Abstract
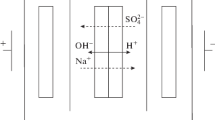
Characteristics of an аMB-2m bipolar membrane containing ion-polymer with phosphoric-acid groups, catalytically active in the water dissociation reaction, were studied by the electrochemical-impedance spectroscopy. The study is carried out in 0.1 М nitric acid–0.1 М sodium hydroxide system. The аMB-2m membrane bipolar region resistance is shown to be an order of magnitude less than that of the MB-1 and MB‑2 commercial membranes. The process of nitric acid and sodium hydroxide production from 0.5 М sodium nitrate solution, as well as from 0.5 М sodium nitrate solution containing 0.75 М boric acid is studied in an electrodialysis apparatus with three-chamber unit cells comprised of Ralex CMH cation-exchange membrane, аMB-2m bipolar membrane, and Ralex AMH anion-exchange membrane. The electrochemical characteristics (the current efficiency, the specific energy consumption, and the specific productivity) are shown to remain unchanged in the presence of boric acid, its transfer into the acid and alkali chambers of the electrodialyzer does not exceed 7%. A probable mechanism of the boric acid and borate ion transfer through the ion-exchange membranes into the acid and alkali chambers is suggested.













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
International Program on Chemical Safety. Environmental Health Criteria for Boron, Geneva: World Health Organization, 1998, vol. 204.
Kot, F.S., Boron in the Environment, in Boron Separation Processes, Kabay, N., Bryjak, M., and Hilal, N., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015, p. 1.
Weinthal, E., Parag, Y., Vengosh, A., Muti, A., and Kloppmann, W., The EU drinking water directive: The boron standard and scientific uncertainty, Eur. Environ., 2005, vol. 15, p. 1.
Sanitary Rules and Regulations 2.1.4.1074-01. Drinking Water. Hygienic Requirements for Water Quality of Centralized Drinking Water Supply Systems. Quality Control. Hygienic Requirements for Ensuring the Safety of Hot Water Systems, Moscow: Ministry of Health of Russia, 2002.
Sanitary Rules and Regulations 2.1.4.1116-02. Potable Water. Hygienic Requirements for Quality of Bottled Water. Quality Control, Moscow: Ministry of Health of Russia, 2002.
Princi, M.P., Lupini, A., Araniti, F., Longo, C., Mauceri, A., Sunseri, F., and Abenavoli, M.R., Boron toxicity and tolerance in plants: Recent advances and future perspectives, in Plant Metal Interaction, Parvaiz Ahmad, Ed., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2016, p. 115.
Roessner, U., Patterson, J., Forbes, M., Fincher, G., Langridge, P., and Bacic, A., An investigation of boron toxicity in barley using metabolomics, Plant Physiol., 2006, vol. 142, p. 1087.
Chatzissavvidis, C. and Antonopoulou, C., Boron toxicity in fruit crops: Agronomic and physiological implications, in Fruit Crops: Diagnosis and Management of Nutrient Constraints, Srivastava, A.K. and Hu, C., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020, p. 211.
Schoderboeck, L., Mühlegger, S., Losert, A., Gausterer, C., and Hornek, R., Effects assessment: Boron compounds in the aquatic environment, Chemosphere, 2011, vol. 82, p. 483.
Fail, P., Chapin, R., Price, C., and Heindel, J., General reproductive, developmental, and endocrine toxicity of boronated compounds, Reprod. Toxicol., 1998, vol. 12, p. 1.
Boron in Drinking-water. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1998. 2009.
Smith, B.M., Todd, P., and Bowman, C., Boron removal by polymer-assisted ultrafiltration, Separ. Sci. Technol., 1995, vol. 30, p. 3849.
Melnik, L., Vysotskaja, O., and Kornilovich, B., Boron behavior during desalination of sea and underground water by electrodialysis, Desalination, 1999, vol. 124, p. 125.
Melnyk, L., Goncharuk, V., Butnyk, I., and Tsapiuk, E., Boron removal from natural and wastewaters using combined sorption/membrane process, Desalination, 2005, vol. 185, p. 147.
Turek, M., Dydo, P., Ciba, J., Trojanowska, J., Kluczka, J., and Palka-Kupczak, B., Electrodialytic treatment of boron-containing wastewater with univalent permselective membranes, Desalination, 2005, vol. 185, p. 139.
Oren, Y., Linder, C., Daltrophe, N., Mirsky, Y., Skorka, J., and Kedem, O., Boron removal from desalinated seawater and brackish water by improved electrodialysis, Desalination, 2006, vol. 199, p. 52.
Jacob, C., Seawater desalination: boron removal by ion exchange technology, Desalination, 2007, vol. 205, p. 47.
