Abstract
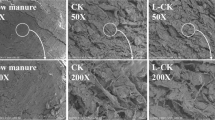
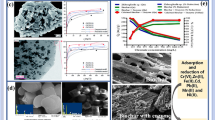
Adsorption via various organic and inorganic amendments is a principal mechanism to remediate cadmium contamination and decrease its entry into food chain. In present study, alkaline sandy clay loam soil, the cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2-NPs), rice husk biochar (RHB), rock gypsum (RGy) and farm manure (FYM) and alkaline sandy clay loam soil amended (1%) with these amendments were tested for effective Cd adsorption-desorption properties. The soil Langmuir estimated maximum Cd adsorption (Qmax) was found to be 0.60 mg g–1 (linear isotherm) and 0.65 mg g–1 (non-linear isotherm) while among different amendments, CeO2-NPs had the maximum (88.23, 89.33 mg g–1) Qmax and addition of this to soil resulted in 166% and 128% increase, while RHB, RGy and FYM also resulted in substantial increment in Cd Qmax of soil. Second model was Freundlich isotherm (linear and nonlinear) which shows significant adsorption capacity (Kf) and adsorption intensity (N) on the amended soils. The Temkin isotherm gave us information about equilibrium binding (A) and latent heat of sorption (B) suggesting the adsorption reaction were overall exothermic in nature. The Cd adsorption trend as estimated by pseudo second order kinetic model (PSO) suggest that soil has a net adsorbed Cd (Qa) of 0.76 mg g–1 while a net desorption (Qd) of 0.23 was observed making a net 30% desorption. The inclusion of CeO2-NPs in soil (1%) resulted Qa of 1.97 mg g–1 and Qd of 0.42 mg g–1 which is a net 21% desorption. Other amendments RHB, RGy and FYM also resulted in net lower Cd desorption with 22, 27 and 26% Qd respectively. The CeO2-NPs is best amendment for effective Cd removal from water.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
F. A. Abu Al-Rub, M. Kandah, and N. Al-Dabaybeh, “Competitive adsorption of nickel and cadmium on sheep manure wastes: experimental and prediction studies,” Sep. Sci. Technol. 38, 483–497 (2003).
H. R. Ahmad, M. Zia-ur-Rehman, M. I. Sohail, M. A. Haq, H. Khalid, M. A. Ayub, and G. Ishaq, “Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on plants,” in Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae, and Microorganisms (Academic Press, 2018), pp. 239–275.
K. Aftab, S. Iqbal, M. R. Khan, R. Busquets, R. Noreen, N. Ahmad, S. G. T. Kazimi, A. M. Karami, N. M. S. Al Suliman, and M. Ouladsmane, “Wastewater-irrigated vegetables are a significant source of heavy metal contaminants: toxicity and health risks,” Molecules 28 (3), 1371 (2023).
A. Al-Kinani, M. Eftekhari, M. Gheibi, and M. Chamsaz, “Polyaniline-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent for preconcentration of ultra-trace levels of cadmium (II) followed by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry,” Spectrosc. Lett. 51, 287–296 (2018).
V. R. Angelova, V. I. Akova, N. S. Artinova, and K. I. Ivanov, “The effect of organic amendments on soil chemical characteristics,” Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 19, 958–971 (2013).
M. A. Ayub, M. I. Sohail, M. Umair, M. Z. Rehman, M. Usman, M. Sabir, M. Rizwan, S. Ali, and Z. Ahmad, “Cerium oxide nanoparticles: advances in synthesis, prospects and application in agro-ecosystem,” in Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry (Elsevier, 2019), Vol. 87, pp. 209–250.
M. R. Awual, M. Khraisheh, N. H. Alharthi, M. Luqman, A. Islam, M. Rezaul Karim, M. M. Rahman, and M. A. Khaleque, “Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium (II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials,” Chem. Eng. J. 343, 118–127 (2018).
M. Azhar, M. Z. Rehman, S. Ali, M. F. Qayyum, A. Naeem, M. A. Ayub, M. A. Haq, A. Iqbal, and M. Rizwan, “Comparative effectiveness of different biochars and conventional organic materials on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium accumulation in cereals,” Chemosphere 227, 72–81 (2019).
