Abstract
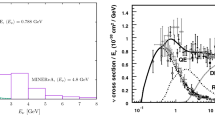
The contribution of neutrino electromagnetic properties to elastic neutrino–proton scattering is considered in detail. The neutrino electromagnetic properties are introduced via the charge, magnetic, electric, and anapole form factors in the basis of neutrino mass eigenstates. The effects of mixing of three neutrino states are taken into account along with effects of the change in the flavor of a neutrino that moves from the source to the detector. The weak neutral and electromagnetic nucleon form factors are also taken into account. The differential cross section calculated numerically for elastic neutrino–proton scattering obtained with allowance for the neutrino charge radius and magnetic moment are compared with the predictions of the Standard Model for reactor and accelerator neutrinos.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Giunti and A. Studenikin, Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 531 (2015).
C. Giunti, K. A. Kouzakov, Y.-F. Li, A. V. Lokhov, A. I. Studenikin, and S. Zhou, Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 528, 198 (2016).
A. I. Studenikin and K. A. Kouzakov, Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 75, 379 (2020).
J. Bernabéu, L. G. Cabral-Rosetti, J. Papavassiliou, and J. Vidal, Phys. Rev. D 62, 113012 (2000).
J. Bernabéu, J. Papavassiliou, and J. Vidal, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 101802 (2002).
J. Bernabéu, J. Papavassiliou, and J. Vidal, Nucl. Phys. B 680, 450 (2004).
K. Fujikawa and R. Shrock, Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 963 (1980).
L. Alvarez Ruso et al., arXiv: 2203.09030 [hep-ph].
Q. Chen, Theses and Dissertations–Physics and Astronomy (Univ. of Kentucky, 2021), p. 86.
O. Tomalak, P. Machado, V. Pandey, and R. Plestid, J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 97 (2021).
O. Tomalak, Q. Chen, R. J. Hill, and K. S. McFarland, arXiv: 2105.07939.
O. Tomalak, Q. Chen, R. J. Hill, and K. S. McFarland, Nat. Commun. 13, 5286 (2022).
R. S. Sufian, K.-F. Liu, and D. G. Richards, J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 1 (2020).
G. D. Megias, S. Bolognesi, M. B. Barbaro, and E. Tomasi-Gustafsson, Phys. Rev. C 101, 025501 (2020).
X. Zhang, T. J. Hobbs, and G. A. Miller, Phys. Rev. D 102, 074026 (2020).
J. Liang and K.-F. Liu, arXiv: 2008.12389 [hep-lat].
D. Z. Freedman, Phys. Rev. D 9, 1389 (1974).
D. Akimov et al., Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 357, 1123 (2017).
J. Yang, J. A. Hernandez, and J. Piekarewicz, Phys. Rev. C 100, 054301 (2019).
C. G. Payne, S. Bacca, G. Hagen, W. G. Jiang, and T. Papenbrock, Phys. Rev. C 100, 061304(R) (2019).
M. Hoferichter, J. Menendez, and A. Schwenk, Phys. Rev. D 102, 074018 (2020).
M. Cadeddu, C. Giunti, K. A. Kouzakov, Y. F. Li, A. I. Studenikin, and Y. Y. Zhang, Phys. Rev. D 98, 113010 (2018).
O. G. Miranda, D. K. Papoulias, G. Sanchez Garcia, O. Sanders, M. Tórtola, and J. W. F. Valle, J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 130 (2020).
M. Cadeddu, F. Dordei, C. Giunti, Y. F. Li, E. Picciau, and Y. Y. Zhang, Phys. Rev. D 102, 015030 (2020).
H. Bonet, A. Bonhomme, C. Buck, K. Fülber, J. Hakenmüller, J. Hempfling, G. Heusser, T. Hugle, M. Lindner, W. Maneschg, T. Rink, H. Strecker, R. Wink, and CONUS Collab., Eur. Phys. J. C 82, 813 (2022).
M. Atzori Corona, M. Cadeddu, N. Cargioli, F. Dordei, C. Giunti, Y. F. Li, C. A. Ternes, and Y. Y. Zhang, J. High Energy Phys. 2022, 164 (2022).
F. An et al., J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 43, 030401 (2016).
M. Nowakowski, E. A. Paschos, and J. M. Rodriguez, Eur. J. Phys. 26, 545 (2005).
Particle Data Group (R. L. Workman et al.), Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 083C01 (2022).
E. Aprile et al., Phys. Rev. D 102, 072004 (2020).
A. I. Ternov, JETP Lett. 104, 75 (2016).
A. I. Ternov, Phys. Rev. D 94, 093008 (2016).
K. S. Babu and R. N. Mohapatra, Phys. Rev. D 41, 271 (1990).
G. G. Raffelt, Phys. Rep. 320, 319 (1999).
W. C. Haxton and C. E. Wieman, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 51, 261 (2001).
C. Giunti and C. W. Kim, Fundamentals of Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 2007).
W. M. Alberico, S. M. Bilenky, C. Giunti, and K. M. Graczyk, Phys. Rev. C 79, 065204 (2009).
D. K. Papoulias and T. S. Kosmas, Adv. High Energy Phys. 2016, 1490860 (2016).
G. T. Garvey, W. C. Louis, and D. H. White, Phys. Rev. C 48, 761 (1993).
K. A. Kouzakov and A. I. Studenikin, Phys. Rev. D 95, 055013 (2017).
MicroBooNE Collab. (P. Abratenko et al.), Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 151801 (2022).
Funding
This work was supported by Russian Science Foundation (project no. 22-22-00384). F.M. Lazarev gratefully acknowledges the support of National Centre for Physics and Mathematics (Sarov, Russia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouzakov, K.A., Lazarev, F.M. & Studenikin, A.I. Neutrino Electromagnetic Properties in Elastic Neutrino–Proton Scattering. Phys. Atom. Nuclei 86, 257–265 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778823030122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778823030122