Abstract
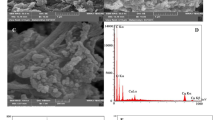
Fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin (Cip) is an antibiotic used to treat some bacterial infections such as bone, joint, respiratory tract, skin, typhoid fever and urinary tract infections. Cip can also cause severe allergic reactions. So, clinical and pharmaceutical analysis of Cip is very important. Herein nitrogen doped porous reduced graphene oxide (N-prGO) as active material in electrochemical sensors was synthesized in ammonia media. The results indicated that presence of heteroatoms in the N-prGO increases the active sites and enhances the electrical conductivity. A new electrochemical sensor was developed based on the use of N‑prGO on carbon paste electrode (CPE) for the detection of Cip. The introduction of N-prGO porous support can provide high surface area, facilitate the diffusion and mass transport of reactants, and makes the sensor more sensitive and accurate for the detection of Cip. The N-prGO-based CPE presented a linear response for Cip concentration range of 0.1 to 10 µM, sensitivity of 820 µA mM–1and detection limit of 39 nM by differential pulse voltammetry. The developed method was successfully applied for detection of Cip in human serum and pharmaceutical samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Feier, B., Blidar, A., Pusta, A., and Cecilia Cristea, P.C., Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for the detection of cephalexin, Biosensors, 2019, vol. 9, p. 31.
Genamo, E.S., Gebeyehu Bayisa, H., and Ditamo, R., Assessment of antibiotics use for hospitalized children in butajira general hospital, southern part of Ethiopia, Int. J. Pediatr., 2019, vol. 7, p. 8845.
Choudhury, D.K. and Bezbaruah, B.K., Antibiotic prescriptions pattern in paediatric in-patient department gauhati medical college and hospital, Guwahati, J. Appl. Pharm. Sci., 2013, vol. 3, p. 144.
Kim, S. and Aga, D.S., Potential ecological and human health impacts of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria from wastewater treatment plants, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B, 2007, vol. 10, p. 559.
Grenni, P., Ancona, V., and Barra Caracciolo, A., Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems, Microchem. J., 2018, vol. 136, p. 25.
Manyi-Loh, Ch., Mamphweli, S., Meyer, E., and Okoh, A., Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: potential public health implications, Molecules, 2018, vol. 23, p. 795.
Fedorowicz, J. and Sączewski, J., Modifications of quinolones and fluoroquinolones: hybrid compounds and dual-action molecules, Monatsh. Chem., 2018, vol. 149, p. 1199.
Qassim, A.W., Spectrophotometric determination of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulation ciproxin, Int. J. Adv. Sci. Tech. Res., 2015, vol. 3, p. 135.
Kumar, M., Jaiswal, Sh., Kaur Sodhi, K., Dileep Kumar Singh, P.Sh., and Shukla, P., Antibiotics bioremediation: perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance, Enviroment. Int., 2019, vol. 124, p. 448.
Puttaswamy Deepak, M. and Puttagiddappa Mamatha, G., Voltammetric studies of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride at poly(L-tyrosine)/SnO2 nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode, Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem., 2015, vol. 7, p. 523.
Bantarapiwat, K., Rojsanga, P., Ruangwises, N., and Buranaphalin, S., Simultaneous determination of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and dexamethasone in ophthalmic solution by high performance liquid chromatography and derivative spectrophotometry, J. Pharm. Sci., 2016, vol. 43, p. 183.
Emami, J. and Rezazadeh, M., A simple and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of ciprofloxacin in bioavailability studies of conventional and gastroretentive prolonged-release formulations, Adv. Biomed. Res., 2016, vol. 5, p. 163.
Solangi, A.R., Memon, S.Q., Mallah, A., Memon, N., Khuhawar, M.Y., and Bhanger, M.I., Development and implication of a capillary electrophoresis methodology for ciprofloxacin, paracetamol and diclofenac sodium in pharmaceutical formulations and simultaneously in human urine samples, Pak. J. Pharm. Sci., 2011, vol. 24, p. 539.
Zhang, H.T., Jiang, J.Q., Wang, Z.l., Chang, X.Y., Liu, X.Y., Wang, S.H., Zhao, K., and Chen, J.Sh., Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for simultaneous detection of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 2011, vol. 12, p. 884.
Baeza, A.N., Urraca, J.L., Chamorro, R., Orellana, G., Castellari, M., and Moreno-Bondi, M.C., Multiresidue analysis of cephalosporin antibiotics in bovine milk based on molecularly imprinted polymer extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. A, 2016, vol. 1474, p. 121.
Li, W., Shen, H., Hong, Y., Zhang, Y., Yuan, F., and Zhang, F., Simultaneous determination of 22 cephalosporins drug residues in porkmuscle using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. B, 2016, vol. 1022, p. 298.
Lata, K., Sharma, R., Naik, L., Rajput, Y.S., and Mann, B., Synthesis and application of cephalexin imprinted polymer for solid phase extraction in milk, Food Chem., 2015, vol. 184, p. 176.
Ali Ahmed, S.M., Elbashir, A.A., and Aboul-Enein, H.Y., New spectrophotometric method for determination of cephalosporins in pharmaceutical formulations, Arab. J. Chem., 2015, vol. 8, p. 233.
Buglak, A.A., Shanin, I.A., Eremin, S.A., Lei, H.T., Li, X., Zherdev, A.V., and Dzantiev, B.B., Ciprofloxacin and clinafloxacin antibodies for an immunoassay of quinolones: quantitative structure–activity analysis of cross-reactivities, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, vol. 20, p. 265.