M. Bakshi and P. C. Abhilash, “Nanotechnology for soil remediation: revitalizing the tarnished resource,” in Nano-Materials as Photocatalysts for Degradation of Environmental Pollutants (Elsevier, 2020), pp. 345–370.
K. S. Balkhair and M. A. Ashraf, “Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia,” Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 23, S32–S44 (2016).
S. Bashir, M. S. Rizwan, A. Salam, Q. Fu, J. Zhu, M. Shaaban, and H. Hu, “Cadmium immobilization potential of rice straw-derived biochar, zeolite and rock phosphate: extraction techniques and adsorption mechanism,” Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 100, 727–732 (2018).
S. Bashir, M. Adeel, A. B. Gulshan, J. Iqbal, S. Khan, M. Rehman, and M. Azeem, “Effects of organic and inorganic passivators on the immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soils: a review,” Environ. Eng. Sci. 36 (9), 986–998 (2019).
A. Bogusz, P. Oleszczuk, and R. Dobrowolski, “Adsorption and desorption of heavy metals by the sewage sludge and biochar-amended soil,” Environ. Geochem. Health 41, 1663–1674 (2019).
A. Bhatnagar, M. Sillanpää, and A. Witek-Krowiak, “Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification–a review,” Chem. Eng. J. 270, 244–271 (2015).
A. R. Contreras, A. Garcia, E. Gonzalez, E. Casals, V. Puntes, A. Sánchez, X. Font, and S. Recillas, “Potential use of CeO2, TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the removal of cadmium from water,” Desalin. Water Treat. 41, 296–300 (2012).
A. R. Contreras, E. Casals, V. Puntes, D. Komilis, A. Sánchez, X. Font, “Use of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles for the adsorption of dissolved cadmium (II), lead (II) and chromium (VI) at two different pHs in single and multi-component systems,” Global Nest J. 17, 536–543 (2015).
A. R. Contreras Rodríguez, J. E. McCarthy, A. Alonso, J. Moral-Vico, X. Font, Y. K. Guńko, and A. Sánchez, “Cerium oxide nanoparticles anchored onto graphene oxide for the removal of heavy metal ions dissolved in water,” Desalin. Water Treat. 124, 134–145 (2018).
L. Cui, J. Yan, L. Li, G. Quan, C. Ding, T. Chen, C. Yin, J. Gao, and Q. Hussain, “Does biochar alter the speciation of Cd and Pb in aqueous solution?,” Bioresources 10, 88–104 (2015).
D. Chen, T. Awut, B. Liu, Y. Ma, T. Wang, and I. Nurulla, “Functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions,” e-Polymers 16, 313–322 (2016).
M. H. Dehghani, S. Tajik, A. Panahi, M. Khezri, A. Zarei, Z. Heidarinejad, and M. Yousefi, “Adsorptive removal of noxious cadmium from aqueous solutions using poly urea-formaldehyde: a novel polymer adsorbent,” MethodsX 5, 1148–1155 (2018).
F. I. El-Dib, D. E. Mohamed, O. A. El-Shamy, and M. R. Mishrif, “Study the adsorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of different synthesized surfactants for heavy metal ions removal,” Egypt. J. Pet. 29, 1–7 (2020).
M. Esfandbod, M. Esfandbod, A. Forghani, E. Adhami, and M. R. Rashti, “Cadmium adsorption behavior of some soils from northern Iran,” in Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soil Science: Soil Solutions for a Changing World (Brisbane, 2010), pp. 1–6.
A. Es-said, H. Nafai, G. Lamzougui, A. Bouhaouss, and R. Bchitou, “Comparative adsorption studies of cadmium ions on phosphogypsum and natural clay,” Sci Afr. 13, e00960 (2021).
H. Feng and J. Cheng, “Whole-process risk management of soil amendments for remediation of heavy metals in agricultural soil—a review,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20 (3), 1869 (2023).
M. P. F. Fontes and P. C. Gomes, “Simultaneous competitive adsorption of heavy metals by the mineral matrix of tropical soils,” Appl. Geochem. 18, 795–804 (2003).
S. Gran, R. Aziz, M. T. Rafiq, M. Abbasi, A. Qayyum, A. Y. Elnaggar, H. H. Elganzory, Z. M. El-Bahy, and E. E. Hussein, “Development of cerium oxide/corncob nanocomposite: a cost-effective and eco-friendly adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals,” Polymers 13, 4464 (2021).
