Abstract
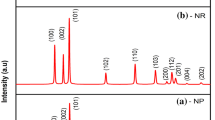
The present work outlines the synthesis of prismatic shaped zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostructures through microwave combustion method using different microwave power (160, 320, 480, 640, and 800 W) using Zinc nitrate as a precursor and ethylene glycol as solvent. The structural characterization of the synthesized ZnO nanostructures has been accessed by X-ray diffraction study (XRD), Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE–SEM), UV-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), energy-dispersive analysis using X-rays (EDAX) and photoconductivity technique. The XRD and FE–SEM results confirmed that the crystal size and growth of ZnO nanostructures depended on the heating of microwave powers. EDAX shows the existence of Zn and O in the synthesized ZnO microstructures. The optical properties and band gap studies were undertaken by UV-Visible spectroscopy. I–V characterization study was performed to determine the electrical property of ZnO films.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Venkatanarayanan, A., Temperature sensing materials, E. Spain, compress, Mater. Process., 2014, vol. 13, p. 57.
Hong, R.Y., Li, J.H., Chen, L.L., Liu, D.Q., Li, H.Z., Zheng, Y., and Ding, J., Synthesis, surface modification and photocatalytic property of ZnO nanoparticles, Powder Technol., 2009, vol. 189, p. 426.
Singh, J., Dutta, T., Kim, K.H., Rawat, M., Samddar, P., and Kumar, P., Green synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2018, vol. 16, p. 20.
Han, B.S., Caliskan, S., Sohn, W., Kim, M., Lee, J.K., and Jang, H.W., Room temperature deposition of crystalline nanoporous ZnO nanostructures for direct use as flexible DSSC photoanode, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2016, vol. 11, p. 221.
Maleh, H.K., Ahanjan, K., Taghavi, M., and Ghaemy, M., A novel voltammetric sensor employing zinc oxide nanoparticles and a new ferrocene-derivative modified carbon paste electrode for determination of captopril in drug samples, Anal. Methods, 2016, vol. 8, p. 1780.
Zhang, J., Gu, P., Xu, J., Xue, H., and Pang, H., High performance of electrochemical lithium storage batteries: ZnO-based nanomaterials for lithium-ion and lithium-sulfur batteries, Nanoscale, 2016, vol. 8, p. 18595.
He, X., Yoo, J.E., Lee, M.H., and Bae, J., Morphology engineering of ZnO nanostructures for high performance supercapacitors: enhanced electrochemistry of ZnO nanocones compared to ZnO nanowires, Nanotechnology, 2017, vol. 28, p. 6.
Suresh Sandhu, J.S., ZnO nanobelt: an efficient catalyst for synthesis of 5-arylitidine 2,4-thiazolidinediones and 5-arylidine-rhodanine, Int. J. Org. Chem., 2012, vol. 2, p. 305.
Osmond, M.J. and Mccall, M.J., Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: an analysis of potential exposure and hazard, Nanotoxicology, 2010, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 25.
Yatskiv, R., Grym, J., Zdansky, K., and Piksova, K., Semimetal graphite/ZnO Schottky diodes and their use for hydrogen sensing, Carbon, 2012, vol. 50, p. 3928.
Wojnarowicz, J., Chudoba, T., Koltsov, I., Gierlotka, S., Dworakowska, S., and Lojkowski, W., Size control mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles obtained in microwave solvothermal synthesis, Nanotechnology, 2018, vol. 29, no. 6, p. 065601.
Wojnarowicz, J., Chudoba, T., Gierlotka, S., and Lojkowski, W., Effect of microwave radiation, power on the size of aggregates of ZnO NPs prepared using microwave solvothermal synthesis, Nanomaterials, 2018, vol. 8, p. 10.
Ghosh, S., Majumder, D., Sen, A., and Roy, S., Facile sonochemical synthesis of zinc oxide nanoflakes at room temperature, Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 130, p. 215.
