Abstract—
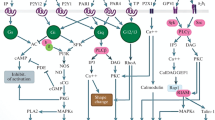
Glycoproteins IIb-IIIa (GPIIb-IIIa), also known as αIIbβ3 integrins, are key platelet adhesion receptors. These molecules are the most abundant (over 10 000 copies per cell) transmembrane receptors playing a crucial role in thrombus formation by promoting platelet aggregation. Integrins need to undergo activation and transit to high-affinity state for their ligands – fibrinogen, fibrin, and von Willebrand factor (VWF) – in order to form bonds between platelets. Activation of integrins is mediated by a set of various messengers through intracellular signalization. Integrins αIIbβ3, like other integrins, are capable of reverse signal transmission inside the cell, called “outside-in” signaling. Recent studies have shown heterogeneity of the thrombus structure and the existence of a stable and dense inner core and a fluid-like loose shell. Since platelet aggregation is provided by integrin-mediated interactions, one can suggest that it is the features of integrin activation and clustering that strongly influence the formation of thrombus architecture. This work is intent on systematizing recent data concerning activation and functioning of platelet integrins αIIbβ3 and searching for correlations between thrombus heterogeneity and the state of integrins on the platelets surface.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bouvard D., Brakebusch C., Gustafsson E., Aszódi A., Bengtsson T., Berna A., Fässler R. 2001. Functional consequences of integrin gene mutations in mice. Circ. Res. 89 (3), 211–223.
Yakimenko A.O., Sveshnikova A.N., Artemenko E.O., Panteleev M.A. 2014. This mysterious platelet. Priroda (Rus.). (2002), 3–8.
Bennett J.S. 1990. The molecular biology of platelet membrane proteins. Semin. Hematol. 27 (2), 186–204.
Plow E.F., Byzova T. 1999. The biology of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. Coron. Artery Dis. 10 (8), 547–551.
Stalker T.J., Newman D.K., Ma P., Wannemacher K.M., Brass L.F. 2012. Platelet signaling. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. (210), 59–85.
Panteleev M.A., Ananyeva N.M., Greco N.J., Ataullakhanov F.I., Saenko E.L. 2005. Two subpopulations of thrombin-activated platelets differ in their binding of the components of the intrinsic factor X-activating complex. J. Thromb. Haemost. 3 (11), 2545–2553.
Stalker T.J., Traxler E.A., Wu J., Wannemacher K.M., Cermignano S.L., Voronov R., Diamond S.L., Brass L.F. 2013. Hierarchical organization in the hemostatic response and its relationship to the platelet-signaling network. Blood. 121 (10), 1875 –1885.
Niiya K., Hodson E., Bader R., Byers-Ward V., Koziol J.A., Plow E.F., Ruggeri Z.M. 1987. Increased surface expression of the membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex induced by platelet activation. Relationship to the binding of fibrinogen and platelet aggregation. Blood. 70 (2), 475–483.
Wagner C.L., Mascelli M.A., Neblock D.S., Weisman H.F., Coller B.S., Jordan R.E. 1996. Analysis of GPIIb/IIIa receptor number by quantification of 7E3 binding to human platelets. Blood. 88 (3), 907–914.
Stouffer G.A., Smyth S.S. 2003. Effects of thrombin on interactions between beta3-integrins and extracellular matrix in platelets and vascular cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23 (11), 1971–1978.
Harrison P., Cramer E.M. 1993. Platelet alpha-granules. Blood Rev. 7 (1), 52–62.
Plow E.F., Haas T.A., Zhang L., Loftus J., Smith J.W. 2000. Ligand binding to integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (29), 21785–21788.
Plow E.F., D’Souza S.E., Ginsberg M.H. 1992. Ligand binding to GPIIb-IIIa: A status report. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 18 (3), 324–332.
Savage B., Cattaneo M., Ruggeri Z.M. 2001. Mechanisms of platelet aggregation. Curr. Opin. Hematol., 8 (5), 270–276.
Panteleev M.A., Ananyeva N.M., Ataullakhanov F.I., Saenko E.L. 2007. Mathematical models of blood coagulation and platelet adhesion: Clinical applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13 (14), 1457–1467.