F. U. Haider, C. Liqun, J. A. Coulter, S. A. Cheema, J. Wu, R. Zhang, M. Wenjun, and M. Farooq, “Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 211, 111887 (2021).
M. C. Hoyos-Sánchez, A. C. Córdoba-Pacheco, L. F. Rodríguez-Herrera, and R. Uribe-Kaffure, “Removal of Cd (II) from aqueous media by adsorption onto chemically and thermally treated rice husk,” J. Chem., (2017).
B. Huang, D. Li, Z. Yuan, M. Zheng, C. Liang, Y. Liao, and C. Liu, “Adsorption characteristics of cadmium onto aggregates of various acidic red soils from South China,” J. Soils Sediments, 1–14 (2021).
Z. L. He, H. P. Xu, Y. M. Zhu, X. E. Yang, and G. C. Chen, “Adsorption-desorption characteristics of cadmium in variable charge soils,” J. Environ. Sci. Health 40, 805–822 (2005).
A. P. Jackson and B. J. Alloway, “The transfer of cadmium from agricultural soils to the human food chain,” in Biogeochemistry of Trace Metals (2017), pp. 121–170.
C. K. Jain and M. K. Sharma, “Adsorption of cadmium on bed sediments of river Hindon: adsorption models and kinetics,” Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 137, 1–19 (2002).
M. K. John, “Cadmium adsorption maxima of soils as measured by the Langmuir isotherm,” Can. J. Soil Sci. 52, 343–350 (1972).
Y. Jia, S. Shi, J. Liu, S. Su, Q. Liang, X. Zeng, and T. Li, “Study of the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of biochar,” Appl Sci. 8, 1019 (2018).
H. Jiang, T. Li, X. Han, X. Yang, and Z. He, “Effects of pH and low molecular weight organic acids on competitive adsorption and desorption of cadmium and lead in paddy soils,” Environ. Monit. Assess. 184, 6325–6335 (2012).
M. I. Kandah, F. A. A. Al-Rub, and N. Al-Dabaybeh, “The aqueous adsorption of copper and cadmium ions onto sheep manure,” Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 21, 501–509 (2003).
A. F. Khafaga, A. El-Hack, E. Mohamed, A. E. Taha, S. S. Elnesr, and M. Alagawany, “The potential modulatory role of herbal additives against Cd toxicity in human, animal, and poultry: a review,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 4588–4604 (2019).
A. Kubier, R. T. Wilkin, and T. Pichler, “Cadmium in soils and groundwater: a review,” Appl. Geochem. 108, 104388 (2019).
S. Kızıltas Demir and N. Tugrul, “Zinc and cadmium adsorption from wastewater using hydroxyapatite synthesized from flue gas desulfurization waste,” Water Sci. Technol. 84, 1280–1292 (2021).
P. Kucharski, B. Białecka, A. Śliwińska, and A. Pieprzyca, “Evaluation of specific capacity of poultry litter in heavy metal sorption,” Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 232, 1–11 (2021).
P. Loganathan, S. Vigneswaran, J. Kandasamy, and R. Naidu, “Cadmium sorption and desorption in soils: a review,” Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 489–533 (2012).
S. G. Lu and Q. F. Xu, “Competitive adsorption of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by different soils of Eastern China,” Environ. Geol. 57, 685–693 (2009).
W. Lu, Y. Liu, H. Ye, D. Lin, G. Li, Y. Zhao, T. Deng, H. Li, and R. Wang, “Adsorption and desorption characteristics of cadmium on different contaminated paddy soil types: kinetics, isotherms, and the effects of soil properties,” Sustainability 13, 7052 (2021).
Y. Li, S. Dong, J. Qiao, S. Liang, X. Wu, M. Wang, H. Zhao, and W. Liu, “Impact of nanominerals on the migration and distribution of cadmium on soil aggregates,” J. Cleaner Prod. 262, 121355 (2020).
S. Ma, F. Jing, S. P. Sohi, and J. Chen, “New insights into contrasting mechanisms for PAE adsorption on millimeter, micron-and nano-scale biochar,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 18636–18650 (2019).
S. Ma, Y. Hu, Q. Zeng, Z. Xu, Y. Cui, Y. Ma, J. Su, and Z. Nan, “Temporal changes of calcareous soil properties and their effects on cadmium uptake by wheat under wastewater irrigation for over 50 years,” Chemosphere 263, 127971 (2021).
