Abstract
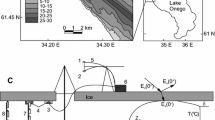
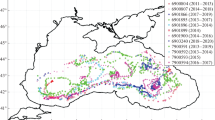
We investigated the influence of deep forced temperature convection on aeration of the bottom water layer in the pelagic zone of Baikal. Temperature T (± 0.002°C) and oxygen O2 concentration (± 0.01 mg/L) were measured by using the SBE-25 probe with the SBE-43 oxygen sensor in May-July 2006−2007 and 2009−2013. Oxygen input into the bottom layer with cold intrusions was determined for 79 cases. The study revealed a quantitative correlation between the heat deficit and the rise in oxygen content in the bottom layer during cold intrusions. This correlation was used to reconstruct the values of intrusion aeration of the bottom layer during 1993−2005. It is ascertained that the intrusion-caused 2006−2013-average oxygen input into Baikal’s bottom layer is virtually close to the annual oxygen demand for oxidation processes in the water column and bottom sediments. In the southern and middle parts of Baikal, intrusion-caused input of oxygen corresponds to a higher rate of its demand (4.5−4.6x10-4 mg/L per day). A slight increase in oxygen concentration was detected in the bottom layer of the South and Middle Baikal and a slight decrease in the bottom layer of North Baikal during 1993−2013.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vereshchagin, G.Yu., Hydrochemical Observations in Southern Baikal in Summer 1926, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 1927, no. 20, pp. 327–332 [in Russian].
Tolmachev, V.A., On Seasonal Variations in Dissolved Oxygen at Great Depths of Baikal, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 1957, vol. 113, no. 2, pp. 395–398 [in Russian].
Votintev, K.K., Hydrochemical Conditions in the Deep Region of Lake Baikal, Trudy Baikal. Limnol. Stantsii ANSSSR, 1965, vol. 6(26), pp. 71–114 [in Russian].
Vereshchagin, G.Yu., Some Data on the Deep Water Regime in the Area of Maritui, Trudy Komissii po Izucheniyu Ozera Baikal, 1927, vol. 2, pp. 77–138 [in Russian].
Weiss, R.F., Carmack, E.C. and Koropalov, V.M., Deep-Water Renewal and Biological Production in Lake Baikal, Nature, 1991, no. 6311, pp. 665–669.
Shimaraev, M.N. and Granin, N.G., Concerning the Stratification and the Convection Mechanism in Baikal, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 1991, vol. 321, no. 2, pp. 381–385 [in Russian].
Shimaraev, M.N., Zhdanov, A.A., Gnatovskii, Yu.R., Blinov, V.V., and Ivanov, V.G., Specific Features of Cold Bottom Intrusion in Baikal According to Observations in 1993–2009, Water Resour., 2011, vol. 38, issue 2, pp. 169–174.
Shimaraev, M.N., Gnatovskii, R.Yu., Blinov, V.V., and Ivanov, V.G., Concerning Deep-Water Renewal of Baikal, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 2011, vol. 438, no. 1, pp. 121–124 [in Russian].
Wüest, A., Ravens, A.T., Granin, N.G., Kocsis, O., Schurter, M., and Sturm M., Cold Intrusions in Lake Baikal: Direct Observational Evidence for Deep-Water Renewal, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2005, vol. 50, issue 1, pp. 184–196.
Schmid, M., Budnev, N.M., Granin, N.G., Sturm, M., Schurter, M., and Wüest, A., Lake Baikal Deepwater Renewal Mystery Solved, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, vol. 35, issue 9, pp. 1–5.
Domysheva, V.M., Shimaraev, M.N. and Gorbunova, L.A., Specific Features of Baikal’s Deep-Water Aeration at the Period of Spring Circulation, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 1996, no. 1, pp. 64–72 [in Russian].
Domysheva, V.M., Spatial Distribution Patterns and Oxygen Dynamics in the Deep-Water Region of Baikal, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Geogr.) Dissertation, Irkutsk, 2001 [in Russian].
Hohmann R., Kipfer R., Peeters F., Piepke G., Shimaraev M. N., Imboden D. M. Processes of Deep-Water Renewal in Lake Baikal //Limnol. Ocenogr. 1997.–Vol. 42 (5). p. 841–855.
Shimaraev, M.N., Troitskaya, E.S., Blinov, V.V., Ivanov, V.G., and Gnatovskii, R.Yu., On the Upwellings in Lake Baikal, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 2012, vol. 442, no. 5, pp. 696–700 [in Russian].
Gitel’zon, I.I., Granin, N.G., Levin, L.A., and Zavoruev, V.V., The Mechanisms of Formation and Sustenance of the Inhomogeneities in the Spatial Distribution of the Phytoplankton in Lake Baikal, Doklady Akad. Nauk, 1991, vol. 318, no. 2, pp. 505–508 [in Russian].
Mizandrontsev, I.B., Gorbunova, L.A., Domysheva, V.M., Mizandronteva, K.N., and Shimaraev, M.N., Gas Exchange of Baikal With the Atmosphere at the Period of Spring Warming-up, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 1996, no. 2, pp. 74–84 [in Russian].
Mizandrontsev, I.B., Bottom Sediments, in Elements of the Baikal Ecosystem, Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1993, pp. 46–96 [in Russian].
Killworth, P.D., Carmack, E.C., Weiss, R.F., and Matear, R., Modeling Deep-Water Renewal in Lake Baikal, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1996, vol. 41, issue 7, pp. 1521–1538.
Hohmann, R., Hofer, M., Kipfer, R., Peeters, F., Imboden, D.M., Baur, H., and Shimaraev, M.N., Distribution of Helium and Tritium in Lake Baikal, J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 1998, vol. 103, issue C6, pp. 12823–12838.
Votintsev, K.K., Meshcheryakova, A.I. and Popovskaya, G.I., Primary Production, in The Problems of Baikal, G.I. Galazii and K.K. Votintsev, Eds., Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1978, pp. 169–179 [in Russian].
Shimarayev, M.N., Troitskaya, E.S. and Gnatovsky, R.Yu., Deep Water Temperature Variation of Lake Baikal During 1972–2007, Geogr. Nat. Resour., 2009, vol. 30, issue 3, pp. 258–264.
Kumagai, W.F., Vincent, K., Ishikawa, A. and Aota, Y., Lessons From Lake Biwa and Other Asian Lakes: Global and Local Perspectives, in Freshwater Management. Global Versus Local Perspectives, M. Kumagai and W.F. Vincent, Eds., Springer, 2003, pp. 1–22.
Anneville, O., Molinero, J.C., Souissi, S., Balvay, G., and Gerdeaux, D., Long-Term Changes in the Copepod of Lake Geneva, J. Plankton Res., 2007, vol. 29, suppl. 1, pp. i49–i59.
O’Reilly, C.M., Alin, S.R., Plisner, P-D., Kohen, A.S., and McKee, B.A., Climate Change Decreases Aquatic Ecosystem Productivity of Lake Tanganyika, Africa, Nature, 2003, no. 424, pp. 766–768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.N. Shimaraev, V.M. Domysheva, R.Yu. Gnatovskii, V.V. Blinov, M.V. Sakirko, 2016, published in Geografiya i Prirodnye Resursy, 2016, Vol. 37, No. 3, pp. 70–77.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimaraev, M.N., Domysheva, V.M., Gnatovskii, R.Y. et al. The influence of deep convection on aeration of the bottom zone in Baikal. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 37, 212–219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1875372816030045
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1875372816030045