Welsh J.D., Stalker T.J., Voronov R., Muthard R.W., Tomaiuolo M., Diamond S.L., Brass L.F. 2014. A systems approach to hemostasis: 1. The interdependence of thrombus architecture and agonist movements in the gaps between platelets. Blood. 124 (11), 1808–1815.
Tomaiuolo M., Stalker T.J., Welsh J.D., Diamond S.L., Sinno T., Brass L.F. 2014. A systems approach to hemostasis: 2. Computational analysis of molecular transport in the thrombus microenvironment. Blood. 124 (11), 1816–1823.
Shattil S.J., Kim C., Ginsberg M.H. 2010. The final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 288.
Buensuceso C., de Virgilio M., Shattil S.J. 2003. Detection of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 clustering in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278 (17), 15217–15224.
Bunch T.A. 2010. Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation in Chinese hamster ovary cells and platelets increases clustering rather than affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 285 (3), 1841–1849.
Hato T., Pampori N., Shattil S.J. 1998. Complementary roles for receptor clustering and conformational change in the adhesive and signaling functions of integrin alphaIIb beta3. J. Cell Biol. 141 (7), 1685–1695.
Banno A., Ginsberg M.H. 2008. Integrin activation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36 (Pt 2), 229–234.
Böttcher R.T., Fässler R. 2014. Membrane tension drives ligand-independent integrin signaling. EMBO J. 33 (21), 2439–2442.
Shattil S.J., Newman P.J. 2004. Integrins: Dynamic scaffolds for adhesion and signaling in platelets. Blood. 104 (6), 1606–1615.
Moroi A.J., Watson S.P. 2015. Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase enhance C-type lectin-like receptor 2-mediated platelet activation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3α/β. J. Thromb. Haemost. 13 (6), 1139–1150.
Lova P., Paganini S., Sinigaglia F., Balduini C., Torti M. 2002. A Gi-dependent pathway is required for activation of the small GTPase Rap1B in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (14), 12009–12015.
Mangin P.H., Onselaer M.-B., Receveur N., Le Lay N., Hardy A.T., Wilson C., Sanchez X., Loyau S., Dupuis A., Babar A.K., Miller J.L., Philippou H., Hughes C.E., Herr A.B., Ariëns R.A., Mezzano D., Jandrot-Perrus M., Gachet C., Watson S.P. 2018. Immobilized fibrinogen activates human platelets through glycoprotein VI. Haematologica. 103 (5), 898–907.
Boylan B., Gao C., Rathore V., Gill J.C., Newman D.K., Newman P.J. 2008. Identification of FcgammaRIIa as the ITAM-bearing receptor mediating alphaIIbbeta3 outside-in integrin signaling in human platelets. Blood. 112 (7), 2780–2786.
Antenucci L., Hytönen V.P., Ylänne J. 2018. Phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs and integrin cytoplasmic domains activate spleen tyrosine kinase via distinct mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (13), 4591–4602.
Lawler J., Hynes R.O. 1989. An integrin receptor on normal and thrombasthenic platelets that binds thrombospondin. Blood. 74 (6), 2022–2027.
Rivas G.A., González-Rodríguez J. 1991. Calcium binding to human platelet integrin GPIIb/IIIa and to its constituent glycoproteins. Effects of lipids and temperature. Biochem. J. 276 (Pt 1), 35–40.
Sheldrake H.M., Patterson L.H. 2009. Function and antagonism of beta3 integrins in the development of cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 9 (4), 519–540.
Uzan G., Prenant M., Prandini M.H., Martin F., Marguerie G. 1991. Tissue-specific expression of the platelet GPIIb gene. J. Biol. Chem. 266 (14), 8932–8939.
Oki T., Kitaura J., Eto K., Lu Y., Maeda-Yamamoto M., Inagaki N., Nagai H., Yamanishi Y., Nakajima H., Kumagai H., Kitamura T. 2006. Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 induces the adhesion and activation of mast cells through interaction with fibrinogen. J. Immunol. 176 (1), 52–60.