Hamnca, S., Phelane, L., Iwuoha, E., and Baker, P., Electrochemical determination of neomycin and norfloxacin at a novel polymer nanocomposite electrode in aqueous solution, Anal. Lett., 2017, vol. 50, p. 1887.
Feier, B., Gui, A., Cristea, C., and Săndulescu, R., Electrochemical determination of cephalosporins using a bare boron-doped diamond electrode, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2017, vol. 976, p. 25.
Yi, H. and Li, Ch., Voltammetric determination of ciprofloxacin based on the enhancement effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) at carbon paste electrode, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2007, vol. 43, p. 1377.
Zhang, Sh. and Wei, Sh., Electrochemical determination of ciprofloxacin based on the enhancement effect of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, Bull. Korean. Chem. Soc., 2007, vol. 28, p. 543.
Yuan, Y., Zhang, F., Wang, H., Gao, L., and Wang, Z., A sensor based on Au nanoparticles/carbon nitride/graphene composites for the detection of chloramphenicol and ciprofloxacin, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol., 2018, vol. 7, p. M201.
Cinková, K., Andrejčáková, D., and Švorc, L., Electrochemical method for point-of-care determination of ciprofoxacin using boron-doped diamond electrode, Acta Chim. Slov., 2016, vol. 9, p. 146.
Uslu, B., Bozal, B., and Emin Kuscu, M., Anodic voltammetry of ciprofloxacin and its analytical applications, Open Chem. Biomed. Methods J., 2010, vol. 3, p. 108.
Shan, J., Liu, Y., Li, R., Wu, C., Zhu, L., and Zhang, J., Indirect electrochemical determination of ciprofloxacin by anodic stripping voltammetry of Cd(II) on graphene-modified electrode, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2015, vol. 738, p. 123.
Ensafi, A.A., Allafchian, A.R., and Mohammadzadeh, R., Characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles as a novel electrochemical sensor: application for the voltammetric determination of ciprofloxacin, Anal. Sci., 2012, vol. 28, p. 705.
Mahon, P.J., Lai, G., and Yu, A., Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite modified electrodes for sensitive detection of ciprofloxacin, Electroanalysis, 2018, vol. 30, p. 2185.
Xie, A.J., Chen, Y., Luo, S.P., Tao, Y.W., Jin, Y.S., and Li, W.W., Electrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin based on graphene modified glassy carbon electrode, J. Mater. Technol. Adv. Perform. Mater., 2015, vol. 30, p. 362.
Chen, Zh., Yan, H., Liu, T., and Niu, S., Nanosheets of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide as hybrid fillers improved the mechanical and tribological properties of bismaleimide composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 125, p. 47.
Ambrosi, A., Chua, C.K., Bonanni, A., and Pumera, M., Electrochemistry of graphene and related materials, Chem. Rev., 2014, vol. 114, p. 7150.
Chabot, V., Higgins, D., Yu, A., Xiao, X., Chen, Z., and Zhang, J., A review of graphene and graphene oxide sponge: material synthesis and applications to energy and the environment, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, vol. 7, p. 1564.
Nolan, H., Mendoza-Sanchez, B., Ashok Kumar, N., Mc Evoy, N., O’Brien, S., Nicolosi, V., and Duesberg, G.S., Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, vol. 16, p. 2280.
Wang, H., Maiyalagan, T., and Wang, X., Review on recent progress in nitrogen-doped graphene: synthesis, characterization, and its potential applications, ACS Catal., 2012, vol. 2, p. 781.
Qu, L., Liu, Y., Baek, J.B., and Dai, L., Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells, ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, p. 1321.
Wang, Y., Shao, Y., Matson, D.W., Li, J., and Lin, Y., Nitrogen-doped graphene and its application in electrochemical biosensing, ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, p. 1790.
Chekin, F., Vasilescu, A., Jijie, R., Singh, S.K., Kurungot, S., Iancu, M., Badea, G., Boukherroub, R., and Szunerits, S., Sensitive electrochemical detection of cardiac troponin I in serum an saliva by nitrogen-doped porous reduced graphene oxide electrode, Sens. Actuators B, 2018, vol. 262, p. 180.
Chekin, F., Myshin, V., Ye, R., Melinte, S., Singh, S.K., Kurungot, S., Boukherroub, R., and Szunerits, S., Graphene-modified electrodes for sensing doxorubicin hydrochloride in human plasma, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2019, vol. 411, p. 1509.
Nikkhah, Sh., Tahermansouri, H., and Chekin, F., Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties of the modified graphene oxide with 4,4'-methylenedianiline, Mater. Lett., 2018, vol. 211, p. 323.
Zareyy, B., Chekin, F., and Fathi, Sh., NiO/porous reduced graphene oxide as active hybrid electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2019, vol. 55, p. 333.
Hazhir, N., Chekin, F., Raoof, J.B., and Fathi, Sh., Porous reduced graphene oxide/chitosan-based nanocarrier for delivery system of doxorubicin, RSC Adv., 2019, vol. 9, p. 30729.
Amirighadi, S., Raoof, J.B., Chekin, F., and Ojani, R., A sensitive voltammetric detection of pramipexole based on 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisilazane carbon nano tube modified electrode, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2017, vol. 75, p. 784.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reyhane Rahimpour, Sabeti, B. & Chekin, F. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Nitrogen Doped Porous Reduced Graphene Oxide to Detection of Ciprofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Samples. Russ J Electrochem 57, 654–662 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120186
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193520120186