Abstract
Novel hydrazone and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione derivatives were obtained via the reaction of N1,N3,2-triaryl-6-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamides with acid hydrazides and thiosemicarbazide, respectively. Structure of the products was proved using IR and 1H NMR spectroscopy methods. Some of the synthesized compounds were tested for antimicrobial activity
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
The synthesis and determination of the practical value of hydrazones are relevant, since a hydrazone fragment is present in the molecules of a number of biologically active compounds [1], which have antimicrobial [2–5], anti-inflammatory [6], analgesic [7], antiprotozoal [8], antituberculous [9], anticonvulsant [10], and cardioprotective activity [11]. The combination of different functional groups in hydrazones results in a large number of compounds with unique physical and chemical properties. Some of them can be used in the treatment of diseases of the central nervous system [12], as well as in molecular targeted therapy of drug treatment of cancer [13, 14]. Structural analogs of hydrazones have shown good results in their study as growth promoters in plants of Nicotiana tabacum L. and Arabidopsis thaliana species [15].
The 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione fragment occurs in the structure of many natural and biologically active compounds [16, 17], for example, in bicyclic anxiolytic drugs, estazolam, alprazolam (Scheme 1), in the triptan 5-HT1 agonist (rizatriptan) and in antimicrobial agents based on spiropiperidinyl-1,2,4-triazolidine-3-thione [18–22]. For the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds with antimicrobial activity with a 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione moiety, the reaction of ketones with thiosemicarbazide is used [23–27].
In this regard, the synthesis of compounds with hydrazone and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione fragments is promising for the preparation of biologically active compounds and for the creation of new drugs based on them.
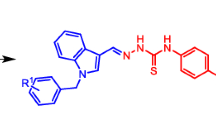
Scheme 1 shows examples of biologically active hydrazones and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione derivatives, which have antimicrobial (1) [4], antiprotozoal (2) [8], antimicrobial (3) [21], and anti-inflammatory activity (4) [6]. Hydrazone 5 inhibits the phosphodiesterase 10A enzyme responsible for neurological and psychological disorders (schizophrenia) [14].
Previously, we have obtained new oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide derivatives by the condensation of acetoacetic acid amides with aromatic aldehydes in the presence of a basic piperidine catalyst in ethanol at room temperature [28–31]. The reactions of the obtained compounds with N-nucleophiles [29] and Baeyer–Villiger oxidation [33] have been studied.
In continuation of studying the reactivity of cyclohexanone derivatives [28–34] and in order to obtain new compounds with potential biological activity, herein we reported the reactions of N1,N3,2-triaryl-6-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamides with acid hydrazides and thiosemicarbazide. New derivatives of hydrazones and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione were obtained, respectively. The reaction of equimolar amounts of 4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamides 6a–6l with hydrazides of salicylic, isonicotinic, and p-toluenesulfonic acids upon boiling in ethanol proceeds at the carbonyl group of the alicycle to form the corresponding hydrazones 7a–7d, 8a, 8b, 9a–9f (Scheme 2).
The hydrazone form of compounds 7–9 is confirmed by the presence in the NMR spectra of the spin-spin coupling between the protons at the C3 (3.65–4.42 ppm) C2 atoms of the ring (3.12–4.04 ppm). The proton signal of the NH group not linked to the benzene ring also proves the proposed structure. The chemical shifts of the proton singlets of the two NH groups of the arylamide substituents are shifted to a stronger field compared to the chemical shifts of the starting compounds 6a–6o [28–30].
Existence of compounds 7–9 in the hydrazone form can be explained by its stabilization due to intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Heterocyclization apparently does not proceed due to the low nucleophilicity of nitrogen atoms in acid hydrazides.
The reaction of cyclohexanone derivatives 6d, 6m–6o with thiosemicarbazide in an equimolar ratio under similar conditions gave N6,N8,7-triaryl-9-hydroxy-9-methyl-3-thioxo-1,2,4-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-6,8-dicarboxamides 10a–10d.