Oki T., Eto K., Izawa K., Yamanishi Y., Inagaki N., Frampton J., Kitamura T., Kitaura J. 2009. Evidence that integrin alpha IIb beta 3-dependent interaction of mast cells with fibrinogen exacerbates chronic inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (45), 31463–31472.
Emambokus N.R., Frampton J. 2003. The glycoprotein IIb molecule is expressed on early murine hematopoietic progenitors and regulates their numbers in sites of hematopoiesis. Immunity. 19 (1), 33–45.
Nurden A.T., Pillois X., Wilcox D.A. 2013. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: State of the art and future directions. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 39 (6), 642–655.
Di Minno G., Zotz R.B., d’Oiron R., Bindslev N., Di Minno M.N.D., Poon M.-C. 2015. The international, prospective Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Registry: Treatment modalities and outcomes of non-surgical bleeding episodes in patients with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Haematologica. 100 (8), 1031–1037.
Tsuji S., Sugimoto M., Miyata S., Kuwahara M., Kinoshita S., Yoshioka A. 1999. Real-time analysis of mural thrombus formation in various platelet aggregation disorders: Distinct shear-dependent roles of platelet receptors and adhesive proteins under flow. Blood. 94 (3), 968–975.
Springer T.A. 1997. Folding of the N-terminal, ligand-binding region of integrin alpha-subunits into a beta-propeller domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94 (1), 65–72.
Springer T.A. 2002. Predicted and experimental structures of integrins and beta-propellers. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12 (6), 802–813.
Xiong J.P., Stehle T., Diefenbach B., Zhang R., Dunker R., Scott D.L., Joachimiak A., Goodman S.L., Arnaout M.A. 2001. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alpha Vbeta3. Science. 294 (5541), 339–345.
Ma Y.-Q., Qin J., Plow E.F. 2007. Platelet integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3): Activation mechanisms. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5 (7), 1345–1352.
Campbell I.D., Humphries M.J. 2011. Integrin structure, activation, and interactions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 3 (3), a004994.
Zhu J., Luo B.-H., Xiao T., Zhang C., Nishida N., Springer T.A. 2008. Structure of a complete integrin ectodomain in a physiologic resting state and activation and deactivation by applied forces. Mol. Cell. 32 (6), 849–861.
Luo B.-H., Carman C. V., Springer T.A. 2007. Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 619–647.
Calvete J.J., Henschen A., Gonzalez-Rodriguez J. 1989. Complete localization of the intrachain disulphide bonds and the N-glycosylation points in the alpha-subunit of human platelet glycoprotein IIb. Biochem. J. 261 (2), 561–568.
Xiong J.-P., Stehle T., Goodman S.L., Arnaout M.A. 2003. Integrins, cations and ligands: Making the connection. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1 (7), 1642–1654.
Xiong J.-P., Mahalingham B., Alonso J.L., Borrelli L.A., Rui X., Anand S., Hyman B.T., Rysiok T., Muller-Pompalla D., Goodman S.L., Arnaout M.A. 2009. Crystal structure of the complete integrin alphaVbeta3 ectodomain plus an alpha/beta transmembrane fragment. J. Cell Biol. 186 (4), 589–600.
Beglova N., Blacklow S.C., Takagi J., Springer T.A. 2002. Cysteine-rich module structure reveals a fulcrum for integrin rearrangement upon activation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9 (4), 282–287.
Takagi J., Petre B.M., Walz T., Springer T.A. 2002. Global conformational rearrangements in integrin extracellular domains in outside-in and inside-out signaling. Cell. 110 (5), 511–599.
Yang J., Ma Y.-Q., Page R.C., Misra S., Plow E.F., Qin J. 2009. Structure of an integrin alphaIIb beta3 transmembrane-cytoplasmic heterocomplex provides insight into integrin activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106 (42), 17729–17734.
Liu S., Calderwood D.A., Ginsberg M.H. 2000. Integrin cytoplasmic domain-binding proteins. J. Cell Sci. 113 (Pt 2), 3563–3571.
Aylward K., Meade G., Ahrens I., Devocelle M., Moran N. 2006. A novel functional role for the highly conserved alpha-subunit KVGFFKR motif distinct from integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation processes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 4 (8), 1804–1812.
