses,” Plant Growth Regulat. 40, 157–162 (2003).
M. Khodakovskaya, E. Dervishi, M. Mahmood, et al., “Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth,” ACS Nano 3, 3221–3227 (2009).
W. Larcher, Physiological Plant Ecology: Ecophysiology and Stress Physiology of Functional Groups (Springer, Berlin, 1995).
S. Hojjat and H. Hojjat, “Effect of nano silver on seed germination and seedling growth in Fenugreek seed,” Int. J. Food Eng. 1, 106–110 (2015).
S. Hojjat, “The effect of silver nanoparticle on lentil seed germination under drought stress,” Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 5, 208–212 (2016).
K. Loza, J. Diendorf, C. Sengstock, et al., “The dissolution and biological effects of silver nanoparticles in biological media,” J. Mater. Chem. B 2, 1634–1643 (2014).
A. Muscolo, M. R. Panussio, and M. Sidari, “The effect of phenols on respiratory enzymes in seed germination: Respiratory enzyme activities during germination of Pinus laricio seeds treated with phenols extracted from different forest soils,” Plant Growth Regul. 35, 31–35 (2001).
Applications and Properties of LUVITEC (Agriculture, BASF, 2019). www.luvitec.de.
M. Kumar, A. Kumar, R. Kumar, et al., “Effect of seed enhancement treatment on field performance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.),” J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 7, 557–561 (2015).
M. Tomita and M. Tomita, “Polyvinylpyrrolidone enhances seed germination and development of Cypripedium macranthos Sw. in vitro,” Plant Biotechnol. 15, 145–146 (1998).
K. Yu, H. Zhang, S. Biggs, et al., “The rheology of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silica nanoparticles positioned at the air-aqueous interface,” J. Colloid Interface Sci. 527, 346–355 (2018).
L. R. Khot, S. Sankaran, J. M. Maja, et al., “Applications of nanomaterials in agricultural production and crop protection: A review,” Crop Protect. 35, 64–70 (2012).
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Center for Plant Sciences, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad and Center of Excellence in Nanotechnology (COEN), Asian Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seyed Saeid Hojjat, Mozumder, C., Bora, T. et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Coated Silver Nanoparticle Mitigation of Salinity on Germination and Seedling Parameters of Bitter Vetch (Vicia ervilia L.) Plants. Nanotechnol Russia 14, 582–587 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019060077
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019060077