Abstract
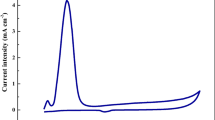
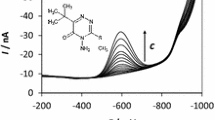
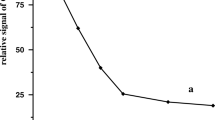
Fast-scan anodic stripping voltammetry (FSASV) was applied to sensitively detect Pb2+ on a mercury film electrode (MFE). The method was involved with a controlled preconcentration by accumulation of Pb2+ on the MFE followed by FSASV measurement. At the scan rate of 500 V/s, a linear relationship between the anodic stripping peak current and the logarithm of Pb2+ concentration in the solution was observed in the range from 0.1 µmol/L to 0.1 pmol/L with a detection limit of 0.1 pmol/L. The proposed method was successfully applied for the determination of Pb2+ in spiked water samples with satisfying recoveries in the range of 98.6 to 104.3%, and the corresponding relative standard deviation ranged from 3.7 to 5.5%. Therefore, FSASV is a sensitive, fast, cost-effective and simple method for the detection of Pb2+ at picomolar level and would be very promising in heavy metal determination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flora, G., Gupta, D., and Tiwari, A., Toxicity of lead: a review with recent updates, Interdiscip. Toxicol., 2012, vol. 5, p. 47.
Nino, W.R.G. and Chaverri, J.P., Protective effect of curcumin against heavy metals-induced liver damage, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2014, vol. 69, p. 182.
Jomova, K. and Valko, M., Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease, Toxicology, 2011, vol. 283, p. 65.
The Council of the European Union, On the quality of water intended for human consumption, Official J. Eur. Commun., 1998, Council Directive 98/83/EC.
Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed., Genewa: World Health Organization, 2011.
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations, United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2009, no. 816-F-09–004.
Goullé, J.P., Saussereau, E., Mahieu, L., and Guerbet, M., Current role of ICP-MS in clinical toxicology and forensic toxicology: a metallic profile, Bioanalysis, 2014, vol. 6, p. 2245.
Burylina, M.Y. and Pupyshevb, A.A., Development of electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry in 2005–2016, J. Anal. Chem., 2017, vol. 72, p. 935.
Smith, J.W. and Saykally, R.J., Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy of liquids and solutions, Chem. Rev, 2017, vol. 117, p. 13909.
Renfrew, A.K., Spectroscopic approaches to tracking metal-based drugs in cells and tissue, Chimia, 2017, vol. 71, p. 112.
Labatzke, T. and Schlemmer, G., Ultratrace determination of mercury in water following EN and EPA standards using atomic fluorescence spectrometry, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2004, vol. 378, p. 1075.
Mandil, A., Idrissi, L., and Amine, A., Stripping voltammetric determination of mercury(II) and lead(II) using screen-printed electrodes modified with gold films, and metal ion preconcentration with thiol-modified magnetic particles, Microchim. Acta, 2010, vol. 170, p. 299.
Companys, E., Galceran, J., Pinheiro, J.P., Puy, J., and Salaun, P., A review on electrochemical methods for trace metal speciation in environmental media, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 3, p. 144.
Bansod, B.K., Kumar, T., Thakur, R., Rana, S., and Singh, I., A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, vol. 94, p. 443.
Lu, Y.Y., Liang, X.Q., Niyungeko, C., Zhou, J.J., Xu, J.M., and Tian, G.M., A review of the identification and detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by voltammetry, Talanta, 2018, vol. 178, p. 324.
Mehta, J., Bhardwaj, S.K., Bhardwaj, N., Paul, A.K., Kumar, P., Kim, K.H., and Deep, A., Progress in the biosensing techniques for trace-level heavy metals, Biotechnol. Adv., 2016, vol. 34, p. 47.
Saidur, M.R., Aziz, A.R.A., and Basirun, W.J., Recent advances in DNA-based electrochemical biosensors for heavy metal ion detection: a review, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, vol. 90, p. 125.