Vinogradova O., Velyvis A., Velyviene A., Hu B., Haas T.A., Plow E.F., Qin J. 2002. A Structural mechanism of integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) “inside-out” activation as regulated by its cytoplasmic face. Cell. 110 (5), 587–597.
Weljie A.M., Hwang P.M., Vogel H.J. 2002. Solution structures of the cytoplasmic tail complex from platelet integrin alpha IIb- and beta 3-subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99 (9), 5878–5883.
Calderwood D.A., Fujioka Y., de Pereda J.M., Garcia-Alvarez B., Nakamoto T., Margolis B., McGlade C.J., Liddington R.C., Ginsberg M.H. 2003. Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: A structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100 (5), 2272–2277.
Calderwood D.A., Zent R., Grant R., Rees D.J., Hynes R.O., Ginsberg M.H. 1999. The Talin head domain binds to integrin beta subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (40), 28071–28074.
Tadokoro S., Shattil S.J., Eto K., Tai V., Liddington R.C., de Pereda J.M., Ginsberg M.H., Calderwood D.A. 2003. Talin binding to integrin beta tails: A final common step in integrin activation. Science. 302 (5642), 103–106.
Martel V., Racaud-Sultan C., Dupe S., Marie C., Paulhe F., Galmiche A., Block M.R., Albiges-Rizo C. 2001. Conformation, localization, and integrin binding of talin depend on its interaction with phosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (24), 21217–21227.
Wegener K.L., Partridge A.W., Han J., Pickford A.R., Liddington R.C., Ginsberg M.H., Campbell I.D. 2007. Structural basis of integrin activation by talin. Cell. 128 (1), 171–182.
D’Souza M.-A.M.A., Kimble R.M., McMillan J.R. 2010. Kindler syndrome pathogenesis and fermitin family homologue 1 (kindlin-1) function. Dermatol. Clin. 28 (1), 115–118.
Moser M., Legate K.R., Zent R., Fassler R. 2009. The tail of integrins, talin, and kindlins. Science. 324 (5929), 895–899.
Kammerer P., Aretz J., Fässler R. 2017. Lucky kindlin: A cloverleaf at the integrin tail. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 114 (35), 9234–9236.
Brunner M., Millon-Fremillon A., Chevalier G., Nakchbandi I.A., Mosher D., Block M.R., Albiges-Rizo C., Bouvard D. 2011. Osteoblast mineralization requires beta1 integrin/ICAP-1-dependent fibronectin deposition. J. Cell Biol. 194 (2), 307–322.
Shock D.D., Naik U.P., Brittain J.E., Alahari S.K., Sondek J., Parise L.V. 1999. Calcium-dependent properties of CIB binding to the integrin alphaIIb cytoplasmic domain and translocation to the platelet cytoskeleton. Biochem. J. 342 (Pt 3), 729–735.
Larkin D., Murphy D., Reilly D.F., Cahill M., Sattler E., Harriott P., Cahill D.J., Moran N. 2004. ICln, a novel integrin alphaIIbbeta3-associated protein, functionally regulates platelet activation. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (26), 27286–27293.
Kato A., Kawamata N., Tamayose K., Egashira M., Miura R., Fujimura T., Murayama K., Oshimi K. 2002. Ancient ubiquitous protein 1 binds to the conserved membrane-proximal sequence of the cytoplasmic tail of the integrin alpha subunits that plays a crucial role in the inside-out signaling of alpha IIbbeta 3. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (32), 28934–28941.
Vijayan K.V., Liu Y., Li T.-T., Bray P.F. 2004. Protein phosphatase 1 associates with the integrin alphaIIb subunit and regulates signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (32), 33039–33042.
Rantala J.K., Pouwels J., Pellinen T., Veltel S., Laasola P., Mattila E., Potter C.S., Duffy T., Sundberg J.P., Kallioniemi O., Askari J.A., Humphries M.J., Parsons M., Salmi M., Ivaska J. 2011. SHARPIN is an endogenous inhibitor of beta1-integrin activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 13 (11), 1315–1324.
