Abstract
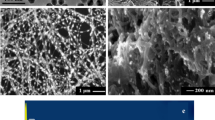
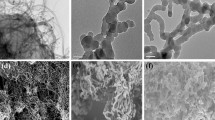
A novel quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensor based on molecular imprint polymer (MIP) has been developed for the detection of andrographolide in the medicinal plant extracts. The MIP and non-imprinted polymer (NIP) were synthesized using a precipitation polymerization method. The polymers were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and cyclic voltammetry. Both MIP and NIP were deposited on quartz crystal platform using an electro-polymerization method. A linear Langmuir isotherm model revealed that the MIP-QCM sensor has the maximum binding sites 18.02 ng cm–2. It was found that 92.8% of andrographolide was detected in 0.10 μg mL–1 of plant extract, and the limits of detection and quantification values were 1.21 and 4.02 ng cm–2, respectively. This research showed that the andrographolide imprinted polymer could be used to detect and quantify andrographolide in Andrographis paniculata plant extract in both analytical separation and sensor development.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Katiyar, C., Gupta, A., Kanjilal, S., and Katiyar, S., Drug discovery from plant sources: an integrated approach, Int. Q. J. Res. Ayurveda, 2012, vol. 33, p. 10.
Islam, A.K.M.S., Ismail, Z., Ahmad, M.N., Othman, A.R., Dharmaraj, S., and Shakaff, A.Y.M., Taste profiling of centella asiatica by a taste sensor, Sens. Mater., 2003, vol. 15, p. 209.
Xu, F.F., Fu, S.J., Gu, S.P., Wang, Z.M., Wang, Z.Z., He, X., and Xiao, W., Simultaneous determination of andrographolide, dehydroandrographolide and neoandrographolide in dog plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a dog pharmacokinetic study of Andrographis paniculata tablet, J. Chromatogr. B, 2015, vol. 990, p. 125.
Li, Q.Q., Zhang, J., Liu, J.H., and Yu, B.Y., Morphological and chemical studies of artificial Andrographis paniculata polyploids, Chin. J. Nat. Med., 2018, vol. 16, p. 81.
Kurzawa, M., Filipiak-Szok, A., Kłodzinska, E., and Szlyk, E., Determination of phytochemicals, antioxidant activity and total phenolic content in Andrographis paniculata using chromatographic methods, J. Chromatogr. B, 2015, vol. 995–996, p. 101.
Soo, H.L., Quah, S.Y., Sulaiman, I., Sagineedu, S.R., Lim, J.C.W., and Stanslas, J., Advances and challenges in developing andrographolide and its analogues as cancer therapeutic agents, Drug Discovery Today, 2019, vol. 24, p. 1890.
Song, Y.X., Liu, S.P., Jin, Z., Qin, J.F., and Jiang, Z.Y., Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Andrographis paniculata by rapid resolution liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry, Molecules, 2013, vol. 18, p. 12192.
Lok, C.M. and Son, R., Review article application of molecularly imprinted polymers in food sample analysis—a perspective, Int. Food Res. J., 2009, vol. 140, p. 127.
Chen, L., Xu, S., and Li, J., Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, vol. 40, p. 2922.
Shen, X. and Ye, L., Interfacial molecular imprinting in nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions, Macromolecules, 2011, vol. 44, p. 5631.
Granado, V.L.V., Gomes, M.T.S.R., and Rudnitskaya, A., Molecularly imprinted polymer thin-film electrochemical sensors, in Biomimetic Sensing, Fitzgerald, J. and Fenniri, H., Eds., New York: Humana, 2019.
Sohn, S. and Kim, D., Modification of Langmuir isotherm in solution systems – definition and utilization of concentration dependent factor, Chemosphere, 2005, vol. 58, p. 115.
Pinsrithong, S. and Bunkoed, O., Hierarchical porous nanostructured polypyrrole-coated hydrogel beads containing reduced graphene oxide and magnetite nanoparticles for extraction of phthalates in bottled drinks, J. Chromatogr. A, 2018, vol. 1570, p. 19.
Pardeshi, S., Dhodapkar, R., and Kumar, A., Molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared using precipitation polymerisation method for selective extraction of gallic acid from Emblica officinalis, Food Chem., 2014, vol. 146, p. 385.
Farrington, K., Magner, E., and Regan, F., Predicting the performance of molecularly imprinted polymers: selective extraction of caffeine by molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, vol. 566, p. 60.
Sharma, P.S., Pietrzyk-Le, A., D’Souza, F., and Kutner, W., Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing, Bioanal. Chem., 2012, vol. 402, p. 3177.