Cengeloglu, Y., Arslan, G., Tor, A., Kocak, I., and Dursun, N., Removal of boron from water by using reverse osmosis, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2008, vol. 64, p. 141.
Tu, K.L., Ngheim, L.D., and Chivas, A.R., Boron removal by reverse osmosis membranes in seawater desalination applications, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2010, vol. 75, p. 87.
Hilal, N., Kim, G.J., and Somerfield, C., Boron removal from saline water: A comprehensive review, Desalination, 2011, vol. 273, p. 23.
Kir, E., Gurler, B., and Gulec, A., Boron removal from aqueous solution by using plasma-modified and unmodified anion-exchange membranes, Desalination, 2011, vol. 267, p. 114.
Wolska, J. and Bryjak, M., Methods for boron removal from aqueous solutions—a review, Desalination, 2013, vol. 310, p. 18.
Tagliabue, M., Reverberi, A.P., and Bagatin, R., Boron removal from water: needs, challenges and perspectives, J. Clean. Prod., 2014, vol. 77, p. 56.
Wang, B., Guo, X., and Bai, P., Removal technology of boron dissolved in aqueous solutions—A review, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2014, vol. 444, p. 338.
Guan, Z., Lv, J., Bai, P., and Guo, X., Boron removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption—A review, Desalination, 2016, vol. 383, p. 29.
Tang, Y. P., Luo, L., Thong, Z., and Chung, T.S., Recent advances in membrane materials and technologies for boron removal, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, vol. 541, p. 434.
Demkin, V.I., Adamovich, D.V., Amelin, V.S., and Panteleev, V.I., Membrane technology for the processing of salt liquid radioactive solutions, Seriya. Kriticheskiye tekhnologii. Membrany (in Russian), 2002, no. 15, p. 10.
Panteleev, V.I., Demkin, V.I., and Adamovich, D.V., Sorption-membrane technologies for the processing of radioactive solutions, Bezopasnost’ okruzhayushchey sredy (in Russian), 2008, no. 3, p. 82.
Watanabe, S., Ogi, H., Araia, Y., Aihara, H., Takahatake, Y., Shibata, A., Nomura, K., Kamiya, Y., Asanuma, N., Matsuura, H., Kubota, T., Seko, N., Arai, T., and Moriguchi, T., STRAD project for systematic treatments of radioactive liquid wastes generated in nuclear facilities, Progress Nuclear Energy, 2019, vol. 117, p. 103090.
Chechel’nitskij, G.M., Rabinovich, S.M., Sinjavskij, P.N., Kim, V.V., Tereshchenko, L.I., and Bessonov, O.V., RF Patent 2012076, 1994.
Asenov, V.V., US Patent 7323613, 2008.
Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G., Advances in membrane technologies for the treatment of liquid radioactive waste, Desalination, 2013, vol. 321, p. 119.
Ivanenko, V.I., Sedneva, T.A., Lokshin, E.P., and Korneykov, R.I., RF Patent 2141642, 2017.
Dmitriyev, S.A., Lifanov, F.A., Savkin, A.Ye., and Lashchenkov, S.M., Treatment of distillation residues of nuclear power plants, Atomnaya energiya (in Russian), 2000, no. 89, p. 365.
Nagasawa, H., Iizuka, A., Yamasaki, A., and Yanagisawa, Y., Utilization of bipolar membrane electrodialysis for the removal of boron from aqueous solution, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, vol. 50, p. 6325.
Bunani, S., Arda, M., Kabay, N., Yoshizuka, K., and Nishihama, S., Effect of process conditions on recovery of lithium and boron from water using bipolar membrane electrodialysis (BMED), Desalination, 2017, vol. 416, p. 10.
Noguchi, M., Nakamura, Y., Shoji, T., Iizuka, A., and Yamasaki, A., Simultaneous removal and recovery of boron from wastewater by multi-step bipolar membrane electrodialysis, J. Water Process Eng., 2018, vol. 23, p. 299.
İpekçia, D., Kabay, N., Bunani, S., Altıok, E., Arda, M., Yoshizuka, K., and Nishihama, S., Application of heterogeneous ion exchange membranes for simultaneous separation and recovery of lithium and boron from aqueous solution with bipolar membrane electrodialysis (EDBM), Desalination, 2020, vol. 479, p. 114313.
Svitsov, A.A. and Saltykov, B.V., Obtaining valuable components from deactivated wastewater, Proc. Int. Conf. dedic. to the 90th birthday of acad. B.A. Purin (in Russian), Moscow: Mendeleev Ros. Khim.-Tech. Univ., 2018, p. 111.