Mary, J.A., Vijaya, J.J., Bououdina, M., Kennedy, L.J., Daie, J.H., and Song, Y., Effect of Ce and Cu co-doping on the structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystals and first principle investigation of their stability and magnetic properties, Phys. E, 2015, vol. 66, p. 209.
Basith, N.M., Vijaya, J.J., Kennedy, L.J., Bououdina, M., Jenefar, S., and Kaviyarasan, V., Influence of Co doping on combined photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 30, p. 1108.
Djurisic, A.B., Ng, A.M.C., and Chen, X.Y., ZnO nanostructures for optoelectronics: material properties and device applications, Prog. Quant. Electron., 2010, vol. 34, p. 191.
Sherly, E.D., Vijaya, J.J., Selvam, N.C.S., and Kennedy, L.J., Microwave assisted combustion synthesis of coupled ZnO–ZrO2 nanoparticles and their role in the photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol, Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, p. 5681.
Pal, U. and Santiago, P., Controlling the morphology of ZnO nanostructures in a low-temperature hydrothermal process, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, vol. 109, p. 15317.
Sherly, E.D., Vijaya, J.J., and Kennedy, L.J., Effect of CeO2 coupling on the structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticle, J. Mol. Struct., 2015, vol. 1099, p. 114.
Suresh, P., Vijaya, J.J., and Kennedy, L.J., Fabrication of hexagonal ZnO nanorods on porous carbon matrix by microwave irradiation, J. Nanosci. Nanotech., 2013, vol. 13, p. 3068.
Shamhari, N.M., Wee, B.S., Chin, S.F., and Kok, K.Y., Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with small particle size distribution, Acta Chim. Slov., 2018, vol. 65, p. 578.
Sharma, D., Sharma, S., Kaitha, B.S., Rajput, J., and Kaur, M., Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using surfactant free in-air, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, vol. 257, p. 9661.
Mary, J.A., Vijaya, J.J., Dai, J.H., Bououdina, M., Kennedy, L.J., and Song, Y., Experimental and first-principles DFT studies of electronic, optical and magnetic properties of cerium–manganese co-doped zinc oxide nanostructures, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc., 2015, vol. 34, p. 38.
Zhao, Y., Zhu, J.J., Hong, J.M., Bian, N., and Chen, H.Y., Microwave-induced polyol-process synthesis of copper and copper oxide nanocrystals with controllable morphology, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2004, vol. 2004, p. 4072.
Darwish, M., Mohammadi, A., Assi, N., Manuchehri, Q.S., and Alahmad, Y., Shape-controlled ZnO nanocrystals synthesized via auto combustion method and enhancement of the visible light catalytic activity by decoration on graphene, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 703, p. 406.
Yathisha, R.O. and Nayaka, Y.A., Structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc incorporated copper oxide nanoparticles: doping effect of Zn, J. Mater. Sci., 2018, vol. 53, p. 678.
Zhang, B.J., Lian, J.S., Zhao, L., and Jiang, Q., Structural, optical and electrical properties of Zn1−xCdxO thin films prepared by PLD, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, vol. 257, p. 5657.
Freedsman, J.J., Kennedy, L.J., Kumar, R.T., Sekaran, G., and Vijaya, J.J., Studies on the structural and optical properties of zinc oxide nanobushes and Co-doped ZnO self-aggregated nanorods synthesized by simple thermal decomposition route, Mater. Res. Bull., 2010, vol. 45, p. 1486.
Cullity, B.D., Elements of X-ray Diffraction, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1978.
Shafi, P.M. and Bose, A.C., Impact of crystalline defects and size on X-ray line broadening: a phenomenological approach for tetragonal SnO2 nanocrystals, AIP Adv., 2015, vol. 5, p. 7.
Herring, N.P., Panchakarla, L.S., and El-Shall, M.S., P-type nitrogen-doped ZnO nanostructures with controlled shape and doping level by facile microwave synthesis, Langmuir, 2014, vol. 30, p. 2230.
