Abstract
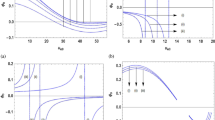
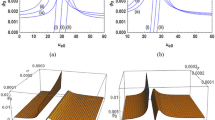
Two distinct classes of dust ion acoustic (DIA) solitary waves based on relativistic ions and electrons, dust charge Z d and ion-to-dust mass ratio Q’ = m i /m d are established in this model of multicomponent plasmas. At the increase of mass ratio Q’ due to increase of relativistic ion mass and accumulation of more negative dust charges into the plasma causing decrease of dust mass, relativistic DIA solitons of negative potentials are abundantly observed. Of course, relativistic compressive DIA solitons are also found to exist simultaneously. Further, the decrease of temperature inherent in the speed of light c causes the nonlinear term to be more active that increases the amplitude of the rarefactive solitons and dampens the growth of compressive solitons for relatively low and high mass ratio Q’, respectively. The impact of higher initial streaming of the massive ions is observed to identify the point of maximum dust density N d to yield rarefactive relativistic solitons of maximum amplitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. C. Whipple, T. G. Northrop, and D. A. Mendis, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 7405 (1985).
P. V. Bliokh and V. V. Yaroshenko, Sov. Astron. 29, 330 (1985).
U. de Angelis, V. Formisano, and M. Giordano, J. Plasma Phys. 40, 399 (1998).
N. N. Rao, P. K. Shukla, and M. Y. Yu, Planet. Space Sci. 38, 543 (1990).
F. Verheest, Planet. Space Sci. 40, 1 (1992).
A. Barkain, R. L. Merlino, and N. D’Angelo, Phys. Plasmas 2, 3563 (1995).
A. A. Mamun, R. A. Cairns, and P. K. Shukla, Phys. Plasmas 3, 702 (1996).
P. K. Shukla and A. A. Mamun, Introduction to Dusty Plasma Physics (IOP, London, 2002).
W. S. Duan, X. R. Hong, Y. R. Shi, and J. A. Sun, Chaos Solitons Fractals 16, 767 (2003).
Y. Y. Wang and J. F. Jhang, Phys. Lett. A 352, 155 (2006).
A. A. Mamun, R. A. Cairns, and P. K. Shukla, Phys. Plasmas 3, 2610 (1996).
F. Verheest and S. R. Pillay, Phys. Plasmas 15, 013703 (2008).
H. R. Pakzad, Astrophys. Space Sci. 324, 41 (2009).
M. M. Masud and A. A. Mamun, JETP Lett. 96, 765 (2013).
N. R. Kundu, M. M. Masud, K. S. Ashraf, and A. A. Mamun, Astrophys. Space Sci. 343, 279 (2013).
C.-R. Choi, D.-Y. Lee, Y.-H. Kim, and N. C. Lee, Phys. Plasmas 16, 043701 (2009).
F. Verheest and A. M. Hellberg, Phys. Plasmas 16, 064701 (2009).
M. Tribeche, S. Boukhalfa, and H. T. Zerguini, Phys. Plasmas 17, 064501 (2010).
H.-F. Liu, S.-Q. Wang, Z.-L. Wang, F.-Z. Yang, Y. Liu, and S. Li, Adv. Space Res. 51, 2368 (2013).
B. C. Kalita and S. Das, Astrophys. Space Sci. 352, 585 (2014).
N. D. Angelo, Planet. Space Sci. 42, 507 (1994).
Y. Nakamura, H. Bailung, and P. K. Shukla, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1602 (1999).
S. Ghosh, S. Sarkar, H. Khan, and M. R. Gupta, Phys. Lett. A 274, 162 (2000).
Y. Nakamura and A. Sarma, Phys. Plasmas 8, 3623 (2001).
S. I. Popel, T. V. Losseva, A. P. Golub’, R. L. Merlino, and S. N. Andreev, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 45, 461 (2005).
S. Gh. Dezfuly and D. Dorranian, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 53, 564 (2013).
S. I. Popel, S. N. Andreev, A. A. Gisko, A. P. Golub’, and T. V. Losseva, Plasma Phys. Rep. 30, 284 (2004).
W. Masood, A. Mushtaq, and R. Khan, Phys. Plasmas 14, 123702 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, B.C., Choudhury, M. Solitary waves in dusty plasmas with weak relativistic effects in electrons and ions. Plasma Phys. Rep. 42, 996–1004 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063780X16100093
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063780X16100093