Abstract
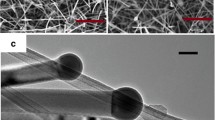
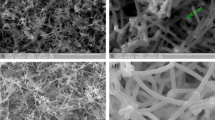
The results of studying the growth of filamentous Ge structures in aqueous electrolytes at various temperatures using In and Sn nanoparticle arrays as nucleation sites are given. The temperature of Ge cathodic deposition process from aqueous solutions has a significant effect on the layer structure deposited onto the surface. In the presence of metal particles in the molten state, filamentous Ge structures grow due to the cathodic reduction of Ge-containing ions on the electrode surface, followed by dissolution and crystallization in the melt at the substrate interface. The results obtained show the crucial role of liquid metal particles during the electrochemical formation of germanium nanowires.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Wu, C. Han, J. Iocozzia, M. Lu, R. Ge, R. Xu, and Z. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 7898 (2016).
J.-H. Yun, Y. C. Park, J. Kim, H-J. Lee, W. A. Anderson, and J. Park, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 287 (2011).
Y. Jung, S. W. Nam, and R. Agarwal, Nano Lett. 11, 1364 (2011).
L. Tang, S. E. Kocabas, S. Latif, A. K. Okyay, D.-S. Ly-Gagnon, K. C. Saraswat, and D. A. B. Miller, Nat. Photon 2, 226 (2008).
J. Andzane, N. Petkov, A. I. Livshits, J. J. Boland, J. D. Holmes, and D. Erts, Nano Lett. 9, 1824 (2009).
V. Schmidt and U. Gösele, Science 316, 698 (2007).
X. Liang, Y. Kim, D. Gebergziabiher, and J. Stickney, Langmuir 26, 2877 (2010).
M. Wu, G. Vanhoutte, N. R. Brooks, K. Binnemans, and J. Fransaer, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 12080 (2015).
N. Chandrasekharan and S. C. Sevov, J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, 140 (2010).
R. Al-Salman, J. Mallet, M. Molinari, P. Fricoteaux, F. Martineau, M. Troyon, S. Zein El Abedin, and F. Endres, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 6233 (2008).
X. Li, G. Meng, Q. Xu, M. Kong, X. Zhu, Z. Chu, and A.-P. Li, Nano Lett. 11, 1704 (2011).
A. I. Carim, S. M. Collins, J. M. Foley, and S. Maldonado, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 13292 (2011).
E. Fahrenkrug, J. Biehl, and S. Maldonado, Chem. Mater. 27, 3389 (2015).
S. Usui, T. Yamasaki, and J. Shimoizaka, J. Phys. Chem. 71, 3195 (1967).
J. Gu, S. M. Collins, A. I. Carim, X. Hao, B. M. Bartlett, and S. Maldonado, Nano Lett. 12, 4617 (2012).
D. G. Gromov and S. A. Gavrilov, in Thermodynamics— Physical Chemistry of Aqueous Systems, Ed. by J. C. Moreno Piraján (InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, 2011), Chap. 7, p.157.
D. G. Gromov, L. M. Pavlova, A. I. Savitskii, and A. Yu. Trifonov, Phys. Solid State 57, 173 (2015).
N. K. Mahenderkar, Y.-C. Liu, J. A. Koza, and J. A. Switzer, ACS Nano 8, 9524 (2014).
D. G. Gromov and S. A. Gavrilov, Phys. Solid State 51, 2135 (2009).
A. P. Babichev, N. A. Babushkina, and A. M. Bratkovskii, Physical Quantities (Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1991), Chap. 14, p. 330 [in Russian].
L. V. Gurvich, I. V. Veits, and V. A. Medvedev, Thermodynamic Properties of Individual Substance (Nauka, Moscow, 1981; Hemisphere, New York, London, 1989), Vol. 3, Pt. 1, Chap. 23, rus. p.189.
L. V. Gurvich, I. V. Veits, and V. A. Medvedev, Thermodynamic Properties of Individual Substance (Nauka, Moscow, 1979; Hemisphere, New York, London, 1989), Vol. 2, Pt. 1, Chap. 18, rus. p.294.
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, Structure of Binary Alloys (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1958; Metallurgizdat, Moscow, 1962), Vol. 1, rus. p.812.
M. Wautelet, J. P. Dauchot, and M. Hecq, Nanotechnology 11, 6 (2000).
G. Garzel, J. Janczak-Rusch, and L. Zabdyr, Calphad 36, 52 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.M. Gavrilin, D.G. Gromov, A.A. Dronov, S.V. Dubkov, R.L. Volkov, A.Yu. Trifonov, N.I. Borgardt, S.A. Gavrilov, 2017, published in Fizika i Tekhnika Poluprovodnikov, 2017, Vol. 51, No. 8, pp. 1110–1115.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavrilin, I.M., Gromov, D.G., Dronov, A.A. et al. Effect of electrolyte temperature on the cathodic deposition of Ge nanowires on in and Sn particles in aqueous solutions. Semiconductors 51, 1067–1071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782617080115
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782617080115