Abstract
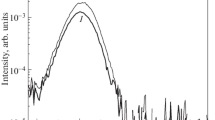
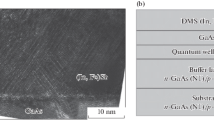
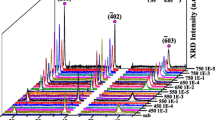
The diode structures with narrow-gap ferromagnetic A3FeB5 semiconductors in the function of only p-region (p-GaFeSb/n-InGaAs), only n-region (n-InFeSb/p-InGaAs), p- and n-regions (p‑GaFeSb/ n-InFeSb, p-GaFeSb/n-InFeAs) of the p–n junction were manufactured by the method of pulsed laser deposition in vacuum. Composition of the ferromagnetic semiconductor layers and their thicknesses determined by the results of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy in total correspond to the technological information for diode structures. More specifically, thickness of the GaFeSb layer is 25–30 nm, thicknesses of the InFeAs and InFeSb layers is 35–40 nm. The iron content in InFeSb ranges from 25 to 35 at %. The GaFeSb layer contains from 15 to 41 at % of iron, while 35 at % of iron is registered in InFeAs layer. Presence of Fe‒As(Sb), In–Fe, and Fe–Ga chemical bonds was found at chemical analysis of the structures. Because of this, it may be assumed that, in the manufactured structures, the Fe atoms can displace the elements of III and V groups simultaneously. All the structures demonstrates the effect of negative magnetoresistance at sufficiently low potentials of observation of the effect (to 50 mV), in small magnetic fields (to 3600 Oe) and at high temperature of measurements. For the GaFeSb/InFeSb, GaFeSb/InFeAs diodes, the negative magnetoresistance was observed for the first time up to room temperature. The hysteresis form of the dependences of resistance on magnetic field suggests an effect of ferromagnetic properties of the narrow-gap semiconductor layers on the carrier transport in the structures.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. T. Tu, P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, Phys. Rev. B 92, 144403 (2015).
D. Sasaki, L. D. Anh, P. N. Hai, and M. Tanaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 142406 (2014).
L. D. Anh, D. Kaneko, P. N. Hai, and M. Tanaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 232405 (2015).
N. T. Tu, P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 192401 (2016).
A. V. Kudrin, Yu. A. Danilov, V. P. Lesnikov, M. V. Dorokhin, O. V. Vikhrova, D. A. Pavlov, Yu. V. Usov, I. N. Antonov, R. N. Kriukov, A. V. Alaferdov, and N. A. Sobolev, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 183901 (2017).
A. V. Kudrin, Yu. A. Danilov, V. P. Lesnikov, and E. A. Pitirimova, Tech. Phys. Lett. 42, 88 (2016).
L. D. Anh, P. N. Hai, and M. Tanaka, Nat. Commun. 7, 13810 (2016).
L. D. Anh, P. N. Hai, and M. Tanaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 102402 (2018).
N. T. Tu, P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 122409 (2018).
K. Takiguchi, L. D. Anh, T. Chiba, T. Koyama, D. Chiba, and M. Tanaka, Nat. Phys. 15, 1134 (2019).
A. V. Kudrin, V. P. Lesnikov, D. A. Pavlov, Yu. V. Usov, Yu. A. Danilov, M. V. Dorokhin, O. V. Vikhrova, V. E. Milin, R. N. Kriukov, Yu. M. Kuznetsov, V. N. Trushin, and N. A. Sobolev, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 487, 165321 (2019).
Yu. A. Danilov, A. V. Kudrin, V. P. Lesnikov, O. V. Vikhrova, R. N. Kryukov, I. N. Antonov, D. S. Tolkachev, A. V. Alaferdov, Z. E. Kun’kova, M. P. Temiryazeva, and A. G. Temiryazev, Phys. Solid State 60, 2178 (2018).
D. Briggs and M. P. Seah, Practical Surface Analysis by Auger and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, 3rd ed. (Wiley, New York, 1985).
A. V. Boryakov, S. I. Surodin, R. N. Kryukov, D. E. Nikolichev, and S. Yu. Zubkov, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 229, 132 (2018).
http://www.nd.edu/gsnider.
F. Hatami, N. N. Ledentsov, M. Grundmann, J. Bohrer, F. Heinrichsdorff, M. Beer, D. Bimberg, S. S. Ruvimov, P. Werner, U. Gosele, J. Heydenreich, U. Richter, S. V. Ivanov, B. Ya. Meltser, P. S. Kop’ev, and Zh. I. Alferov, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 656 (1995).
F. Matsukura, H. Ohno, and T. Dietl, in Handbook of Magnetic Materials, Ed. by K. H. J. Buschow (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2002), Vol. 14, p. 1.
H. Ohno, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 110 (1999).
Funding
The work was supported by Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-19-00545 manufacturing and investigation of the structures with one layer of magnetic semiconductor, and project no. 18-79-10088 manufacturing and investigation of the structures with two layers of magnetic semiconductors).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Translated by G. Levina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesnikov, V.P., Ved’, M.V., Vikhrova, O.V. et al. Diode Heterostructures with Narrow-Gap Ferromagnetic A3FeB5 Semiconductors of Various Conduction Type. Phys. Solid State 63, 1028–1035 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783421070131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783421070131