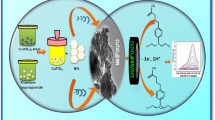
Abstract
In the present investigation, a new electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode was applied to simultaneous determine the tramadol, olanzapine and acetaminophen for the first time. The CuO/reduced graphene nanoribbons (rGNR) nanocomposites and 1-ethyl 3-methyl imidazolinium chloride as ionic liquid (IL) were employed as modifiers. The electro-oxidation of these drugs at the surface of the modified electrode was evaluated using cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and chronoamperometry. Various techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive X-Ray analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), were used to validate the structure of CuO-rGNR nanocomposites. This sensor displayed a superb electro catalytic oxidation activity and good sensitivity. Under optimized conditions, the results showed the linear in the concentration range of 0.08–900 μM and detection limit (LOD) was achieved to be 0.05 μM. The suggested technique was effectively used to the determination of tramadol in pharmaceuticals and human serum samples. For the first time, the present study demonstrated the synthesis and utilization of the porous nanocomposites to make a unique and sensitive electrode and ionic liquid for electrode modification to co-measurement of these drugs.








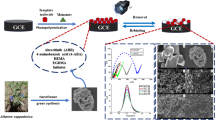
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ricardo-Teixeira Tarley C, de Cássia Mendonça J, Rianne da Rocha L, Boareto Capelari T, Carolyne Prete M, Cecílio Fonseca M, Midori de-Oliveira F, César Pereira A, Luiz Scheel G, Bastos Borges K, Gava Segatelli M (2020) Development of a molecularly imprinted poly(acrylic acid)-MWCNT nanocomposite electrochemical sensor for tramadol determination in pharmaceutical samples. Electroanalysis 32:1130–1137. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201900148
Pereira FJ, Rodríguez-Cordero A, López R, Robles LC, Aller AJ (2021) Development and validation of an rp-hplc-pda method for determination of paracetamol, caffeine and tramadol hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulations. Pharmaceuticals. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050466
Patteet L, Morrens M, Maudens KE, Niemegeers P, Sabbe B, Neels H (2012) Therapeutic drug monitoring of common antipsychotics. Ther Drug Monit 34:629–651. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e3182708ec5
Mohammadi-Behzad L, Gholivand MB, Shamsipur M, Gholivand K, Barati A, Gholami A (2016) Highly sensitive voltammetric sensor based on immobilization of bisphosphoramidate-derivative and quantum dots onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified gold electrode for the electrocatalytic determination of olanzapine. Mater Sci Eng C 60:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.068
Rouhani M, Soleymanpour A (2019) A new selective carbon paste electrode for potentiometric analysis of olanzapine. Meas J Int Meas Confed 140:472–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.04.018
Muthusankar A, Sangili SM, Chen R, Karkuzhali M, Sethupathi G, Gopu S, Karthick RK, Devi N (2018) Sengottuvelan, In situ assembly of sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots surrounded iron(III) oxide nanocomposite; a novel electrocatalystanesan for highly sensitive detection of antipsychotic drug olanzapine. J Mol Liq 268:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.059
Filik H, Avan AA, Aydar S, Çetintaş G (2014) Determination of acetaminophen in the presence of ascorbic acid using a glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(Caffeic acid). Int J Electrochem Sci 9:148–160
Jahani PM, Mohammadi SZ, Khodabakhshzadeh A, Asl MS, Jang HW, Shokouhimehr M, Zhang K, Van Le Q, Peng W (2020) Simultenous voltammetric detection of acetaminophen and tramadol using molybdenum tungsten disulfide-modified graphite screen-printed electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 15:9024–9036. https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.09.12
Shi H, Zheng Y, Karimi-Maleh H, Fu L (2021) Alginate-modified Cassava fiber loaded palladium for electochemical paracetamol analysis. Int J Electrochem Sci 16:1–10. https://doi.org/10.20964/2021.10.24
Islam MM, Arifuzzaman M, Rushd S, Islam MK, Rahman MM (2022) Electrochemical sensor based on poly (aspartic acid) modified carbon paste electrode for paracetamol determination. Int J Electrochem Sci. https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.02.39
Zheng B, He X, Zhang Q, Duan M (2022) A novel molecularly imprinted membrane for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of paracetamol. Int J Electrochem Sci 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.07.37
Beakley BD, Kaye AM, Kaye AD (2015) Tramadol, pharmacology, side effects, and serotonin syndrome: a review. Pain Physician 18:395–400. https://doi.org/10.36076/ppj.2015/18/395
Dahshan HE, Helal MA, Mostafa SM, Elgawish MS (2019) Development and validation of an HPLC-UV method for simultaneous determination of sildenafil and tramadol in biological fluids: Application to drug-drug interaction study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 168:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.02.025
Atila Karaca S, Yeniceli Uğur D (2018) Development of a validated hplc method for simultaneous determination of olanzapine and aripiprazole in human plasma, Marmara. Pharm J 22:493–501. https://doi.org/10.12991/jrp.2018.90