Sveshnikova A.N., Balatskiy A.V., Demianova A.S., Shepelyuk T.O., Shakhidzhanov S.S., Balatskaya M.N., Pichugin A. V., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Systems biology insights into the meaning of the platelet’s dual-receptor thrombin signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 14 (10), 2045–2057.
Horowitz L.F., Hirdes W., Suh B.-C., Hilgemann D.W., Mackie K., Hille B. 2005. Phospholipase C in living cells: Activation, inhibition, Ca2+ requirement, and regulation of M current. J. Gen. Physiol. 126 (3), 243–262.
Shaturny V.I., Shakhidzhanov S.S., Sveshnikova A.N., Panteleev M.A. 2014. Activators, receptors and signal transduction pathways of blood platelets. Biomed. Khimiya (Rus). 60 (2), 182–200.
Burkhart J.M., Vaudel M., Gambaryan S., Radau S., Walter U., Martens L., Geiger J., Sickmann A., Zahedi R.P. 2012. The first comprehensive and quantitative analysis of human platelet protein composition allows the comparative analysis of structural and functional pathways. Blood. 120 (1528–0020 (Electronic)), e73–e82.
Lian L., Wang Y., Draznin J., Eslin D., Bennett J.S., Poncz M., Wu D., Abrams C.S. 2005. The relative role of PLC and PI3K in platelet activation. Blood. 106 (1), 110–117.
Tsang E., Giannetti A.M., Shaw D., Dinh M., Tse J.K.Y., Gandhi S., Ho A., Wang S., Papp E., Bradshaw J.M. 2008. Molecular mechanism of the Syk activation switch. J. Biol. Chem. 283 (47), 32650–32659.
Watson S.P., Herbert J.M.J., Pollitt A.Y. 2010. GPVI and CLEC-2 in hemostasis and vascular integrity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 8 (7), 1456–1467.
Dunster J.L., Mazet F., Fry M.J., Gibbins J.M., Tindall M.J. 2015. Regulation of early steps of GPVI signal transduction by phosphatases: A systems biology a pproach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11 (11), 1–26.
Pasquet J.M., Gross B., Quek L., Asazuma N., Zhang W., Sommers C.L., Schweighoffer E., Tybulewicz V., Judd B., Lee J.R., Koretzky G., Love P.E., Samelson L.E., Watson S.P. 1999. LAT is required for tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase cgamma2 and platelet activation by the collagen receptor GPVI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (12), 8326–8334.
Moroi A.J., Watson S.P. 2015. Impact of the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway on ITAM and hemITAM receptors: Haemostasis, platelet activation and antithrombotic therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 94 (3), 186–194.
Suzuki-Inoue K., Tulasne D., Shen Y., Bori-Sanz T., Inoue O., Jung S.M., Moroi M., Andrews R.K., Berndt M.C., Watson S.P. 2002. Association of Fyn and Lyn with the proline-rich domain of glycoprotein VI regulates intracellular signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (24), 21561–21566.
Nieswandt B., Bergmeier W., Schulte V., Rackebrandt K., Gessner J.E., Zirngibl H. 2000. Expression and function of the mouse collagen receptor glycoprotein VI is strictly dependent on its association with the FcR gamma chain. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (31), 23998–24002.
May F., Hagedorn I., Pleines I., Bender M., Vogtle T., Eble J., Elvers M., Nieswandt B. 2009. CLEC-2 is an essential platelet activating receptor in hemostasis and thrombosis. Blood. 114 (16), 3464–3473.
Sveshnikova A.N., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2015. Compartmentalized calcium signaling triggers subpopulation formation upon platelet activation through PAR1. Mol. BioSyst. 11 (4), 1052–1060.
Stefanini L., Bergmeier W. 2014. CalDAG-GEFI and platelet activation. Platelets. 21 (4), 239–243.
Stefanini L., Bergmeier W. 2016. RAP1-GTPase signaling and platelet function. J. Mol. Med. 94 (1), 13–19.
Stefanini L., Paul D.S., Robledo R.F., Chan E.R., Getz T.M., Campbell R.A., Kechele D.O., Casari C., Piatt R., Caron K.M., Mackman N., Weyrich A.S., Parrott M.C., Boulaftali Y., Adams M.D., Peters L.L., Bergmeier W. 2015. RASA3 is a critical inhibitor of RAP1-dependent platelet activation. J. Clin. Invest. 125 (4), 1419–1432.