Egorov, E.N., Svitsov, A.A., Dudnik, S.N., and Demkin, V.I., Fractionation of multicomponent solutions by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes, Petr. Chem., 2012, vol. 57, p. 583.
Tanaka, Y., Ion exchange membranes, Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Ed., Elsevier Science, 2015, p. 531.
Ishibashi, N. and Hirano, K., Preparation of caustic soda and hydrochloric acid by use of bipolar ion-exchange membrane, J. Electrochem. Soc. Japan, 1959, vol. 26, no. 1–3, p. 8.
Greben’, V.P. and Rodzik, I.T., Effect of the concentration of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide on the numbers of ion transfer through heterogeneous bipolar ion-exchange membranes, Ionnyy Obmen Khromatografiya (in Russian), 1984, p. 158.
Greben’, V.P., Pivovarov, N.Ya., and Latskov, V.L., Production of concentrated caustic soda and hydrochloride acid solutions from sodium chloride by electrodialysis with the aid of bipolar ion-exchange membranes, Sov. J. Appl. Chem., 1988, vol. 61, no. 5, p. 903.
Carmen, C., Pilot performance of Tokuyama soda bipolar membrane in sodium chloride salt splitting, Membr. Technol., 1993, vol. 41, p. 5.
Bobrinskaya, G.A. and Bobreshova, O.V., Preparation of acid and alkali from sodium chloride of varied concentration in four-chamber electrodialyzer with bipolar membranes, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2000, vol. 73, no. 2, p. 241.
Yang, Y., Gao, X., Fan, A., Fu, L., and Gao, C., An innovative beneficial reuse of seawater concentrate using bipolar membrane electrodialysis, J. Membr. Sci., 2014, vol. 449, p. 119.
Bobrinskaya, G.A., Pavlova, T.V., and Shatalov, Ya.A., Recovery of acids and sodium hydroxide from solutions of sodium sulfate and sodium chloride with the use of bipolar membranes, Sov. J. Appl. Chem., 1985, vol. 58, p. 711.
Raucq, D., Pourcelly, G., and Gavach, C., Production of sulphuric acid and caustic soda from sodium sulphate by electromembrane processes. Comparison between electro-electrodialysis and electrodialysis on bipolar membrane, Desalination, 1993, vol. 91, no. 2, p. 163.
Pinacci, P., Development of electro-membrane processes for waste-stream treatment, Membr. Technol., 2001, vol. 134, p. 11.
Berkessa, Y.W., Lang Q., Yan, B., Kuang S., Mao, D., Shu, L., and Zhang, Y., Anion exchange membrane organic fouling and mitigation in salt valorization process from high salinity textile wastewater by bipolar membrane electrodialysis, Desalination, 2019, vol. 465, p. 94.
Cherif, A.T. and Molenat, J., Nitric acid and sodium hydroxide generation by electrodialysis using bipolar membranes, J. Appl. Electrochem., 1997, vol. 27, p. 1069.
Ben Ali, M.A., Rakib, M., Laborie, S., Viers, Ph., and Durand, G., Coupling of bipolar membrane electrodialysis and ammonia stripping for direct treatment of wastewaters containing ammonium nitrate, J. Membr. Sci., 2004, vol. 244, p. 89.
Linden, N., Bandinu, G.L., Vermaas, D. A., Spanjers, H., and Lier, J.B., Bipolar membrane electrodialysis for energetically competitive ammonium removal and dissolved ammonia production, J. Clean. Prod., 2020, vol. 259, p. 120788.
Nagasubramanian, P.K., Chlanda, F.P., and Liu, K.J., Use of bipolar membranes for generation of acid and base—an engineering and economic analysis, J. Membr. Sci., 1977, vol. 2, p. 109.
Mani, K.N., Chlanda, F.P., and Byszewski, C.H., AQUATECH membrane technology for recovery of acid/base values from salt streams, Desalination, 1988, vol. 68, p. 149.
Mani, K.N., Electrodialysis water splitting technology, J. Membr. Sci., 1991, vol. 58, p. 117.
Kim, Y.H. and Moon, S.H., Lactic acid recovery from fermentation broth using one-stage electrodialysis, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2001, vol. 76, p. 169.
Strathmann, H., Ion-exchange Membrane Separation Processes, Elsevier, 2004.
Kemperman, A.J.B., Handbook on Bipolar Membrane Technology, Enschede: Twente Univ., 2000.
Pourcelly, G., Electrodialysis with bipolar membranes: principles, optimization, and applications, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2002, vol. 38, p. 919.
MEGA Group; RALEX® electro separation membranes. Bipolar membranes RALEX® BM: roll/sheet | EDBM; https://www.mega.cz/membranes/.
Limited Liability Company United Chemical Company “SHCHEKINOAZOT”; http://n-azot.ru/product/ heterogeneous-ion-exchange-membranes?lang=EN.