In the IR spectra of compounds 10а–10d there are no stretching vibrations of the conjugated CO group of the alicycle and С=С bonds. The presence of stretching vibration bands of the N(C=S)N fragment at 1336– 1360 cm–1 and the С=S moiety at 1592–1600 cm–1 , as well as the presence of proton signals of the NH groups at the C1 and C2 atoms (8.05‒8.54 ppm), C4 (10.33– 10.46 ppm) and C6 atoms (3.54‒4.46 ppm) resonating with a proton at the C7 atom (3.67–4.00 ppm) in the 1H NMR spectra confirm the proposed structure of spiro compounds 10a–10d and excludes possible alternative enamine and imine structures. When comparing the spectral characteristics of spiro compounds 10a–10d with the starting cyclohexanones 6d, 6m–6o, it was found that the chemical shift of the proton doublet at the C8 atom of the ring in the spectra of compounds 10a–10d is shifted to upfield region (2.78–3.12 ppm, J 11.4–12.0 Hz) [29, 30].
Compounds 7b, 8b, 9c, 10a, and 10c were studied for antimicrobial activity against strains of gram-negative (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922) and gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P), as well as Candida fungi (Candida albicans NCTC 885-653). Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) have been established and range from 500 to 1000 µg/mL (Table 1).
In summary, new derivatives of hydrazones and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione were obtained by the reaction of substituted 6-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamides with acid hydrazides and thiosemicarbazide.
EXPERIMENTAL
IR spectra were recorded on a Specord M-80 instrument from KBr pellets. 1Н NMR spectra were registered on a Bruker DRX 500 (500 MHz) and Bruker AVANCE III HD 400 (400 MHz) spectrometers in DMSO-d6, tetramethylsilane was used as the internal standard. Mass spectra were taken on an ultra-HPLC-MS spectrometer (Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column 1.7 µm, mobile phases were acetonitrile and water, flow rate was 0.6 mL/min, ESI detector MS Xevo TQD). Elemental analysis was performed on an elemental analyzer Euro EA3028-NT for simultaneous determination of C, H, N. Melting points were determined on a Melting Point M-565.
N1,N3,2-Triaryl-6-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamides 6a–6o were prepared according to known methods [28–30].
General procedure for the synthesis of compounds 7–10. A mixture of 0.005 mol of N,N′,2-triaryl-6-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-oxocyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide and 0.005 mol of salicylic (7a–7d), isonicotinic (8a, 8b), and p-toluenesulfonic hydrazides acid (9a–9f) or thiosemicarbazide (10a–10d) in 25 mL of ethanol was refluxed for 2.5 h, then cooled. The precipitated crystals were filtered off and crystallized from ethanol.
2-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-hydroxy-4-[2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene]-6-methyl-N1,N3-diphenylcyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (7a). Yield 56%, mp 200‒201°С. 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.33 s (3Н, Me), 2.35 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.01 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.31 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.75 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.88 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.94 s (1Н, ОН), 6.77‒7.87 m (18Н, 2С6Н5, 2С6Н4), 9.55 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.66 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 11.21 br. s (2H, 2-HOC6H4CONH). Found, %: C 63.34; H 4.87; N 8.81. C33H31BrN4O4. Calculated, %: C 63.16; H 4.98; N 8.93.
6-Hydroxy-4-[2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene]-6-methyl-N1,N3-di(2-methylphenyl)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (7b). Yield 32%, mp 245‒247˚С. 1Н NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.40 s (3Н, СН3), 1.80 s (6Н, (2-MeС6Н4)2), 2.05 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.48 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.10 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.70 t (1Н, С2Н J 12.0 Hz), 3.90 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.10 s (1Н, ОН), 6.88–7.30 m (16Н, 4С6Н4), 7.86 s (1Н, С1СОNН), 9.18 s (1Н, С3СОNН), 11.15 s (1Н, С4=NNНСО), 11.70 s (1Н, 2-НОC6H4). Found, %: С 67.62; Н 5.50; N 8.75. С36Н35ClN4О5. Calculated, %: С 67.65; Н 5.52; N 8.77.