Tanaka H, Naito T, Mino Y, Kawakami J (2016) Validated determination method of tramadol and its desmethylates in human plasma using an isocratic LC-MS/MS and its clinical application to patients with cancer pain or non-cancer pain. J Pharm Heal Care Sci 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40780-016-0059-2
Lu W, Zhao S, Gong M, Sun L, Ding L (2018) Simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and oxycodone in human plasma by LC–MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Anal 8:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2018.01.006
Khelfi A, Azzouz M, Abtroun R, Reggabi M, Alamir B (2018) Sulpiride in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Res Artic Determ Chlorpromazine 2018:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5807218
Kimani MM, Lanzarotta A, Batson JCS (2021) Trace level detection of select opioids (fentanyl, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and tramadol) in suspect pharmaceutical tablets using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with handheld devices. J Forensic Sci 66:491–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.14600
Alharbi O, Xu Y, Goodacre R (2015) Detection and quantification of the opioid tramadol in urine using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 140:5965–5970. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01177a
Al-Otaibi JS, Albrycht P, Mary YS, Mary YS, Księżopolska-Gocalska M (2021) Concentration-dependent SERS profile of olanzapine on silver and silver-gold metallic substrates. Chem Pap 75:6059–6072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01783-9
Sefaty B, Masrournia M, Eshaghi Z, Bozorgmehr MR (2021) Determination of tramadol and fluoxetine in biological and water samples by magnetic dispersive solid-phase microextraction (MDSPME) with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Anal Lett 54:884–902. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1786695
Adegoke OA, Thomas OE, Emmanuel SN (2016) Colorimetric determination of olanzapine via charge-transfer complexation with chloranilic acid. J Taibah Univ Sci 10:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2015.12.002
Shihana F, Dissanayake D, Dargan P, Dawson A (2010) A modified low-cost colorimetric method for paracetamol (acetaminophen) measurement in plasma. Clin Toxicol 48:42–46. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650903443137
Khairy M, Banks CE (2020) A screen-printed electrochemical sensing platform surface modified with nanostructured ytterbium oxide nanoplates facilitating the electroanalytical sensing of the analgesic drugs acetaminophen and tramadol. Microchim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4118-x
Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh F, Shahrokhian S, Mohammadi A, Dinarvand R (2010) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of tramadol and acetaminophen using carbon nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 55:2752–2759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.12.052
Arabali V, Malekmohammadi S, Karimi F (2020) Surface amplification of pencil graphite electrode using CuO nanoparticle/polypyrrole nanocomposite; a powerful electrochemical strategy for determination of tramadol. Microchem J 158:105179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105179
Kolahi-Ahari S, Deiminiat B, Rounaghi GH (2020) Modification of a pencil graphite electrode with multiwalled carbon nanotubes capped gold nanoparticles for electrochemical determination of tramadol. J Electroanal Chem 862:113996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.113996
Rao L, Zhu Y, Duan Z, Xue T, Duan X, Wen Y, Kumar AS, Zhang W, Xu J, Hojjati-Najafabadi A (2022) Lotus seedpods biochar decorated molybdenum disulfide for portable, flexible, outdoor and inexpensive sensing of hyperin. Chemosphere 301:134595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134595
Monsef R, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Hydrothermal architecture of Cu5V2O10 nanostructures as new electro-sensing catalysts for voltammetric quantification of mefenamic acid in pharmaceuticals and biological samples. Biosens Bioelectron 178:113017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113017
Mansoorianfar M, Nabipour H, Pahlevani F, Zhao Y, Hussain Z, Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Hoang HY, Pei R (2022) Recent progress on adsorption of cadmium ions from water systems using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as an efficient class of porous materials. Environ Res 214:114113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114113
Baladi E, Davar F, Hojjati-Najafabadi A (2022) Synthesis and characterization of g–C3N4–CoFe2O4–ZnO magnetic nanocomposites for enhancing photocatalytic activity with visible light for degradation of penicillin G antibiotic. Environ Res 215:114270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114270
Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Rahmanpour MS, Karimi F, Zabihi-Feyzaba H, Malekmohammad S, Agarwal S, Gupta VK, Khalilzadeh MA (2020) Determination of tert-butylhydroquinone using a nanostructured sensor based on CdO/SWCNTs and ionic liquid. Int J Electrochem Sci 15:6969–6980. https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.07.85
Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Aygun A, Tiri RNE, Gulbagca F, Lounissaa MI, Feng P, Karimi F, Sen F (2022) Bacillus thuringiensis based ruthenium/nickel Co-doped zinc as a green nanocatalyst: enhanced photocatalytic activity, mechanism, and efficient H2production from sodium borohydride methanolysis. Ind Eng Chem Res. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c03833