Zarcero, S.M., Quintanilla, D.P., and Sierra, I., A disposable electrochemical sensor based on bifunctional periodic mesoporous organosilica for the determination of lead in drinking waters, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2015, vol. 19, p. 2117.
Raghu, G.K., Sampath, S., and Pandurangappa, M., Chemically functionalized glassy carbon spheres: a new covalent bulk modified composite electrode for the simultaneous determination of lead and cadmium, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2012, vol. 16, p. 1953.
Morales, G.R., Silva, T.R., and Galicia, L., Carbon paste electrodes electrochemically modified with cyclodextrins, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2003, vol. 7, p. 355.
Salmanipour, A. and Taher, M.A., An electrochemical sensor for stripping analysis of Pb(II) based on multiwalled carbon nanotube functionalized with 5-Br-PADAP, J. Solid State Electrochem, 2011, vol. 15, p. 2695.
Simionca, I.M., Arvinte, A., Ardeleanu, R., and Pinteala, M., Siloxane-crown ether polyamide based electrode for electrochemical determination of lead(II) in aqueous solution, Electroanalysis, 2012, vol. 24, p. 1995.
Wang, J., Lu, J., Hocevar, S.B., and Farias, P.A.M., Bismuth-coated carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry, Anal. Chem., 2000, vol. 72, p. 3218.
Wang, T.T., Schlueter, K.T., Riehl, B.L., Johnson, J.M., and Heineman, W.R., Simplified nitrate-reductase-based nitrate detection by a hybrid thin-layer controlled potential coulometry/spectroscopy technique, Anal. Chem., 2013, vol. 85, p. 9486.
Deng, W., Tan, Y., Fang, Z., Xie, Q., Li, Y., Liang, X., and Yao, S., ABTS-multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite/Bi film electrode for sensitive determination of Cd and Pb by differential pulse stripping voltammetry, Electroanalysis, 2009, vol. 21, p. 2477.
Intarakamhang, S., Schuhmann, W., and Schulte, A., Robotic heavy metal anodic stripping voltammetry: ease and efficacy for trace lead and cadmium electroanalysis, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2013, vol. 17, p. 1535.
Pinto, L. and Lemos, S.G., Comparison of different PLS algorithms for simultaneous determination of Cd(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Zn(II) by anodic stripping voltammetry at bismuth film electrode, Electroanalysis, 2014, vol. 26, p. 299.
Sun, Q.W., Wang, J.K., Tang, M.H., Huang, L.M., Zhang, Z.Y., Liu, C., Lu, X.H., Hunter, K.W., and Chen, G.S., A new electrochemical system based on a flow-field shaped solid electrode and 3D-printed thin-layer flow cell: detection of Pb2+ ions by continuous flow accumulation square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry, Anal. Chem., 2017, vol. 89, p. 5024.
Zhao, D.L., Wang, T.T., Han, D., Rusinek, C., Steckl, A.J., and Heineman, W.R., Electrospun carbon nanofiber modified electrodes for stripping voltammetry, Anal. Chem., 2015, vol. 87, p. 9315.
Robinson, J.E., Heineman, W.R., Sagle, L.B., Meyyappan, M., and Koehne, J.E., Carbon nanofiber electrode array for the detection of lead, Electrochem. Commun., 2016, vol. 73, p. 89.
Dali, M., Zinoubi, K., Chrouda, A., Abderrahmane, S., Cherrad, S., and Renault, N.J., A biosensor based on fungal soil biomass for electrochemical detection of lead(II) and cadmium(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2018, vol. 813, p. 9.
Wakabayashi, K.T., Bruno, M.J., Bassb, C.E., and Park, J., Application of fast-scan cyclic voltammetry for the in vivo characterization of optically evoked dopamine in the olfactory tubercle of the rat brain, Analyst, 2016, vol. 141, p. 3746.
