Abstract—
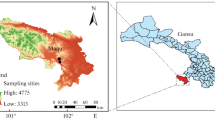
Seven artificial alfalfa grasslands (aged 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11, 12 a) and an abandoned land plot were selected to examine the changes in soil organic carbon content, active organic carbon content, soil organic carbon storage and active organic carbon storage in the 0–200 cm soil layer and their correlation with soil nutrients, soil water content, soil bulk density, alfalfa cover, density, height and aboveground biomass. The results show that the soil organic carbon content was between 2.02 and 4.54 g kg–1 within depths of 0–200 cm, which was higher than that in the abandoned land. The soil organic carbon storage in the 0–40 cm layers accounted for, on average, 29.50 ± 7.13% of the total storage in the 0–200 cm soil layers in the 7-year-old alfalfa grasslands and the abandoned land, and the 0–40 cm layer was the main layer of soil organic carbon storage. The soil organic carbon storage in 12 a grassland was the highest, and the abandoned land had the smallest reserve, with values of 10.22 and 5.06 kg m–2, respectively. In addition, carbon storage was, on average, 1.84 kg m–2 higher in 7-year alfalfa artificial grassland than in abandoned farmland. The proportion of soil AOC storage to SOC storage ranged from 30.24 to 58.11%; the proportion in 5-year grassland was the lowest, while it was the highest in the abandoned land. SOC storage had significant positive correlations with TN and soil active organic carbon storage, and it had negative correlations with soil bulk density at the 0.01 level (p < 0.01).






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Jiang, J.P., Xiong, Y.C., Jia, Y., Li, F.M., and Xu, J.Z., Soil quality dynamics under successional alfalfa field in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of Northwestern China, Arid Land Res. Manag., 2007, vol. 21, pp. 287–303.
Deng, L., Wang, K.B., Li, J.P., Shangguan, Z.P., and Sweeney, S., Carbon storage dynamics in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) fields in the hilly-gully region of the Loess Plateau, China, Clean–Soil, Air,Water, 2014, vol. 9, pp. 1253–1262
Chang, R.Y., Fu, B.J., Liu, G.H., and Liu, S.G., Soil carbon sequestration potential for “Grain for Green” project in Loess Plateau, China, Environ. Manag., 2011, vol. 48, pp. 1158–1172.
Deng, L., Shangguan, Z.P., and Li, R., Effects of the Grain-for-Green Program on soil erosion in China, Int. J. Sediment Res., 2012, vol. 27, pp. 120–127.
Makarov, M.I., Kadulin, M.S., Turchin, S.R., Malysheva, T.I., Aksenova, A.A., Onipchenko, V.G., and Menyailo, O.V., The effect of Vaccinium vitis-idaea on properties of mountain meadow soil under alpine lichen heath, Russ. J. Ecol., 2019, vol. 50, pp. 337–342.
Onipchenko, V.G., Makarov, M.I., and van der Maarel, E., Influence of alpine plants on soil nutrient concentrations in a monoculture experiment, Folia Geobot., 2001, vol. 36, pp. 225‒241.
Zhang, T.J., Wang, Y.W., Wang, X.G., Wang, Q.Z., and Han, J.G., Organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in reed meadow soils converted to alfalfa fields, Soil Tillage Res., 2009, vol. 105, pp. 143–148.
Stumpf, F., Keller, A., Schmidt, K., Mayr, A., Gubler, A., and Schaepman, M., Spatio-temporal land use dynamics and soil organic carbon in Swiss agroecosystems, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2018, vol. 258, pp. 129–142.
Conant, R.T., Paustian, K., and Elliott, E.T., Grassland management and conversion into grassland: Effects on soil carbon, Ecol. Appl., 2001, vol. 11, pp. 343–355.
Lal, R., Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change, Geoderma, 2004, vol. 123, pp. 1–22.
Li, S.B., Ji, B., Wang, Y.L., and Dong, L.G., Comprehensive assessment on different restoration measures to soil environmental effect in Ningnan hilly area, Res.Soil Water Conserv., 2007, vol. 1, pp. 51–53.