Bijad M, Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Asari-Bami H, Habibzadeh S, Amini I, Fazeli F (2021) An overview of modified sensors with focus on electrochemical sensing of sulfite in food samples. Eurasian Chem Commun 3:116–138. https://doi.org/10.22034/ecc.2021.268819.1122
Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Salmanpour S, Sen F, Asrami PN, Mahdavian M, Khalilzadeh MA (2022) A tramadol drug electrochemical sensor amplified by biosynthesized au nanoparticle using mentha aquatic extract and ionic liquid. Top Catal 65:587–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-021-01498-x
Chen D, Feng H, Li J, Al-Nafiey AKH, Lin F, Tong X, Wang Y, Bao J, Wang ZM, Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev AS, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2015) Reduced graphene oxide-based nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:2078–2078. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00128
Karimi-Maleh H, Darabi R, Karimi F, Karaman C, Shahidi SA, Zare N, Baghayeri M, Fu L, Rostamnia S, Rouhi J, Rajendran S (2023) State-of-art advances on removal, degradation and electrochemical monitoring of 4-aminophenol pollutants in real samples: a review. Environ Res 222:115338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115338
Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Mansoorianfar M, Liang T, Shahin K, Karimi-Maleh H (2022) A review on magnetic sensors for monitoring of hazardous pollutants in water resources. Sci Total Environ 824:153844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153844
Buledi JA, Mahar N, Mallah A, Solangi AR, Palabiyik IM, Qambrani N, Karimi F, Vasseghian Y, Karimi-Maleh H (2022) Electrochemical quantification of mancozeb through tungsten oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite: a potential method for environmental remediation. Food Chem Toxicol 161:112843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112843
Cheraghi S, Taher MA, Karimi-Maleh H, Karimi F, Shabani-Nooshabadi M, Alizadeh M, Al-Othman A, Erk N, Yegya Raman PK, Karaman C (2022) Novel enzymatic graphene oxide based biosensor for the detection of glutathione in biological body fluids. Chemosphere 287:132187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132187
Avinash B, Ravikumar CR, Kumar MRA, Nagaswarupa HP, Santosh MS, Bhatt AS, Kuznetsov D (2019) Nano CuO: electrochemical sensor for the determination of paracetamol and D-glucose. J Phys Chem Solids 134:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.06.012
Li Y, Cheng C, Yang YP, Dun XJ, Gao J, Jin XJ (2019) A novel electrochemical sensor based on CuO/H-C3N4/rGO nanocomposite for efficient electrochemical sensing nitrite. J Alloys Compd 798:764–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.137
Terrones M, Botello-Méndez AR, Campos-Delgado J, López-Urías F, Vega-Cantú YI, Rodríguez-Macías FJ, Elías AL, Muñoz-Sandoval E, Cano-Márquez AG, Charlier JC, Terrones H (2010) Graphene and graphite nanoribbons: morphology, properties, synthesis, defects and applications. Nano Today 5:351–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2010.06.010
Liu J, Liu Z, Barrow CJ, Yang W (2015) Molecularly engineered graphene surfaces for sensing applications: a review. Anal Chim Acta 859:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.07.031
Swamy NK, Mohana KNS, Hegde MB, Madhusudana AM, Rajitha K, Nayak SR (2021) Fabrication of graphene nanoribbon-based enzyme-free electrochemical sensor for the sensitive and selective analysis of rutin in tablets. J Appl Electrochem 51:1047–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01557-x
Darabi R, Shabani-Nooshabadi M, Khoobi A (2021) A potential strategy for simultaneous determination of deferoxamine and vitamin C using MCR-ALS with nanostructured electrochemical sensor in serum and urine of Thalassemia and diabetic patients. J Electrochem Soc 168:46514. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abf6ed
Karimi-Maleh H, Sheikhshoaie M, Sheikhshoaie I, Ranjbar M, Alizadeh J, Maxakato NW, Abbaspourrad A (2019) A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and a: N -hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode. New J Chem 43:2362–2367. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj05581e
Matsumoto H, Imaizumi S, Konosu Y, Ashizawa M, Minagawa M, Tanioka A, Lu W, Tour JM (2013) Electrospun composite nanofiber yarns containing oriented graphene nanoribbons. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:6225–6231. https://doi.org/10.1021/am401161b
Shang S, Gan L, Yuen CWM, Jiang SX, Luo NM (2015) The synthesis of graphene nanoribbon and its reinforcing effect on poly (vinyl alcohol). Compos Part A 68:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.10.011
Abdel-Aal SK, Beskrovnyi AI, Ionov AM, Mozhchil RN, Abdel-Rahman AS (2021) Structure investigation by neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction of graphene nanocomposite CuO–rGO prepared by low-cost method. Phys Status Solidi Appl Mater Sci 218:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.202100138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS: Investigation, MS-N: Supervision, Validation, AR-V: Supervision, Investigation, RD: Investigation, Roles/Writing – original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahinfard, H., Shabani-Nooshabadi, M., Reisi-Vanani, A. et al. Electrochemical sensor based on CuO/reduced graphene nanoribbons and ionic liquid for simultaneous determination of tramadol, olanzapine and acetaminophen. Carbon Lett. 33, 1433–1444 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00512-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00512-4