Abstract
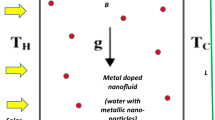
Solar thermal collectors disperse and collect the solar radiation with its further conversion into thermal energy through solar thermal concentrating systems, which frequently use nanofluids as a heat transporter. The present research makes emphasis on the analysis of the magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) of flow of hybrid nanofluid (HNF) and conventional nanofluid (CNF) between two rotating plates. The flow is induced by an exponentially stretching sheet in a parabolic trough solar collector (PTSC). Owing to a similarity transformation, partial differential equations with boundary constraints were converted to a simpler case of nonlinear ordinary-differential formulas. The Keller-box process is introduced for finding an approximate solution of the ordinary reduced differential equations. Hybrid nanofluid, which consists of two kinds of nanoparticles, copper (Cu) and aluminium (Al) with Newtonian water (H2O) base fluid, is considered. The key idea of this article is to scrutinize the impact of variation of significant parameters on the velocity, temperature, and heat transport rate for Al–H2O nanofluid and Cu–Al/H2O hybrid nanofluid. The results evidence that the hybrid nanofluid (Cu–Al/H2O) has a lower friction factor and higher heat transmission rate as compared with the conventional nanofluid (Al–H2O). Furthermore, the rotation parameter decelerates the heat transport rate. To visualize the fluid flow, streamlines are drawn for different values of the suction/injection parameter.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mahian, O., Kianifar, A. Kalogirou, S.A., Pop, I., and Wongwises, S., A Review of the Applications of Nanofluids in Solar Energy, J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2013, vol. 57, pp. 582–594.
Devi, S.S.U. and Devi, S.P.A., Numerical Investigation of Three-Dimensional Hybrid Cu–Al2O3/Water Nanofluid Flow over a Stretching Sheet with Effecting Lorentz Force Subject to Newtonian Heating, Can. J. Phys., 2016, vol. 94, pp. 490–496.
Chaji, H., Ajabshirchi, Y., Esmaeilzadeh, E., Heris, S.Z., Hedayatizadeh, M., and Kahani, M., Experimental Study on Thermal Efficiency of Flat Plate Solar Collector Using TiO2/Water Nanofluid, Modern Appl Sci, 2013, vol. 7, pp. 60–69.
Ghasemi, S.E. and Ahangar, G., Numerical Analysis of Performance of Solar Parabolic Trough Collector with Cu–Water Nanofluid, Int. J. Nano Dimen., 2014, vol. 5, pp. 233–240.
Sharma, K. and Kundan, K., Nanofluid Based Concentrating Parabolic Solar Collector (NBCPSC): A New Alternative, Int. J. Res. Mech. Eng. Technol., 2014, vol. 4, pp. 2249–5762.
Buongiorno, J., Convective Transport in Nanofluids, J. Heat Transfer, 2005, vol. 128, pp. 240–250.
Afzal, K. and Aziz, A., Transport and Heat Transfer of Time Dependent MHD Slip Flow of Nanofluids in Solar Collectors with Variable Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Radiation, Res. Phys., 2016, vol. 6, pp. 746–753.
Ellahi, R., Hassan, M., and Zeeshan, A., A Study of Heat Transfer in Power Law Nanofluid, Thermal Sci., 2016, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 2015–2026.
Bhatti, M.M., Zeeshan, A., and Ellahi, R., Simultaneous Effects of Coagulation and Variable Magnetic Field on Peristaltically Induced Motion of Jeffrey Nanofluid Containing Gyrotactic Microorganism, Microvascular Res., 2017, vol. 110, pp. 32–42.
Jouybari, H.J., Saedodin, S., Zamzamian, A., Nimvari, M.E., and Wongwises, S., Effects of Porous Material and Nanoparticles on the Thermal Performance of a Flat Plate Solar Collector: An Experimental Study, Renewable Energy, 2017, vol. 114, pp. 1407–1418.
Parvin, S., Ahmed, S., and Chowdhury, R., Effect of Solar Irradiation on Forced Convective Heat Transfer through a Nanofluid Based Direct Absorption Solar Collector, AIP Conf. Proc., 2017, vol. 1851, article 020067.
Subramani, J., Nagarajan, P.K., Mahian, O., and Sathyamurthy, R., Efficiency and Heat Transfer Improvements in a Parabolic Trough Solar Collector Using TiO2 Nanofluids under Turbulent Flow Regime, Renewable Energy, 2018, vol. 119, pp. 19–31.
Smit, S. and Kessels W., Variational Method for the Minimization of Entropy Generation in Solar Cells, J. Appl. Phys., 2015, vol. 117, no. 13, article 134504.
Sciacovelli, A., Verda, V., and Sciubba, E., Entropy Generation Analysis as a Design Tool—A Review, Renewable Sust. Energy Rev., 2015, vol. 43, pp. 1167–1181.