Battram A.M., Durrant T.N., Agbani E.O., Heesom K.J., Paul D.S., Piatt R., Poole A.W., Cullen P.J., Bergmeier W., Moore S.F., Hers I. 2017. The phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3) binder Rasa3 regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent integrin αIIbβ3outside-in signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 292 (5), 1691–1704.
Lawrence M.B., McIntire L.V., Eskin S.G. 1987. Effect of flow on polymorphonuclear leukocyte/endothelial cell adhesion. Blood. 70 (5), 1284–1290.
Turner N.A., Sartain S.E., Hui S.-K., Moake J.L. 2015. Regulatory components of the alternative complement pathway in endothelial cell cytoplasm, factor H and factor I, are not packaged in Weibel-Palade bodies. PLoS One. 10 (3), e0121994.
Gralnick H.R., Williams S.B., McKeown L.P., Magruder L., Hansmann K., VAIL M., Parker R.I. 1991. Platelet von Willebrand factor. Mayo Clin. Proc. 66 (6), 634–640.
Yin H., Liu J., Li Z., Berndt M.C., Lowell C.A., Du X. 2008. Src family tyrosine kinase Lyn mediates VWF/GPIb-IX-induced platelet activation via the cGMP signaling pathway. Blood. 112 (4), 1139–1146.
Canobbio I., Balduini C., Torti M. 2004. Signalling through the platelet glycoprotein Ib-V–IX complex. Cell. Signal. 16 (12), 1329–1344.
Litvinov R.I., Farrell D.H., Weisel J.W., Bennett J.S. 2016. The platelet integrin αIIbβ3 differentially interacts with fibrin versus fibrinogen. J. Biol. Chem. 291 (15), 7858–7867.
Schaff M., Tang C., Maurer E., Bourdon C., Receveur N., Eckly A., Hechler B., Arnold C., de Arcangelis A., Nieswandt B., Denis C.V., Lefebvre O., Georges-Labouesse E., Gachet C., Lanza F., Mangin P.H. 2013. Integrin α6β1 is the main receptor for vascular laminins and plays a role in platelet adhesion, activation, and arterial thrombosis. Circulation. 128 (5), 541–552.
Wu Y., Span L.M., Nygren P., Zhu H., Moore D.T., Cheng H., Roder H., DeGrado W.F., Bennett J.S. 2015. The tyrosine kinase c-Src specifically binds to the active integrin αIIbβ3 to initiate outside-in signaling in platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (25), 15825–15834.
Schmaier A.A., Zou Z., Kazlauskas A., Emert-Sedlak L., Fong K.P., Neeves K.B., Maloney S.F., Diamond S.L., Kunapuli S.P., Ware J., Brass L.F., Smithgall T.E., Saksela K., Kahn M.L. 2009. Molecular priming of Lyn by GPVI enables an immune receptor to adopt a hemostatic role. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106 (50), 21167–21172.
Peerschke E.I.B.I. 1995. Bound fibrinogen distribution on stimulated platelets: Examination by confocal scanning laser microscopy. Am. J. Pathol. 147, 678–687.
Obydennyy S.I., Sveshnikova A.N., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Dynamics of calcium spiking, mitochondrial collapse and phosphatidylserine exposure in platelet subpopulations during activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 14 (9), 1867–1881.
Morozova D., Demianova A., Canault M., Panteleev M., Alessi M.-C., Sveshnikova. A. 2018. Identification of platelet intracellular signalling pathways controlling the reversible and irreversible platelet aggregation. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2 (S1), 46.
Mazurov A.V., Vinogradov D.V., Kabaeva N.V., Antonova G.N., Romanov Y.A., Vlasik T.N., Antonov A.S., Smirnov V.N. 1991. A monoclonal antibody, VM64, reacts with a 130 kDa glycoprotein common to platelets and endothelial cells: Heterogeneity in antibody binding to human aortic endothelial cells. Thromb. Haemost. 66 (4), 494—499.