Limited Liability Company Innovative Enterprise “SHCHEKINOAZOT”; http://www.azotom.ru/bipolyarnye-membrany/.
Zabolotskii, V., Sheldeshov, N., and Melnikov, S., Effect of cation-exchange layer thickness on electrochemical and transport characteristics of bipolar membranes, J. Appl. Electrochem., 2013, vol. 43, p. 1117.
Zabolotsky, V.I., Utin, S.V., Bespalov, A.V., and Strelkov, V.D., Modification of asymmetric bipolar membranes by functionalized hyperbranched polymers and their investigation during pH correction of diluted electrolytes solutions by electrodialysis, J. Membr. Sci., 2015, vol. 494, p. 188.
Utin, S.V., Loza, S.A., Bespalov, A.V., and Zabolotsky, V.I., Influence of functionalization and ionogenic groups nature of hyperbranched polymers on electrochemical characteristics of asymmetric bipolar membranes, Petr. Chem., 2018, vol. 58, no. 2, p. 137.
Fu, R.Q., Xu, T.W., Wang, G., Yang, W.H., and Pan, Z.X., Fundamental studies on the intermediate layer of a bipolar membrane. Part 1. PEG-catalytic water splitting in the interface of a bipolar membrane, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, vol. 263, p. 386.
Sheldeshov, N.V. and Zabolotsky, V.I., Bipolar ion-exchange membranes. Preparation. Properties. Application, in Membranes and Membrane Technologies (in Russian), Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Ed., Moscow: Nauchnyi Mir, 2013. p. 70.
Sheldeshov, N.V., Zabolotskii, V.I., Bespalov, A.V., Kovalev, N.V., Alpatova, N.V., Akimova, A.V., Mochalova, T.V., Kovaleva, V.I., and Boyarishcheva, A.Yu., The influence of catalytic additives on electrochemical properties of bipolar membranes, Petr. Chem., 2017, vol. 57, p. 518.
Martínez, R.J. and Farrell, J., Water splitting activity of oxygen-containing groups in graphene oxide catalyst in bipolar membranes, Comput. Theor. Chem., 2019, vol. 1164, p. 112556.
Sun, M., Li, M., Zhang, X., Wu, C., and Wu, Y., Graphene oxide modified porous P84 co-polyimide membranes for boron recovery by bipolar membrane electrodialysis process, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2020, vol. 232, p. 115.
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Jiang, C., Wang, Y., and Xu, T., Improving the water dissociation efficiency in a bipolar membrane with amino-functionalized MIL-101, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, vol. 524, p. 370.
Ionite Membranes. Granules. Powders: Catalog (in Russian), Moscow: NIITEKhim. NII “Plastmassy,” 1977, p. 15.
GOST (State Standard) 20298-74 Ion exchange resins. Cationites. Technical conditions (with changes No. 1–5), 1976.
GOST (State Standard) 20301-74 Ion exchange resins. Anionites. Technical conditions (with changes No. 1–5), 1976.
Semushin, A.M., Yakovlev, V.A., and Ivanova, E.V., Infrared Absorption Spectra of Ion-Exchange Materials, Reference guide (in Russian), Leningrad: Khimiya, 1980.
Zabolotskii, V.I., Gnusin, N.P., and Shel’deshov, N.V., Current-voltage characteristics of the transition region in MB-1 bipolar membrane, Sov. Electrochem., 1984, vol. 20, p. 1238.
Nemodruk, A.A. and Karalova, Z.K., Analytical Chemistry of Boron, Moscow: Nauka, 1964.
Timashev, S.F. and Kirganova, E.V., Mechanism of the electrolytic decomposition of water-molecules in bipolar ion-exchange membranes, Sov. Electrochem., 1981, vol. 17, p. 366.
Umnov, V.V., Shel’deshov, N.V., and Zabolotskii, V.I., Structure of the space-charge region at the anionite/cationite interface in bipolar membranes, Russ. J. Electrochem., 1999, vol. 35, p. 411.
Zabolotskii, V., Sheldeshov, N., and Melnikov, S., Heterogeneous bipolar membranes and their application in electrodialysis, Desalination, 2014, vol. 342, p. 183.
Funding
The work is supported by the State Contract with the Ministry of Sciences and Education of RF (project no. 10.3091.2017/4.6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by Yu. Pleskov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovalev, N.V., Karpenko, T.V., Sheldeshov, N.V. et al. Electrochemical Characteristics of Modified Heterogeneous Bipolar Membrane and Electromembrane Process of Nitric Acid and Sodium Hydroxide Recuperation from Sodium Nitrate and Boric Acid Solution. Russ J Electrochem 57, 122–133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521020063
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521020063