Hu, Y., Pan, J., Zhang, K., Lian, H., and Li, G., Novel applications of molecularly-imprinted polymers in sample preparation, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem., 2013, vol. 43, p. 37.
Sanjuán, A.M., Reglero Ruiz, J.A., García, F.C., and García, J.M., Recent developments in sensing devices based on polymeric systems, React. Funct. Polym., 2018, vol. 133, p. 103.
Hepel, M. and Cateforis, E., Studies of copper corrosion inhibition using Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Nanobalance and Quartz Crystal Immittance techniques, Electrochim. Acta, 2001, vol. 46, p. 3801.
Stobiecka, M., Deeb, J., and Hepel M., Molecularly templated polymer matrix films for biorecognition processes: sensors for evaluating oxidative stress and redox buffering capacity, Electrochem. Soc. Trans., 2009, vol. 19, p. 15.
Cao, Y., Feng, T., Xu, J., and Xue, C., Recent advances of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors in the detection of food safety hazard factors, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, vol. 141, p. 111447.
Ayankojo, A. G., Reut, J., Boroznjak, R., Opik, A., and Syritski, V., Molecularly imprint, ed poly(meta-phenylenediamine) based QCM sensor for detecting Amoxicillin, Sens. Actuators B, 2018, vol. 258, p. 766.
Orihara, K., Hikichi, A., Arita, T., Muguruma, H., and Yoshimi, Y., Heparin molecularly imprinted polymer thin flm on gold electrode by plasma-induced graft polymerization for label-free biosensor, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2018, vol. 151, p. 324.
Ma, X.T., He, X.W., Li, W.Y., and Zhang, Y.K., Oriented surface epitope imprinted polymer-based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for cytochrome c, Talanta, 2019, vol. 191, p. 222.
Islam, A.K.M.S., Krishnan, H., Singh, H., and Ahmad, M.N., A noble molecular imprint polymer biosensor for caffeic acid detection in orthosiphon Stamineus extracts, J. Teknol., 2015, vol. 77, p. 97.
Krishnan, H., Islam, A.K.M.S., Hamzah, Z., Nadaraja, P., and Ahmad, M.N., A novel molecular imprint polymer synthesis for solid phase extraction of andrographolide, Indones. J. Chem., 2019, vol. 19, p. 219.
Mosch, H.L.K.S., Akintola, O., Plass, W., Höppener, S., Schubert, U.S., and Ignaszak, A., Specific surface versus electrochemically active area of the carbon/polypyrrole capacitor: correlation of ion dynamics studied by an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance with BET surface, Langmuir, 2016, vol. 32, p. 4440.
Renkecz, T., László, K., and Horváth, V., Molecularly imprinted microspheres prepared by precipitation polymerization at high monomer concentrations, Mol. Imprinting, 2014, vol. 2, p. 1.
Spivak, D.A., Optimization, evaluation, and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2005, vol. 57, p. 1779.
Yao, C., Zhu, T., Qi, Y., Zhao, Y., Xia, H., and Fu, W., Development of a quartz crystal microbalance biosensor with aptamers as bio-recognition element, Sensors, 2010, vol. 10, p. 5859.
Hepel, M., Electrode-solution interface studied with electrochemical quartz crystal nanobalance, in Interfacial Electrochemistry. Theory, Experiment, and Applications, Wieckowski, A., Ed., New York: Marcel Dekker, 1999, p. 599.
Dabrowski, M., Lach, P., Cieplak, M., and Kutner, W., Nanostructured molecularly imprinted polymers for protein chemosensing, Biosen. Bioelectron., 2018, vol. 102, p. 17.
Alenazi, N.A., Manthorpe, J.M., and Lai, E.P.C., Selectivity enhancement in molecularly imprinted polymers for binding of bisphenol A, Sensors, 2016, vol. 16, p. 1697.
Gultekin, A., Karanfil, G., Kus, M., Sonmezoglu, S., and Say, R., Preparation of MIP-based QCM nanosensor for detection of caffeic acid, Talanta, 2014, vol. 119, p. 533.
Kartal, F, Çimen, D., Bereli, N., and Denizli, A., Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the clinical detection of insulin, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2019, vol. 97, p. 730.
Funding
The authors are grateful to Universiti Sains Malaysia for providing the financial support of this project Bridging grant no. 304.PKIMIA.6316279 and Research Management Centre, IIUM grant no. RPDF19 002 0012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that we do not have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafiqul Islam, A.K., Krishnan, H., Ahmad, M.N. et al. A Novel Molecular Imprint Polymer Quartz Crystal Microbalance Nanosensor for the Detection of Andrographolide in the Medicinal Plant Extract. Russ J Electrochem 57, 671–679 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120228
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120228