Tyagi, S.K., Wang, S., Singhal, M.K., Kaushik, S.C., and Park, S.R., Exergy Analysis and Parametric Study of Concentrating Type Solar Collectors, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 2007, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 1304–1310.
Bejan, A., Kearney, D.W., and Kreith, F., Second Law Analysis and Synthesis of Solar Collector Systems, J. Solar Energy, 1981, vol. 103, pp. 23–28.
Liu, G., Cengel, Y.A., and Turner, R.H., Exergy Analysis of a Solar Heating System, J. Solar Energy, 1995, vol. 117, pp. 249–251.
Ghanbarpour, M. and Khodabandeh, R., Entropy Generation Analysis of Cylindrical Heat Pipe Using Nanofluid, Thermochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 610, pp. 37–46.
Khan, M.I., Hafeez, M.U., Hayat, T., Khan, M.I., and Alsaedi, A., Magneto Rotating Flow of Hybrid Nanofluid with Entropy Generation, Comp. Meth. Progr. Biomed., 2020, vol. 183, p. 105093.
Wang, W., Cai, Y., Wang, L., Liu, C.W., Zhao, F.Y., Sheremet, M., and Liu, D., A Two-Phase Closed Thermosyphon Operated with Nanofluids for Solar Energy Collectors: Thermodynamic Modeling and Entropy Generation Analysis, Solar Energy, 2020, vol. 211, pp. 192–209.
Suzuki, A., A Fundamental Equation for Exergy Balance on Solar Collectors, J. Solar Energy, 1988, vol. 110, pp. 102–106.
Farahat, S., Sarhaddi, F., and Ajam, H., Exergetic Optimization of Flat Plate Solar Collectors, Renewable Energy, 2009, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 1169–1174.
Yejjer, O., Kolsi, L., Aich, W., Rashed, A., Borjini, M., and Aissia, H.B., Study of Three Dimensional Natural Convection and Entropy Generation in an Inclined Solar Collector Equipped with Partitions, Wiley, 2017, pp. 1–15.
Verma, S.K., Tiwari, A.K., and Chauhan, D.S., Experimental Evaluation of Flat Plate Solar Collector Using Nanofluids, Energy Convers. Manag., 2017, vol. 134, pp. 103–115.
Moghadam, M.C., Edalatpour, M., and Solano, J.P., Numerical Study on Conjugated Laminar Mixed Convection of Alumina/Water Nanofluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Entropy Generation within a Tube-on-Sheet Flat Plate Solar Collector, J. Solar Energy, 2017, vol. 139, article 041011.
Nasrin, R., Parvin, S., and Alim, M.A., Heat Transfer and Collector Efficiency through a Direct Absorption Solar Collector with Radiative Heat Flux Effect, Num. Heat Transfer, Part A: Appl., 2015, vol. 68, no. 8, pp. 887–907.
Gupta, M.K. and Kaushik, S.C., Exergetic Performance Evaluation and Parametric Studies of Solar Air Heater, Energy, 2008, vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 1691–1702.
Khan, A., Saeed, A., Gul, T., Mukhtar, S., Ali, I., and Jawad, M., Radiative Swirl Motion of Hydromagnetic Casson Nanofluid Flow over Rotary Cylinder Using Joule Dissipation Impact, Phys. Scr., 2021, vol. 96, no. 4, article 045206.
Ghadikolaei, S., Yassari, M., Sadeghi, H., Hosseinzadeh, K., and Ganji, D., Investigation on Thermophysical Properties of TiO2–Cu/H2O Hybrid Nanofluid Transport Dependent on Shape Factor in MHD Stagnation Point Flow, Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 322, pp. 428–438.
Maskeen, M., Zeeshan, A., Mehmood, O., and Hassan, M., Heat Transfer Enhancement in Hydromagnetic Alumina–Copper/Water Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Stretching Cylinder, J. Thermal An. Calorimetry, 2019, vol. 138, no. 2, pp. 1127–1136.
Hussain, S.T., Haq, R.U., Khan, Z.H., and Nadeem, S., Water Driven Flow of Carbon Nanotubes in a Rotating Channel, J. Molec. Liquids, 2016, vol. 214, pp. 136–144.
Srinivasulu, T. and Goud, S., Effect of Inclined Magnetic Field on Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer of Williamson Nanofluid over a Stretching Sheet, Case Stud. Thermal Engin., 2021, vol. 23, article 100819.
Cebeci, T. and Bradshaw, P., Physical and Computational Aspects of Convective Heat Transfer, New York: Springer, 1988.
Keller, H.B., Numerical Methods for Two-Point Boundary Value Problems. New York: Dover Publ., 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahzad, F., Jamshed, W., Sajid, T. et al. Heat Transfer Simulation for 3D MHD Rotating Hybrid NanoFluid Flow Between Parallel Plates in Parabolic Trough Solar Collector: A Numerical Study. J. Engin. Thermophys. 30, 704–726 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232821040147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232821040147