J. P. Marques, V. G. S. Rodrigues, I. M. Raimondi, and J. Z. Lima, “Increase in Pb and Cd adsorption by the application of peat in a tropical soil,” Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 231, 1–21 (2020).
J. Meng, L. Zhong, L. Wang, X. Liu, C. Tang, H. Chen, and J. Xu, “Contrasting effects of alkaline amendments on the bioavailability and uptake of Cd in rice plants in a Cd-contaminated acid paddy soil,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 8827–8835 (2018).
S. R. Mishra and M. Ahmaruzzaman, “Cerium oxide and its nanocomposites: structure, synthesis, and wastewater treatment applications,” Mater. Today Commun. 28, 102562 (2021).
H. O. Oluwasola, J. N. Asegbeloyin, A. E. Ochonogor, J. U. Ani, U. I. Collins, and E. O. Ebube, “Cadmium and lead adsorption capacities of Nigerian ultisol soil of tropics,” Orient. J. Chem. 35 (3), 1004 (2019).
J. H. Park, J. J. Wang, S. H. Kim, S. W. Kang, C. Y. Jeong, J. R. Jeon, K. H. Park, J. S. Cho, R. D. Delaune, and D. C. Seo, “Cadmium adsorption characteristics of biochars derived using various pine tree residues and pyrolysis temperatures,” J. Colloid Interface Sci. 553, 298–307 (2019).
D. B. Pal, R. Selvasembian, and P. Singh, “Cadmium removal by composite copper oxide/ceria adsorbent from synthetic wastewater,” Biomass Convers. Biorefin., 1–10 (2021).
O. S. Pokrovsky, A. Probst, E. Leviel, and B. H. Liao, “Interactions between cadmium and lead with acidic soils: Experimental evidence of similar adsorption patterns for a wide range of metal concentrations and the implications of metal migration,” J. Hazard. Mater. 199, 358–366 (2012).
V. Prakash, J. Peralta-Videa, D. K. Tripathi, X. Ma, and S. Sharma, “Recent insights into the impact, fate and transport of cerium oxide nanoparticles in the plant-soil continuum,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 221, 112403 (2021).
S. Prapagdee, S. Piyatiratitivorakul, and A. Petsom, “Physico-chemical activation on rice husk biochar for enhancing of cadmium removal from aqueous solution,” Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 13, 27–34 (2016).
V. Ramachandran and T. J. D’souza, “Adsorption of cadmium by Indian soils,” Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 111 (1), 225–234 (1999).
G. Rahimi, L. Gholami, and B. Piran, “Effect of irrigation with industrial wastewater and gypsum amendments on heavy metal in soil and black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seed,” Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 53, 227–242 (2022).
M. Raii, D. P. Minh, F. J. E. Sanz, and A. Nzihou, “Lead and cadmium removal from aqueous solution using an industrial gypsum by-product,” Procedia Eng. 83, 415–422 (2014).
M. Rezaei Rashti, M. Esfandbod, E. Adhami, and P. Srivastava, “Cadmium desorption behaviour in selected sub-tropical soils: effects of soil properties,” J. Geochem. Explor. 144, 230–236 (2014).
M. Z. Rehman, M. Rizwan, S. Ali, A. Naeem, B. Yousaf, G. Liu, H. Khalid, H. F. Saifullah, and M. Azhar, “A field study investigating the potential use of phosphorus combined with organic amendments on cadmium accumulation by wheat and subsequent rice,” Arab. J. Geosci. 11, 594 (2018).
A. A. H. Saeed, N. Y. Harun, M. M. Nasef, A. Al-Fakih, A. A. S. Ghaleb, and H. K. Afolabi, “Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by optimized rice husk biochar using response surface methodology,” Ain Shams Eng. J. 13, 101516 (2022).
T. Sarwar, M. Shahid, S. Khalid, A.H. Shah, N. Ahmad, M. A. Naeem, B. Murtaza, and H. F. Bakhat, “Quantification and risk assessment of heavy metal build-up in soil-plant system after irrigation with untreated city wastewater in Vehari, Pakistan,” Environ. Geochem. Health 42, 4281–4297 (2020).
