Abstract
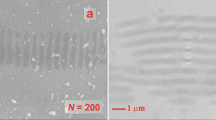
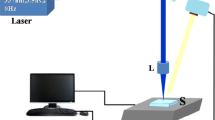
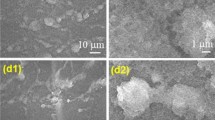
Absorptive properties of surface-structured silicon prepared by femtosecond laser pulses irradiating in SF6 or N2 are measured in a wide wavelength range of 0.3–16.0 μm. The SF6-prepared surface-structured silicon shows enhanced light absorptance up to 80% or more in the entire measured wavelength range. The absorptance for N2_prepared surface-structured silicon in the wavelength range of 9–14 µm is similar to that of a SF6-prepared sample, although it decreases to about 30% in the wavelength range of 2–7 µm. Light absorption varies with the height and density of the spikes formed on silicon surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Fowlkes and A. J. Pedraza, “Microstructural Evolution of Laser-Exposed Silicon Targets in SF6 Atmospheres,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1629–1631 (2000).
T. H. Her, R. J. Finlay, C. Wu, et al., “Microstructuring of Silicon with Femtosecond Laser Pulses,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 1673–1675 (1998).
M. Zhao, G. Yin, J. T. Zhu, and L. Zhao, “Picosecond Pulse Laser Microstructuring of Silicon,” Chin. Phys. Lett. 20, 1789–1791 (2003).
C. Wu, C. H. Crouch, L. Zhao, et al., “Near-Unity Below-Band-Gap Absorption by Microstructured Silicon,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1850–1852 (2001).
R. Younkin, J. E. Carey, E. Mazur, et al., “Infrared Absorption by Conical Silicon Microstructures Made in a Variety of Background Gases Using Femtosecond-Laser Pulses,” J. Appl. Phys. 93, 2626–2629 (2003).
C. H. Crouch, J. E. Carey, J. M. Warerender, et al., “Comparison of Structure and Properties of Femtosecond and Nanosecond Laser-Structured Silicon,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 1850–1852 (2001).
C. H. Crouch, J. E. Carey, M. Shen, et al., “Infrared Absorption by Sulfur-Doped Silicon Formed by Femtosecond Laser Irradiation,” Appl. Phys. A 79, 1635–1641 (2004).
R. A. Mayers, R. Farrell, A. M. Karger, et al., “Enhancing Near-Infrared Avalanche Photodiode Performance by Femtosecond Laser Microstructuring,” Appl. Opt. 45, 8825–8831 (2006).
J. T. Zhu, W. Li, M. Zhao, et al., “Silicon Microstructuring Using Ultrashort Laser Pulses,” Proc. SPIE 276, 5629–5636 (2005).
J. T. Zhu, L. Zhao, W. Li, et al., “Great Enhancement of Infrared Light Absorption of Silicon Surface-Structured by Femtosecond Laser Pulses in N2 Ambient,” Mater. Lett. 60, 2187–2189 (2006).
E. S. Kolesar, Jr., V. M. Bright, and D. M. Sowders, “Optical Reflectance Reduction of Textured Silicon Surefaces Coated with an Antireflective Thin Film,” Thin Sold Films 290–291, 23–29 (1996).
Y. Mo, M. Z. Bazant, and E. Kaxiras, “Sulfur Point Defects in Crystalline and Amorphous Silicon,” Phys. Rev. 70, 205210–205219 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Text © Astro, Ltd., 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liu, S., Wang, Y. et al. Broad band enhanced infrared light absorption of a femtosecond laser microstructured silicon. Laser Phys. 18, 1148–1152 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08100071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08100071