Chen Y., Ju L., Jackson S., Zhu C. 2018. An intermediate state of integrin αIIbβ3 mediates platelet aggregation under disturbed flow. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2 (S1), 43.
Plow E.F., Marguerie G.A. 1980. Participation of ADP in the binding of fibrinogen to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Blood. 56 (3), 553–555.
Plow E.F., Marguerie G.A. 1980. Induction of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by epinephrine and the combination of epinephrine and ADP. J. Biol. Chem. 255 (22), 10971–10977.
Shattil S.J., Hoxie J.A., Cunningham M., Brass L.F. 1985. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex during platelet activation. J. Biol. Chem. 260 (20), 11107–11114.
Bennett J.S., Vilaire G. 1979. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J. Clin. Invest. 64 (5), 1393–1401.
Isenberg W.M., Mcever R.P., Phillips D.R., Shuman M.A., Bainton D.F. 1989. Immunogold-surface replica study of ADP-induced ligand binding and fibrinogen receptor clustering in human platelets. Am. J. Anat. 85, 142–148.
Nguyen T.-H., Palankar R., Bui V.-C., Medvedev N., Greinacher A., Delcea M. 2016. Rupture forces among human blood platelets at different degrees of activation. Sci. Rep. 6, 25402.
Weisel J.W., Litvinov R.I. 2013. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood. 121 (10), 1712–1719.
Höök P., Litvinov R.I., Kim O. V., Xu S., Xu Z., Bennett J.S., Alber M.S., Weisel J.W. 2017. Strong binding of platelet integrin αIIbβ3 to fibrin clots: Potential target to destabilize thrombi. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 13001.
Litvinov R.I., Shuman H., Bennett J.S., Weisel J.W. 2002. Binding strength and activation state of single fibrinogen-integrin pairs on living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99 (11), 7426–7431.
Topalov N.N., Kotova Y.N., Vasil’ev S.A., Panteleev M.A. 2012. Identification of signal transduction pathways involved in the formation of platelet subpopulations upon activation. Br. J. Haematol. 157 (1), 105–115.
Shakhidzhanov S.S., Shaturny V.I., Panteleev M.A., Sveshnikova A.N. 2015. Modulation and pre-amplification of PAR1 signaling by ADP acting via the P2Y12 receptor during platelet subpopulation formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1850 (12), 2518–2529.
Obydennyy S.I., Sveshnikova A.N., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Dynamics of calcium spiking, mitochondrial collapse and phosphatidylserine exposure in platelet subpopulations during activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 14 (9), 1867–1881.
Belyaev A.V., Dunster J.L., Gibbins J.M., Panteleev M.A., Volpert V. 2018. Modeling thrombosis in silico: Frontiers, challenges, unresolved problems and milestones. Phys. Life Rev. 26–27, 57–95.
Panteleev M.A., Saenko E.L., Ananyeva N.M., Ataullakhanov F.I. 2004. Kinetics of Factor X activation by the membrane-bound complex of Factor IXa and Factor VIIIa. Biochem. J. 381 (Pt 3), 779–794.
Zakharova N.V., Artemenko E.O., Podoplelova N.A., Sveshnikova A.N., Demina I.A., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2015. Platelet surface-associated activation and secretion-mediated inhibition of coagulation factor XII. PLoS One. 10 (2), e0116665.
Topalov N.N., Yakimenko A.O., Canault M., Artemenko E.O., Zakharova N.V., Abaeva A.A., Loosveld M., Ataullakhanov F.I., Nurden A.T., Alessi M.-C., Panteleev M.A. 2012. Two types of procoagulant platelets are formed upon physiological activation and are controlled by integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32 (10), 2475–2483.
Dale G.L., Friese P., Batar P., Hamilton S.F., Reed G.L., Jackson K.W., Clemetson K.J., Alberio L. 2002. Stimulated platelets use serotonin to enhance their retention of procoagulant proteins on the cell surface. Nature. 415 (6868), 175–179.