M. I. M. Said, S. Sabri, and S. Azman, “Effect of particle size on cadmium removal by banana peels,” J. Teknol. 72 (4) (2015).
S. Satarug, D. A. Vesey, and G. C. Gobe, “Current health risk assessment practice for dietary cadmium: data from different countries,” Food Chem. Toxicol. 106, 430–445 (2017).
Z. Satti, M. Akhtar, N. Mazhar, S. U. Khan, N. Ahmed, Q. M. Yasir, M. Irshad, R. Pervaiz, and W. Ahmad, “Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution onto untreated gypsum rock material: equilibrium and kinetics,” Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 11, 10755–10764 (2020).
S. Serrano, F. Garrido, C. G. Campbell, and M. T. García-González, “Competitive sorption of cadmium and lead in acid soils of Central Spain,” Geoderma 124 (1–2), 91–104 (2005).
A. Sharma, M. Kaur, J. K. Katnoria, and A. K. Nagpal, “Heavy metal pollution: a global pollutant of rising concern,” in Toxicity and Waste Management using Bioremediation (2016), pp. 1–26.
H. Sharifan, X. Wang, B. Guo, and X. Ma, “Investigation on the modification of physicochemical properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles through adsorption of Cd and As (III)/As (V),” ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 6, 13454–13461 (2018).
T. Sheela, Y. A. Nayaka, R. Viswanatha, S. Basavanna, and T. G. Venkatesha, “Kinetics and thermodynamics studies on the adsorption of Zn (II), Cd (II) and Hg (II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles,” Powder Technol. 217, 163–170 (2012).
C. Shen, Y. Zhao, W. Li, Y. Yang, R. Liu, and D. Morgen, “Global profile of heavy metals and semimetals adsorption using drinking water treatment residual,” Chem. Eng. J. 372, 1019–1027 (2019).
V. Siracusa and I. Blanco, “Bio-Polyethylene (Bio-PE), Bio-Polypropylene (Bio-PP) and Bio-Poly (ethylene terephthalate) (Bio-PET): recent developments in bio-based polymers analogous to petroleum-derived ones for packaging and engineering applications,” Polymers 12, 1641 (2020).
M. I. Sohail, A. A. Waris, M. A. Ayub, M. Usman, M. Rehman, M. Sabir, and T. Faiz, “Environmental application of nanomaterials: a promise to sustainable future,” in Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry (2019), Vol. 87, pp. 1–54.
M. I. Sohail, M. Z. Rehman, M. Rizwan, B. Yousaf, S. Ali, M. A. Haq, A. Anayat, and A. A. Waris, “Efficiency of various silicon-rich amendments on growth and cadmium accumulation in field-grown cereals and health risk assessment,” Chemosphere 244, 125481 (2020).
C. Su, “A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: situation, impact and remediation techniques,” Environ. Skeptics Critics 3, 24 (2014).
S. Tong, H. Deng, L. Wang, T. Huang, S. Liu, and J. Wang, “Multi-functional nanohybrid of ultrathin molybdenum disulfide nanosheets decorated with cerium oxide nanoparticles for preferential uptake of lead (II) ions,” Chem. Eng. J. 335, 22–31 (2018).
US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry-ATSDR (1999).
A. Ullah, A. Tahir, H. U. Rashid, T. Rehman, S. Danish, B. Hussain, and H. Akca, “Strategies for reducing Cd concentration in paddy soil for rice safety,” J. Cleaner Prod. 316, 128116 (2021).
Y. Wang, X. Tang, Y. Chen, L. Zhan, Z. Li, and Q. Tang, “Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cd (II) on loess soil from China,” J. Hazard. Mater. 172, 30–37 (2009).
M. Wang, Z. Chen, W. Song, D. Hong, L. Huang, and Y. Li, “A review on cadmium exposure in the population and intervention strategies against cadmium toxicity,” Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 106, 65–74 (2021).
B. Wang, J. Lan, C. Bo, B. Gong, and J. Ou, “Adsorption of heavy metal onto biomass-derived activated carbon,” RSC Adv. 13, 4275–4302 (2023).
M. Wołowiec, M. Komorowska-Kaufman, A. Pruss, G. Rzepa, and T. Bajda, “Removal of heavy metals and metalloids from water using drinking water treatment residuals as adsorbents: a review,” Minerals 9 (8), 487 (2019).
