Abstract
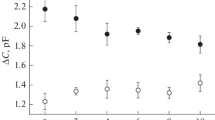
Electrogenic binding of ions from the cytoplasmic side of the Na+,K+-ATPase has been studied by measurements of changes of the membrane capacitance and conductance triggered by a jump of pH or of the sodium-ion concentration in the absence of ATP. The pH jumps were performed in experiments with membrane fragments containing purified Na+,K+-ATPase adsorbed to a bilayer lipid membrane (BLM). Protons were released in a sub-millisecond time range from a photosensitive compound (caged H+) triggered by a UV light flash. The sodium concentration jumps were carried out by a fast solution exchange in experiments with membrane fragments attached to a solid-supported membrane deposited on a gold electrode. The change of the membrane capacitance triggered by the pH jump depended on the sodium-ion concentration. Potassium ions had a similar effect on the capacitance change triggered by a pH jump. The effects of these ions are explained by the their competition with protons in the binding sites on cytoplasmic side of the Na+,K+-ATPase. The approximation of the experimental data by a theoretical model yields the dissociation constants, K, and the cooperativity coefficients, n, of the binding sites for sodium ions (K = 2.7 mM, n = 2) and potassium ions (K = 1.7 mM, n = 2). In the presence of magnesium ions the apparent dissociation constants of sodium increased. A possible reason of the inhibition of sodium-ion binding by magnesium ions can be an electrostatic or conformational effect of magnesium ions bound to a separate site of the Na+,K+-ATPase close to the entrance to the sodium-ion binding sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Läuger P. 1991. Electrogenic ion pumps. Sunderland, Massachusets, USA: Sinauer associates, Inc.
Toyoshima C. 2009. How Ca2+-ATPase pumps ions across the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1793 (6), 941–946.
Morth J.P., Pedersen B.P., Toustrup-Jensen M.S., Sorensen T.L., Petersen J., Andersen J.P., Vilsen B., Nissen P. 2007. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature. 450 (7172), 1043–1049.
Ogawa H., Shinoda T., Cornelius F., Toyoshima C. 2009. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase) with bound potassium and ouabain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106 (33), 13742–13747.
Shinoda T., Ogawa H., Cornelius F., Toyoshima C. 2009. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4 Å resolution. Nature. 459 (7245), 446–450.
Kanai R., Ogawa H., Vilsen B., Cornelius F., Toyoshima C. 2013. Crystal structure of a Na+-bound Na+,K+-ATPase preceding the E1P state. Nature. 502 (7470), 201–206.
Apell H.J., Diller A. 2002. Do H+ ions obscure electrogenic Na+ and K+ binding in the E1 state of the Na,K-ATPase? FEBS Lett. 532 (1–2), 198–202.
Apell H.J., Benz G., Sauerbrunn D. 2011. Proton diet for the sodium pump. Biochemistry. 50 (3), 409–418.
Khater K.A., Rakowski R.F. 1997. Na/K-ATPase and related transport ATPases. Structure, mechanism and regulation. L.A. Beauge, D.C. Gadsby, P.J. Garrahan, Eds. New York: Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. pp. 350–353.
Vasilyev A., Khater K., Rakowski R.F. 2004. Effect of extracellular pH on presteady-state and steady-state current mediated by the Na+/K+ pump. J. Membr. Biol. 198 (2), 65–76.
Vedovato N., Gadsby D.C. 2014. Route, mechanism, and implications of proton import during Na+/K+ exchange by native Na+/K+-ATPase pumps. J. Gen. Physiol. 143 (4), 449–464.
Or E., Goldshleger R., Karlish S.J.D. 1996. An effect of voltage on binding of Na+ at the cytoplasmic surface of the Na+,K+ pump. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2470–2477.
Sokolov V.S., Shcherbakov A.A., Lenz A.A., Chizmadzhev Yu.A., Apell H.-J. 2008. Electrogenic transport of sodium ions in cytoplasmic and extracellular ion access channels of Na+,K+-ATPase probed by admittance measurement technique. Biochem. (Moscow) Suppl. Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology. 2 (2), 161–180.
Pintschovius J., Fendler K., Bamberg E. 1999. Charge translocation by the Na+/K+-ATPase investigated on solid supported membranes: Cytoplasmic cation binding and release. Biophys. J. 76 (2), 827–836.
Schneeberger A., Apell H.J. 2001. Ion selectivity of the cytoplasmic binding sites of the Na,K-ATPase: II. Competition of various cations. J. Membr. Biol. 179 (3), 263–273.
Schneeberger A., Apell H.J. 1999. Ion selectivity of the cytoplasmic binding sites of the Na,K-ATPase: I. Sodium binding is associated with a conformational rearrangement. J. Membr. Biol. 168 (3), 221–228.
Glynn I.M. 1985. The enzymes of biological membranes. A.N. Martonosi, Ed. New York: Plenum Press, pp. 35–114.
Schwappach B., Stürmer W., Apell H.J., Karlish S.J. 1994. Binding of sodium ions and cardiotonic steroids to native and selectively trypsinized Na,K pump, detected by charge movements. J. Biol. Chem. 269 (34), 21620–21626.
Tashkin V.Yu., Shcherbakov A.A., Apell H.-J., Sokolov V.S. 2013. The competition transport of sodium ions and protons in cytoplasmic access channel of the Na+,K+ATPase. Biol. Memb. (Rus.). 30 (2), 105–114. [Transl. version: Tashkin V.Yu., Shcherbakov A.A., Apell H.-J., Sokolov V.S. 2013. The competition transport of sodium ions and protons at the cytoplasmic side of Na,K-ATPase. Biochemistry (Moscow) Suppl. Series A: Membr. Cell Biol. 7 (2), 102–114].
Tadini-Buoninsegni F., Bartolommei G., Moncelli M.R., Fendler K. 2008. Charge transfer in P-type ATPases investigated on planar membranes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 476 (1), 75–86.
Pintschovius J., Fendler K. 1999. Charge translocation by the Na+/K+-ATPase investigated on solid supported membranes: Rapid solution exchange with a new technique. Biophys. J. 76 (2), 814–826.
Jorgensen P.L. 1974. Isolation of the Na,K-ATPase. Meth. Enzymol. 32, 277–290.
Fendler K., Grell E., Haubs M., Bamberg E. 1985. Pump currents generated by the Na+,K+-ATPase from kidney on black lipid membranes. EMBO J. 4, 3079–3085.
Borlinghaus R., Apell H.J., Läuger P. 1987. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: I. Current and voltage transients after photochemical release of ATP. J. Membr. Biol. 97 (3), 161–178.
Apell H.J., Karlish S.J. 2001. Functional properties of Na,K-ATPase, and their structural implications, as detected with biophysical techniques. J. Membr. Biol. 180 (1), 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.Yu. Tashkin, A.N. Gavrilchik, A.I. Ilovaisky, H.-J. Apell, V.S. Sokolov, 2015, published in Biologicheskie Membrany, 2015, Vol. 32, No. 2, pp. 110–118.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tashkin, V.Y., Gavrilchik, A.N., Ilovaisky, A.I. et al. Electrogenic binding of ions at the cytoplasmic side of the Na+,K+-ATPase. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 9, 92–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747815020105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747815020105