6-Hydroxy-4-[2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene]-6-methyl-N1,N3-di(2-methylphenyl)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (7c). Yield 51%, mp 234‒235°С. 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.41 s (3Н, Me), 1.81 s (3Н, 2-MeС6Н4), 1.82 s (3Н, 2-MeС6Н4), 2.36 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.99 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.18 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.90 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.95 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.11 s (1Н, ОН), 6.76‒8.43 m (16Н, 3С6Н4, Py), 9.06 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.23 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 11.12 s (1H, 2-HOC6H4CONH), 11.60 br. s (1H, 2-OHC6H4CONH). Found, %: C 70.86; H 6.00; N 12.24. C34H35N5O4. Calculated, %: C 70.69; H 6.11; N 12.12.
6-Hydroxy-4-[2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene]-6-methyl-2-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-N1,N3-di(2-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (7d). Yield 53%, mp 203‒204°С. 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.37 s (3Н, Me), 2.47 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.93 s [6Н, 4-(Me)2NC6H4], 3.04 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.69 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.85 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.09 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.49 s (1Н, ОН), 6.46‒7.87 m (16Н, 4С6Н4), 9.39 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.41 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 11.21 br. s (2H, 2-OHC6H4CONH). Found, %: C 63.87; H 5.41; N 10.43. C35H35Сl2N5O4. Calculated, %: C 63.64; H 5.34; N 10.60.
6-Hydroxy-4-(2-isonicotinoylhydrazinylidene)-6-methyl-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl-N1,N3-diphenylcyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (8a). Yield 30%, mp 231‒232°С. 1Н NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.30 s (3Н, Me), 2.48 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.93 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.10 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.58 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н3), 3.60 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н3), 3.90 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.42 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.88 br. s (1Н, ОН), 6.70–7.50 m (17Н, 2С6Н5, С6Н3, Py), 9.48 s (1Н, С1СОNН), 9.67 s (1Н, С3СОNН), 10.80 s (1Н, NH). Found, %: С 67.60; Н 5.66; N 11.23. С35Н35N5О6. Calculated, %: С 67.62; Н 5.67; N 11.27.
6-Hydroxy-4-(2-isonicotinoylhydrazinylidene)-6-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)-N1,N3-di(2-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (8b). Yield 30%, mp 231‒232°С. 1Н NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.31 s (3Н, Me), 2.13 s (3Н, 4-MeС6Н4), 2.35 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.84 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.12 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.69 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.75 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 4.00 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.31 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.51 br. s (1Н, ОН), 6.70–7.11 m (16Н, 3С6Н4, Py), 8.73 s (1Н, С1СОNН), 9.12 s (1Н, С3СОNН), 10.78 s (1Н, NH). Found, %: С 68.00; Н 5.85; N 11.00. С36Н37N5О6. Calculated, %: С 68.02; Н 5.87; N 11.02.
6-Hydroxy-6-methyl-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)-N1,N3,2-triphenylcyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9a). Yield 60%, mp 235‒236°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3400 (OH), 3342 (CONHAr), 3200 (NH), 1668 (CONHAr), 1552 (NH, C=N), 1344, 1168 (SO2), 904 (S‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.30 s (3Н, Me), 2.18 s (3H, 4-MeC6H4SO2), 2.49 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.81 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.18 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.86 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.97 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.03 s (1Н, ОН), 6.90–7.44 m (19Н, 3С6Н5, С6Н4), 9.38 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.56 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 10.12 c (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 66.62; H 5.68; N 9.08. C34H34N4O5S. Calculated, %: C 66.87; H 5.61; N 9.17.
6-Hydroxy-6-methyl-2-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)-N1,N3-diphenylcyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9b). Yield 54%, mp 213‒214°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3440 (OH), 3344 (CONHAr), 3200 (NH), 1672 (CONHAr), 1552 (NH, C=N), 1344, 1168 (SO2), 968 (S–N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.27 s (3Н, Me), 2.18 s (3H, 4-CH3C6H4SO2), 2.48 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.72 s (6Н, 4-Me2NC6H4), 2.90 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.11 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.65 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.78 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.80 s (1Н, ОН), 6.37–7.39 m (18Н, 2С6Н5, 2С6Н4), 9.31 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.42 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 9.50 c (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 66.38; H 5.94; N 10.60. C36H39N5O5S. Calculated, %: C 66.14; H 6.01; N 10.71.