Nelson, D.W. and Sommers, L.E., Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter, in Methods of Soil Analysis, part 2: Chemical and Microbial Properties, Page, A.L., Ed., Madison, WI: ASA SSSA, 1982, pp. 539–579.
Chan, K.Y., Bowman, A., and Oates, A., Oxidizible organic carbon fractions and soil quality changes in an oxic Paleustalf under different pasture leys, Soil Sci., 2001, vol. 166, pp. 61–67.
Shen, H., Cao, Z., and Xu, Z., Effects of fertilization on different carbon fractions and carbon pool management index in soils, Acta Pedol. Sinica, 2000, vol. 37, pp. 166–173.
Bremner, J.M., Nitrogen-total, in Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3, Sparks, D.L., Ed., Madison, WI: American Society of Agronomy 1996, pp. 1085–1121.
Parkinson, J.A. and Allen, S.E., Nutrients in biological material, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 1975, vol. 6, pp. 1–11.
Guo, L.B. and Gifford, R.M., Soil carbon stocks and land use change: A meta-analysis, Global Change Biol., 2002, vol. 8, pp. 345–360.
Ding, Y.K., Study on soil organic carbon pool under different vegetation types in Mu Us desert, Dissertation for Master’s Degree, Inner Mongolia Univ., 2011.
Wang, S.Q. and Zhou, C.H., Estimating soil carbon reservoir of terrestrial ecosystem in China, Geogr. Res., 1999, vol. 8, pp. 349–355.
Liu, M.Y., An, S.S., and Chang, Q.R., Features of soil organic carbon under different land use in mountain area of Southern Ningxia, Res.Soil Water Conserv., 2005, vol. 3, pp. 47–49.
Kong, L. and Chu, L.M., Subtropical urban turfs: Carbon and nitrogen pools and the role of enzyme activity, J. Environ. Sci., 2018, vol. 65, pp. 18–28.
Zhou, H., Variation characteristics of organic carbon and its fractions in soil of alfalfa grassland with different growing years, Dissertation for Master’s Degree, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016.
Dad, J.M., Organic carbon stocks in mountain grassland soils of northwestern Kashmir Himalaya: Spatial distribution and effects of altitude, plant diversity and land use, Carbon Manag., 2019, vol. 10, pp. 149–162.
Maslov, M.N., Kopein, E.I., Zudkin, A.G., Korolev, N.E., Shulakov, A.A., Onipchenko, V.G., and Makarov, M.I., Stocks of phytomass and organic carbon in tundra ecosystems of northern Fennoscandia, Moscow Univ. Soil Sci. Bull., 2016, vol. 71, pp. 113–119.
Piovanelli, C., Gamba, C., Brandi, G., Simoncini, S., and Batistoni, E., Tillage choices affect biochemical properties in the soil profile, Soil Tillage Res., 2006, vol. 90, pp. 84–92.
Zhang, T.J., Wang, Y.W., Wang, X.G., Wang, Q.Z., and Han, J.G., Organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in reed meadow soils converted to alfalfa fields, Soil Tillage Res., 2009, vol. 105, pp. 143–148.
Li, F.M., Wang, T.C., and Cao, J., Effect of organic matter on total amount and availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in loess soil of Northwest China, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 1998, vol. 29, pp. 947–953.
Li, Y.S. and Huang, M.B., Pasture yield and soil water depletion of continuous growing alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2008, vol. 124, pp. 24–32.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the head and members of the Institute of Desert Management, Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science Academy, for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by the Whole Industry Chain Innovation Demonstration Project (YES-16-10, YES-16-1002), the Construction and Promotion Project of Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science Academy (NKYP-19-06) and the Natural Science Foundation in Ningxia (NZ16106, NZ16095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bo Ji, Wang, Z., Pan, Z. et al. Soil Carbon Storage Characteristics of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Artificial Grasslands in the Semi-Arid Hilly Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Russ J Ecol 51, 466–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413620050045
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413620050045