Pathirathna, P., Yang, Y., Forzley, K., McElmurry, S.P., and Hashemi, P., Fast-scan deposition-stripping voltammetry at carbon-fiber microelectrodes: real-time, subsecond, mercury free measurements of copper, Anal. Chem., 2012, vol. 84, p. 6298.
Sanford, A.L., Morton, S.W., Whitehouse, K.L., Oara, H.M., Lugo-Morales, L.Z., Roberts, J.G., and Sombers, L.A., Voltammetric detection of hydrogen peroxide at carbon fiber microelectrodes, Anal. Chem., 2010, vol. 82, p. 5205.
Zachek, M.K., Takmakov, P., Moody, B., Wightman, R.M., and McCarty, G.S., Simultaneous decoupled detection of dopamine and oxygen using pyrolyzed carbon microarrays and fast-scan cyclic voltammetry, Anal. Chem., 2009, vol. 81, p. 6258.
Hashemi, P., Dankoski, E.C., Lama, R., Wood, K.M., Takmakov, P., and Wightman, R.M., Brain dopamine and serotonin differ in regulation and its consequences, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2012, vol. 109, p. 11510.
Wu, H.P., Dynamics and performance of fast linear scan anodic stripping voltammetry of Cd, Pb, and Cu using in situ-generated ultrathin mercury films, Anal. Chem., 1996, vol. 68, p. 1639.
Munteanu, G., Munteanu, S., and Wipf, D.O., Rapid determination of zeptomole quantities of Pb2+ with the mercury monolayer carbon fiber electrode, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2009, vol. 632, p. 177.
Yang, Y.Y., Ibrahim, A.A., Stockdill, J.L., and Hashemi, P., A density-controlled scaffolding strategy for covalent functionalization of carbon-fiber microelectrodes, Anal. Methods-UK, 2015, vol. 7, p. 7352.
Yang, Y.Y., Ibrahim, A.A., Hashemi, P., and Stockdill, J.L., Real-time, selective detection of copper(II) using ionophore-grafted carbon-fiber microelectrodes, Anal. Chem., 2016, vol. 88, p. 6962.
Baranski, A.S., Rapid anodic stripping analysis with ultramicroelectrodes, Anal. Chem., 1987, vol. 59, p. 662.
Guo, Z.Y. and Lin, X.Q., Ultrafast cyclic voltammetry at scan rates of up to 3 MV s−1 through a single-opamp circuit with positive feedback compensation of ohmic drop, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2004, vol. 568, p. 45.
Amatore, C., Oleinick, A., and Svir, I., Theoretical analysis of microscopic ohmic drop effects on steadystate and transient voltammetry at the disk microelectrode: a quasi-conformal mapping modeling and simulation, Anal. Chem., 2008, vol. 80, p. 7947.
Wipf, D.O., Ohmic drop compensation in voltammetry: Iterative correction of the applied potential, Anal. Chem., 1996, vol. 68, p. 1871.
Deng, Z.X. and Lin, Q.X., Exponentially expanded grid network approach (EEGNA): an efficient way for the simulation of stiff electrochemical problems, Chinese J. Chem., 2003, vol. 21, p. 1137.
Deng, Z.X. and Lin, Q.X., Digital simulation of fast cyclic voltammogram by integration of the double layer charging current, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1999, vol. 464, p. 215.
Deng, Z.X., Zhao, W., and Lin, X.Q., Simplex optimization-numerical simulation method for FCV curve fitting, Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 1999, vol. 27, p. 383.
Lin, X.Q. and Deng, Z.X., An improved electrochemical numerical simulation for the characterization of the influences of uncompensated solution resistance on cyclic voltammograms, J. Anhui Normal Univ., 1998, vol. 21, p. 333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in Russian in Elektrokhimiya, 2019, Vol. 55, No. 3, pp. 358–365.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Liu, P., Hao, T. et al. Fast-Scan Anodic Stripping Voltammetry for Detection of Pb(II) at Picomolar Level. Russ J Electrochem 55, 222–228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193519020162
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193519020162