6-Hydroxy-6-methyl-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)-N1,N3-diphenyl-2-(4-diethylaminophenyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9c). Yield 64%, mp 207‒208°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3400 (OH), 3344 (CONHAr), 3232 (NH), 1668 (CONHAr), 1552 (NH, C=N), 1380, 1168 (SO2), 912 (S‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 0.92 t [6Н, 4-(CH3CH2)2NC6H4, J 7.0 Hz], 1.16 s (3Н, Me), 1.92 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.18 s (3H, 4-MeC6H4SO2), 2.74 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.12 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.13 q [4Н, 4-(CH3CH2)2NC6H4, J 7.0 Hz], 3.41 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.74 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.80 s (1Н, ОН), 6.39‒7.44 m (18Н, 2С6Н5, 2С6Н4), 9.25 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.41 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 10.02 c (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 67.11; H 6.27; N 10.41. C38H43N5O5S. Calculated, %: C 66.94; H 6.36; N 10.27.
6-Hydroxy-6-methyl-N1,N3-di(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)-2-phenylcyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9d). Yield 54%, mp 227‒228°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3450 (OH), 3352 (CONHAr), 3240 (NH), 1672 (CONHAr), 1540 (NH, C=N), 1336, 1168 (SO2), 904 (S‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.28 s (3Н, Me), 2.19 s (3H, 4-MeC6H4SO2), 2.47 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.85 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.10 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.67 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.77 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.86 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.04 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.32 s (1Н, ОН), 6.59-8.25 m (17Н, 3С6Н4, С6Н5), 8.46 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.12 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 9.99 s (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 64.69; H 5.62; N 8.24. C36H38N4O7S. Calculated, %: C 64.46; H 5.71; N 8.35.
6-Hydroxy-2-(4-isopropylphenyl)-6-methyl-N1,N3-di(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9e). Yield 58%, mp 234‒235°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3460 (OH), 3360 (CONHAr), 3254 (NH), 1660 (CONHAr), 1555 (NH, C=N), 1330, 1168 (SO2), 910 (S‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.08 d (6Н, 4-Me2CHC6H4, J 7.0), 1.26 s (3Н, Me), 2.18 s (3H, 4-MeC6H4SO2), 2.47 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.63 m (1Н, 4-Me2CHC6H4, J 7.0 Hz), 2.73 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.10 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.51 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.66 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.75 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 4.21 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.24 s (1Н, ОН), 6.58‒8.16 m (16Н, 4С6Н4), 8.48 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.04 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 10.01 s (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 70.49; H 6.58; N 5.26. C32H36N2O6. Calculated, %: C 70.57; H 6.66; N 5.14.
6-Hydroxy-6-methyl-2-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-N1,N3-di(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-(2-tosylhydrazinylidene)cyclohexane-1,3-dicarboxamide (9f). Yield 48%, mp 241‒242°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3400 (OH), 3380 (CONHAr), 3304 (NH), 1664 (CONHAr), 1552 (NH, C=N), 1312, 1168 (SO2), 912 (S‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.25 s (3Н, Me), 2.17 s (3H, 4-MeC6H4SO2), 2.47 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 2.73 s (6Н, 4-Me2NC6H4), 2.84 d (1Н, С5НАНВ, J 14.0 Hz), 3.27 d (1Н, С1Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.78 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.94 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.95 d (1Н, С3Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.00 t (1Н, С2Н, J 12.0 Hz), 5.32 s (1Н, ОН), 6.35‒8.28 m (16Н, 4С6Н4), 8.40 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.07 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 9.97 c (1H, C4NNHSO2). Found, %: C 63.73; H 6.14; N 9.92. C38H43N5O7S. Calculated, %: C 63.94; H 6.07; N 9.81.