C. Wu, Y. Li, M. Chen, X. Luo, Y. Chen, N. Belzile, and S. Huang, “Adsorption of cadmium on degraded soils amended with maize-stalk-derived biochar,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15 (11), 2331 (2018).
J. Xiang, Q. Lin, S. Cheng, J. Guo, X. Yao, Q. Liu, G. Yin, and D. Liu, “Enhanced adsorption of Cd (II) from aqueous solution by a magnesium oxide-rice husk biochar composite,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25 (14), 14032–14042 (2018).
D. Xu, Y. Zhao, K. Sun, B. Gao, Z. Wang, J. Jin, Z. Zhang, S. Wang, Y. Yan, X. Liu, and F. Wu, “Cadmium adsorption on plant- and manure-derived biochar and biochar-amended sandy soils: impact of bulk and surface properties,” Chemosphere 111, 320–326 (2014).
Y. Yan, X. Dong, X. Sun, X. Sun, J. Li, J. Shen, W. Han, X. Liu, and L. Wang, “Conversion of waste FGD gypsum into hydroxyapatite for removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from wastewater,” J. Colloid Interface Sci. 429, 68–76 (2014). 89. Y. Yan, Q. Li, X. Sun, Z. Ren, F. He, Y. Wang, and L. Wang, “Recycling flue gas desulphurization (FGD) gypsum for removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from wastewater,” J. Colloid Interface Sci. 457, 86–95 (2015).
S. Yuan, Z. Xi, Y. Jiang, J. Wan, C. Wu, Z. Zheng, and X. Lu, “Desorption of copper and cadmium from soils enhanced by organic acids,” Chemosphere 68 (7), 1289–1297 (2007).
N. Zainab, S. Mehmood, A. Shafiq-ur-Rehman, A. Munir, Z. I. Tanveer, Z. U. Nisa, M. Imran, M. T. Javed, and H. J. Chaudhary, “Health risk assessment and bioaccumulation of potentially toxic metals from water, soil, and forages near coal mines of district Chakwal, Punjab, Pakistan,” Environ. Geochem. Health, 1–26 (2023).
G. Zeng, H. Wu, J. Liang, S. Guo, L. Huang, P. Xu, Y. Liu, Y. Yuan, X. He, and Y. He, “Efficiency of biochar and compost (or composting) combined amendments for reducing Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb bioavailability, mobility and ecological risk in wetland soil,” RSC Adv. 5, 34541–34548 (2015).
B. Ziyadanoğullari, Ö. Yavuz, F. Aydin, I. Aydin, and H. Bingöl, “Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by a soil containing magnesite,” Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 50, 371–376 (2004).
X. Zhao, H. Zhao, X. Huang, L. Wang, F. Liu, X. Hu, J. Li, G. Zhang, and P. Ji, “Effect and mechanisms of synthesis conditions on the cadmium adsorption capacity of modified fly ash,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 223, 112550 (2021).
L. Zhu, L. Tong, N. Zhao, X. Wang, X. Yang, and Y. Lv., “Key factors and microscopic mechanisms controlling adsorption of cadmium by surface oxidized and aminated biochars,” J. Hazard. Mater. 382, 121002 (2020).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study is part of PhD and we would like to acknowledge The Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for providing necessary funds under HEC Indigenous PhD fellowship program for 5000 scholars, HEC (Phase II, Batch III). We would like to acknowledge help and support of Dr. Tariq Aziz (Institute of Soil and Environmental Sciences, UAF; Principal UAF sub-campus Depalpur) for elemental analysis.
Funding
This study is part of PhD, and we would like to acknowledge The Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (under HEC Indigenous PhD fellowship program for 5000 scholars, HEC (Phase II, Batch III)) for providing necessary funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
In preparing this paper, the author(s) used AI TOOL Open AI-Chat GPT-3 in order to change formatting of references from springer general format to aip format. After using this tool/service, Mr. Ayub has reviewed and edited the content as necessary and take full responsibility for the content of the publication as we have verified all references.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayub, M.A., Ahmad, H.R., Zia-ur-Rehman, M. et al. Comparative Investigation of Cd Adsorption on Alkaline Sandy Clay Loam Soil Treated with Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles, Organic and Inorganic Amendments. Eurasian Soil Sc. 56 (Suppl 2), S300–S316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323601555
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323601555