Selvam, N.C.S., Vijaya, J.J., and Kennedy, L.J., Effects of morphology and Zr doping on structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanostructures, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, vol. 51, p. 16345.
Peng, W., Qu, S., Cong, G., and Wang, Z., Synthesis and structures of morphology-controlled ZnO nano- and microcrystals, Cryst. Growth Design, 2018, vol. 6, p. 1518.
Jayathilake, D.S.Y., Nirmal Peiris, T.A., Sagu, J.S., and Potter, D.B., Microwave-assisted synthesis and processing of Al-doped, Ga-doped, and Al, Ga, Co doped ZnO for the pursuit of optimal conductivity for transparent conducting film fabrication, ACS Sust. Chem. Eng., 2017, vol. 5, p. 4820.
Mary, J.A., Vijaya, J.J., Bououdina, M., Kennedy, L.J., and Daie, J.H., Phys. B, 2015, vol. 456, p. 344.
Mahamuni, P.P., Patil, P.M., Dhanvade, M.J., Badiger, M.V., and Shadija, P.G., Investigation of structural, surface morphological, optical properties and first-principles study on electronic and magnetic properties of (Ce,Fe)-Co doped ZnO, Biochem. Biophys. Rep., 2019, vol. 17, p. 89.
Selvam, N.C.S., Vijaya, J.J., and Kennedy, L.J., Comparative studies on influence of morphology and La doping on structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of zinc oxide nanostructures, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2013, vol. 407, p. 215.
Jesudoss, S.K., Vijaya, J.J., Selvam, N.C.S., Kombaiah, K., Sivachidambaram, M., Adinaveen, T., and Kennedy, L.J., Effects of Ba doping on structural, morphological, optical, and photocatalytic properties of self-assembled ZnO nanospheres, Clean. Techn. Environ. Policy, 2016, vol. 18, p. 729.
Yathisha, R.O., Nayaka, Y.A., Manjunatha, P., Vinay, M.M., and Purushothama, H.T., Doping, structural, optical and electrical properties of Ni2+ doped CdO nanoparticles prepared by microwave combustion route, Microchem. J., 2019, vol. 145, p. 641.
Fabbiyola, S., Sailaja, V., Kennedy, L.J., Bououdina, M., and Vijaya, J.J., Optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 694, p. 522.
Bakr, N.A., Khodair, Z.T., and Hassan, S.M.A., Effect of substrate temperature on structural and optical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis method, Res. J. Chem. Sci., 2015, vol. 5, no. 10, p. 51.
Giri, P.K., Bhattacharya, S., Singh, D.K., Kesavamoorthy, R., Panigrahi, B.K., and Nair, K.G.M., High temperature ferromagnetism and optical properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles, J. Appl. Phys., 2007, vol. 102, p. 8.
Mia, M.N.H., Pervez, M.F., Hossin, M.K., Rahman, M.R., and Ghosh, H.K., Influence of Mg content on tailoring optical bandgap of Mg-doped ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel method, Res. Phys., 2017, vol. 7, p. 2689.
Yathisha, R.O., Nayaka, Y.A., Manjunatha, P., Purushothama, H.T., Vinay, M.M., and Basavarajappa, K.V., Study on the effect of Zn2+ doping on optical and electrical properties of CuO nanoparticles, Phys. E, 2019, vol. 108, p. 257.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors are grateful to UGC and SERB, New Delhi for providing financial support in the form of major research Project. The authors wish to thank Dept. of Chemistry, Kuvempu University, for providing laboratory facilities to carry out this work. The authors are also thankful the NIE, Mysore for their support to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yathisha, R.O., Arthoba Nayaka, Y. Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ZnO Nanostructures Synthesized under Different Microwave Power. Russ J Electrochem 57, 784–794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120277
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120277