9-Hydroxy-9-methyl-3-thioxo-N6,N8-diphenyl-7-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-6,8-dicarboxamide (10a). Yield 79%, mp 180‒181°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3460 (OH), 3360, 3240, 3200, 3080 (NH), 1664 (CONHAr), 1600 (C=S), 1376 (N‒CS‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.19 t (3H, 4-MeCH2OC6H4, J 7.0 Hz), 1.28 s (3Н, СН3), 2.14 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.6 Hz), 2.89 d (1Н, С8Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.28 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.6 Hz), 3.55 d (1Н, С6Н, J 12.0 Hz), 3.89 q (2H, 4-MeCH2OC6H4, J 7.0 Hz), 3.91 t (1Н, С7Н, J 12.0 Hz), 4.87 s (1Н, ОН), 6.59‒7.34 m (14Н, 2С6Н5, С6Н4), 8.05 c (1H, N1H), 8.52 s (1H, N2H), 9.42 s (1Н, С8СОNH), 9.62 s (1Н, С6СОNH), 10.46 br. s (1H, N4H). Mass spectrum, m/z: 559 [M + H]+. Found, %: C 64.56; H 5.88; N 12.39. C30H33N5O4S. Calculated, %: C 64.38; H 5.94; N 12.51. M 558.
9-Hydroxy-9-methyl-N6,N8-di(2-methoxyphenyl)-7-(thien-2-yl)-3-thioxo-1,2,4-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-6,8-dicarboxamide (10b). Yield 74%, mp 163‒164°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3460 (OH), 3390, 3280, 3180, 3010 (NH), 1676 (CONHAr), 1604 (C=S), 1360 (N‒CS‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.33 s (3Н, Me), 2.14 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.8 Hz), 2.78 d (1Н, С8Н, J 11.4 Hz), 3.23 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.8 Hz), 3.54 d (1Н, С6Н, J 11.4 Hz), 3.90 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.93 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 4.00 t (1Н, С7Н, J 11.4 Hz), 5.40 s (1Н, ОН), 6.71‒7.76 m (13Н, 2С6Н5, thienyl), 8.20 s (1H, N1H), 8.54 s (1H, N2H), 9.67 s (1Н, С1СОNH), 9.71 s (1Н, С3СОNH), 10.33 br. s (1H, N4H). Mass spectrum, m/z: 581 [M + H]+. Found, %: C 57.99; H 5.45; N 11.90. C28H31N5O5S2. Calculated, %: C 57.81; H 5.37; N 12.04. M 580.
9-Hydroxy-9-methyl-N6,N8-di(2-methoxyphenyl)-7-(pyridin-3-yl)-3-thioxo-1,2,4-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-6,8-dicarboxamide (10c). Yield 81%, mp 188‒189°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3380 (OH), 3288, 3240, 3120, 3000 (NH), 1648 (CONHAr), 1592 (C=S), 1336 (N‒CS‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.42 s (3Н, Me), 2.19 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.8 Hz), 3.12 d (1Н, С8Н, J 11.6), 3.46 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.8 Hz), 3.89 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.91 s (3Н, 2-MeОС6Н4), 3.98 t (1Н, С7Н, J 11.6), 4.46 d (1Н, С6Н, J 11.6), 5.12 s (1Н, ОН), 6.87–7.76 m (12Н, 2С6Н4, Py), 8.41 s (1H, N1H), 8.52 s (1H, N2H), 9.23 s (1Н, С8СОNH), 9.26 s (1Н, С6СОNH), 10.36 br. s (1H, N4H). Mass spectrum, m/z: 576 [M + H]+. Found, %: C 60.21; H 5.66; N 14.72. C29H32N6O5S. Calculated, %: C 60.40; H 5.59; N 14.57; M 575.