Munnix I.C.A., Kuijpers M.J.E., Auger J., Thomassen C.M.L.G.D., Panizzi P., van Zandvoort M.A.M., Rosing J., Bock P.E., Watson S.P., Heemskerk J.W.M. 2007. Segregation of platelet aggregatory and procoagulant microdomains in thrombus formation: Regulation by transient integrin activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27 (11), 2484–2490.
Mattheij N.J.A., Gilio K., van Kruchten R., Jobe S.M., Wieschhaus A.J., Chishti A.H., Collins P., Heem-skerk J.W.M., Cosemans J.M.E.M. 2013. Dual mechanism of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 closure in procoagulant platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (19), 13325–13336.
Artemenko E.O., Yakimenko A.O., Pichugin A. V., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Calpain-controlled detachment of major glycoproteins from the cytoskeleton regulates adhesive properties of activated phosphatidylserine-positive platelets. Biochem. J. 473 (4), 435–448.
Podoplelova N.A., Sveshnikova A.N., Kotova Y.N., Eckly A., Receveur N., Nechipurenko D.Y., Obydennyi S.I., Kireev I.I., Gachet C., Ataullakhanov F.I., Mangin P.H., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Coagulation factors bound to procoagulant platelets concentrate in cap structures to promote clotting. Blood. 128 (13), 1745–1755.
Podoplelova N.A., Sveshnikova A.N., Kurasawa J.H., Sarafanov A.G., Chambost H., Vasil’ev S.A., Demina I.A., Ataullakhanov F.I., Alessi M.-C., Panteleev M.A. 2016. Hysteresis-like binding of coagulation factors X/Xa to procoagulant activated platelets and phospholipids results from multistep association and membrane-dependent multimerization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1858 (6), 1216–1227.
Yakimenko A.O., Verholomova F.Y., Kotova Y.N., Ataullakhanov F.I., Panteleev M.A. 2012. Identification of different proaggregatory abilities of activated platelet subpopulations. Biophys. J. 102 (10), 2261–2269.
Abaeva A.A., Canault M., Kotova Y.N., Obydennyy S.I., Yakimenko A.O., Podoplelova N.A., Kolyadko V.N., Chambost H., Mazurov A.V., Ataullakhanov F.I., Nurden A.T., Alessi M.-C., Panteleev M.A. 2013. Procoagulant platelets form an alpha-granule protein-covered “cap” on their surface that promotes their attachment to aggregates. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (41), 29621–29632.
Yuki K., Bu W., Shimaoka M., Eckenhoff R. 2013. Volatile anesthetics, not intravenous anesthetic propofol bind to and attenuate the activation of platelet receptor integrin αIIbβ3. PLoS One. 8 (4), e60415.
Assinger A., Volf I., Schmid D. 2015. A Novel, rapid method to quantify intraplatelet calcium dynamics by ratiometric flow cytometry. PLoS One. 10 (4), 1–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by V. Kaneva
Abbreviations: ADMIDAS, domain adjacent to MIDAS; Btk, Bruton tyrosine kinase; CalDAG-GEFI, Ca2+ and diacylglycerol regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor I; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary cells; CLEC-2, C-type lectin-like receptor 2; DAG, diacylglycerol; DTS, dense tubular system; EGF, Epidermal Growth Factor; FERM, 4.1 protein, ezrin, radixin, moesin; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor; GPIb, glycoprotein Ib; GPVI, glycoprotein VI; ICln, chloride channel regulatory protein; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; LAT, linker for activation of T cells; LIMBS, ligand-associated metal-binding site; MIDAS, metal-ion dependent adhesion site; PAR, protease-activated receptor; PH domain, pleckstrin homology domain; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCβ(γ-2),Phospholipase Cβ(γ-2); PP1, protein phosphatase 1; RASA3, Ras GTPase-activating protein 3; RIAM, Rap1–GTP-interacting adapter molecule; SFK, Src family kinases; SH-2, Src homology 2 domain; Syk, Spleen tyrosine kinase; TRAP, thrombin receptor-activating peptide; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneva, V.N., Martyanov, A.A., Morozova, D.S. et al. Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3: Mechanisms of Activation and Clustering; Involvement into the Formation of the Thrombus Heterogeneous Structure. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 13, 97–110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747819010033
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747819010033