9-Hydroxy-7-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-9-methyl-3-thioxo-N6,N8-di(2-chlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazaspiro[4.5]decane-6,8-dicarboxamide (10d). Yield 71%, mp 190‒191°С. IR spectrum (KBr), ν, cm–1: 3410 (OH), 3280, 3250, 3131, 3000 (NH), 1668 (CONHAr), 1552 (C=S), 1330 (N‒CS‒N). 1Н NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ, ppm: 1.35 s (3Н, Me), 2.16 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.6 Hz), 2.81 s (6Н, 4-Me2NC6H4), 2.96 d (1Н, С8Н, J 11.6), 3.39 d (1Н, С10НАНВ, J 14.6 Hz), 3.67 t (1Н, С7Н, J 11.6), 4.26 d (1Н, С6Н, J 11.6), 5.45 s (1Н, ОН), 6.46‒7.43 m (12Н, 3С6Н4), 8.13 s (1H, N1H), 8.15 s (1H, N2H), 9.28 s (1Н, С8СОNH), 9.33 s (1Н, С6СОNH), 10.34 br. s (1H, N4H). Found, %: C 57.62; H 5.07; N 13.27. C30H32Cl2N6O3S. Calculated, %: C 57.41; H 5.14; N 13.39.
Antimicrobial activity of compounds 7b, 8b, 9c, 10a, and 10c against Escherichia coli ATCC 6538-P, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25922, and Candida albicans NCTC 885-653 strains was determined by successive dilutions of a solution of the test substances in meat-peptone broth at a bacterial load of 250 000 microbial units per 1 mL of the solution. The minimum inhibitory concentration of the compound, i. e., the maximum dilution leading to complete suppression of the test microbes growth, was taken as the effective dose. As reference drugs, furacilin and dioxidine were used for Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P, fluconazole for Candida albicans NCTC 885-653.
REFERENCES
Verma, G., Marella, A., Shaquiquzzaman, M., Akhtar, M.R., Ali, M.M., and Alam, M., Pharm. J. Bioall. Sci., 2014, vol. 6, no. 2, p. 69. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.129170
Rollas, S., Gulerman, N., and Erdeniz, H., Il Farmaco, 2002, vol. 57, no. 2, p. 171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-827X(01)01192-2
Gein, V.L., Zorina, A.A., Nosova, N.V., Voronina, E.V., Vahrin, M.I., and Kriven’ko, A.P., Pharm. Chem. J., 2007, vol. 41, no. 6, p. 319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-007-0072-8
Secci, D., Bizzarri, B., Bolasco, A., Carradori, S., D’Ascenzio, M., Rivanera, D., Mari, E., Polletta, L., and Zicari, A., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, vol. 53, p. 246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.04.006
Ibrahim, M.N. and Al-Difar, H.A., Der Chemica Sinica, 2011, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 171.
Moldovan, C.M., Oniga, O., Pârvu, A., Tiperciuc, B., Verite, P., Pîrna¢u, A., Crişan, O., Bojiţă, M., and Pop, R., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2011, vol. 46, no. 2, p. 526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.11.032
Dandawate, P., Khan, E., Padhye, S., Gaba, H., Sinha, S., Deshpande, J., Wamy, K.V., Khetmalas, M., Ahmad, A., and Sarkar, F.H., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2012, vol. 22, no. 9, p. 3104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.03.060
Caputto, M.E., Ciccarelli, A., Frank, F., Moglioni, A.G., Moltrasio, G.Y., Vega, D., Lombardo, L., and Finkielsztein, L.M., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, vol. 55, p. 155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.07.013
El-Husseiny, W.M., Magda, A.A., Abdel-Aziz, N.I., El-Azab, A.S., Asiri, Y.A., and Alaa, A.M., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, vol. 158, p. 134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.007
Jain, J., Kumar, Y., Sinha, R., Kumar, R., and Stables, J., Med. Chem., 2011, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 56. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340611794072689
Leal, C.M., Pereira, S.L., Kümmerle, A.E., Leal, D.M., Tesch, R., de Sant’Anna, C.M., Fraga, C.D.M., Barreiro, E.J., Sudo, R.T., and Zapata-Sudo, G., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, vol. 55, p. 49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.06.056
Cutshall, N.S., Onrust, R., Rohde, A., Gragerov, S., Hamilton, L., Harbol, K., Shen, H.-R., McKee, S., Zuta, C., Graderova, G., Florio, V., Wheeler, T.N., and Gage, J.L., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2012, vol. 22, no. 17, p. 5595.
Wahbeh, J. and Milkowski, S., SLAS TECHNOL.: Transl. Life Sci. Innovat., 2019, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 161. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472630318822713
Kucukguzel, I., Rollas, S., and Cevikbas, A., Drug Metab. Drug Interact., 1995, vol. 12, no. 2, p. 151. https://doi.org/10.1515/DMDI.1995.12.2.151
Chuprov-Netochin, R., Neskorodov, Y., Marusich, E., Mishutkina, Y., Volynchuk, P., Leonov, S., Skryabin, K., Ivashenko, A., Palme, K., and Touraev, A., BMC Plant Biology, 2016, vol. 16, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0875-4
Islam, M.R., Huda, Q.N., and Duddeck, H., Indian J. Chem., 1990, vol. 298, p. 376.
Ferrari, M.D., Roon, K.I., Lipton, R.B., and Goadsby, P.J., Lancet, 2001, vol. 358, no. 9294, p. 1668. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06711-3
Chemistry of the Alkaloids, ed. S.W. Pelletier. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1970, p. 503.
The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, O’Neil, M.J., Ed., New Jersey: Merck & Co, Inc. Whitehouse Station, 2006, 2564 p.
Gopalakrishnan, M., Thanusu, J., Kanagarajan, V., and Govindaraju, R., J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 2009, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 406. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360802188099
Thanusu, J., Kanagarajan, V., and Gopalakrishnan, M., Chem. Heterocycl. Compd., 2011, vol. 47, no. 5, p. 575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-011-0801-5
Hussein, A.Q., Herzberger, S., and Jochims, J.C., Chem. Ber., 1979, Bd 112, no. 4, S. 1102. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.19791120406
Ramesh, R. and Lalitha, A., RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, no. 63, p. 51188. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra07726e
Arai, I., Abe, S., and Hagitani, A., Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan, 1973, vol. 46, no. 2, p. 677. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.46.677
Shchelochkova, O.A., Grigoryeva, E.A., and Kriven’ko, A.P., Izv. Vuzov. Ser. Khim. i Khim. Technol., 2006, vol. 49, no. 11, p. 139.
Kanagarajan, V., Thanusu, J., and Gopalakrishnan, M., Med. Chem. Res., 2011, vol. 21, no. 12, p. 3965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9949-x
Patil, P.B., Patil, J.D., Korade, S.N., Kshirsagar, S.D., Govindwar, S.P., and Pore, D.M., Res. Chem. Intermed., vol. 42, no. 5, p. 4171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2267-z
Gein, V.L., Levandovskaya, E.V., Nosova, N.V., Antonova, N.V., Voronina, E.V., Vahrin, M.I., and Kriven’ko, A.P., Pharm. Chem. J., 2007, vol. 41, no. 12, p. 643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-008-0043-8
Gein, V.L., Odegova, T.F., Yankin, A.N., and Nosova, N.V., Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2015, vol. 85, no. 1, p. 46. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363215010089
Gein, V.L., Odegova, T.F., Yankin, A.N., and Nosova, N.V., Pharm. Chem. J., 2015, vol. 49, no. 4, p. 245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-015-1264-2
Gein, V.L., Nosova, N.V., Yankin, A.N., Bazhina, A.Y., and Dmitriev, M.V., Tetrahedron Lett., 2019, vol. 60, no. 24, p. 1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.05.023
Gein, V.L., Yankin, A.N., Nosova, N.V., and Dmitriev, M.V., Russ. J. Org. Chem., 2016, vol. 52, no. 3, p. 379. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070428016030143
Gein, V.L., Yankin, A.N., Nosova, N.V., Dmitriev, M.V., and Nasakin, O.E., Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2016, vol. 86, no. 1, p. 58. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363216010114
Gein, V.L., Yankin, A.N., Nosova, N.V., Dmitriev, M.V., and Slepukhin, P.A., Tetrahedron Lett., 2016, vol. 57, no. 22, p. 2441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.04.082
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Rights and permissions
Open Access. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yankin, A.N., Nosova, N.V., Novikova, V.V. et al. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Novel Hydrazone and 1,2,4-Triazole-3-thione Derivatives. Russ J Gen Chem 92, 166–173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363222020050
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363222020050