Abstract
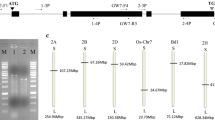
It is reported that GLW7 encoding the transcription factor OsSPL13, positively regulates grain size and shape in rice. We have limited knowledge about its orthologs in wheat. Here, based on the rice OsGLW7 we isolated and identified the TaGLW7 gene in wheat, characterized its nucleotide and protein structures, predicted the cis-elements of its promoter, analyzed its expression patterns. The orthologs in barley (HvGLW7), Brachypodium (BdGLW7), wild emmer (TtGLW7), Aegilops tauschii (AtGLW7) were also used for comparative analysis. As predicated, TaGLW7, HvGLW7, TtGLW7, and AtGLW7 were mapped onto group 2 chromosomes in the respective species. Multiple alignments indicated GLW7 possesses two exons and one intron in the analyzed species. GLW7 contains a conserved domain SBP and two neighboring low complexity regions. GLW7 was highly expressed in spike organs including wheat young spikes, barley inflorescence, and rice anthers. Additionally, biotic stress significantly down-regulated GLW7 in wheat and barley. Significant correlations between the expression patterns of predicted transcription factor ABF2 and TaGLW7 were detected. In conclusion, the conserved structure and expression of GLW7 among the investigated species and the predicted transcription factors significantly related to GLW7 are helpful for further manipulating GLW7 and uncovering its roles in plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hawkesford, M., Araus, J., Park, R., et al., Prospects of doubling global wheat yields, Food Energy Secur., 2013, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 34—48.
Marcussen, T., Sandve, S., Heier, L., et al., Ancient hybridizations among the ancestral genomes of bread wheat, Science, 2014, vol. 345, no. 6194, p.1250092.
Godfray, H.C., Beddington, et al., Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people, Science, 2010, vol. 327, no. 5967, p. 812.
Ma, J., Ding, P., Qin, P., et al., Structure and expression of the TaGW7 in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Plant Growth Regul., 2017, vol. 82, no. 6, pp. 1—11.
Si, L., Chen, J., Huang, X., et al., OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice, Nat. Genet., 2016, vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 447—456.
Ramya, P., Chaubal, A., Kulkarni, K., et al., QTL mapping of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), J. Appl. Genet., 2010, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 421—429.
Xiao, Y., He, S., Yan, J., et al., Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for kernel morphology traits in a non-1BL.1RS × 1BL.1RS wheat cross, Crop Pasture Sci., 2011, vol. 62, no. 8, pp. 625—638.
Okamoto, Yuki, Nguyen, et al., Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling grain size and shape in the D genome of synthetic hexaploid wheat lines, Breed. Sci., 2013, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 423—429.
Cui, F., Zhao, C., Ding, A., et al., Construction of an integrative linkage map and QTL mapping of grain yield-related traits using three related wheat RIL populations, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2014, vol. 127, no. 3, p. 659.
Wu, Q., Chen, Y., Zhou, S., et al., High-density genetic linkage map construction and QTL mapping of grain shape and size in the wheat population Yanda1817 × Beinong6, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 2. e0118144
Su, Z., Jin, S., Lu, Y., et al., Single nucleotide polymorphism tightly linked to a major QTL on chromosome 7A for both kernel length and kernel weight in wheat, Mol. Breed., 2016, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 1—11.
Cheng, R., Kong, Z., Zhang, L., et al., Mapping QTLs controlling kernel dimensions in a wheat inter-varietal RIL mapping population, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2017, 2016, vol. 130, no. 7, pp. 1405—1414.
Choi, H., Mun, J., Kim, D., et al., Estimating genome conservation between crop and model legume species, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004, vol. 101, no. 43, pp.15289—15294.
Vogel, J.P., Garvin, D.F., Mockler, T.C., et al., Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon, Nature, 2010, vol. 463, no. 7283, pp. 763—768.
Mao, H., Sun, S., Yao, J., et al., Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, no. 45, pp. 19579—19584.
Song, X., Huang, W., Shi, M., et al., A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, Nat. Genet., 2007, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 623—630.
Kato, T., Segami, S., Toriyama, M., et al., Detection of QTLs for grain length from large grain rice (Oryza sativa L.), Breed. Sci., 2011, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 269—274.
Shao, G., Wei, X., Chen, M., et al., Allelic variation for a candidate gene for GS7, responsible for grain shape in rice, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2012, vol. 125, no. 6, pp.1303—1312.
Wang, S., Li, S., Liu, Q., et al., The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality, Nat. Genet., 2015, vol. 47, no. 8, p. 949.
Wang, Y., Xiong, G., Hu, J., et al., Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice, Nat. Genet., 2015, vol. 47, no. 8, p. 944.
Guo, L., Ma, L., Jiang, H., et al., Genetic analysis and fine mapping of two genes for grain shape and weight in rice, Bull. Bot., 2009, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 45—51.
Zhao, D., Li, Q., Zhang, C., et al., GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality, Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 1240.
Hu, Z., Lu, S., Wang, M., et al., A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice, Mol. Plant, 2018, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 736—749.
Xia, D., Zhou, H., Liu, R., et al., GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to form extra-long grains in rice, Mol. Plant, 2018, vol. 11, no. 5, p. 754.
Ying, J., Ma, M., Bai, C., et al., TGW3, a major QTL that negatively modulates grain length and weight in rice, Mol. Plant, 2018, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 750—753.
Mayer, K., Rogers, J., Doležel, J., et al., A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome, Science, 2014, vol. 345, no. 6194, p. 1251788.
Dong, L., Wang, F., Liu, T., et al., Natural variation of TaGASR7-A1 affects grain length in common wheat under multiple cultivation conditions, Mol. Plant, 2014, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 937—947.
Zhang, H., Ma, J., Liu, J., et al., Molecular characterization of the TaWTG1 in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Gene, 2018, vol. 678, pp. 23—32.
Mayer, K.F.X., Rogers, J., Doležel, J., et al., A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome, Science, 2014, vol. 345, no. 6194, p. 1251788.
Avni, R., Nave, M., Barad, O., et al., Wild emmer genome architecture and diversity elucidate wheat evolution and domestication, Science, 2017, vol. 357, no. 6346, p. 93.
Schulman, A.H., Hastie, A., Houben, A., et al., A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome, Nature, 2017, vol. 544, no. 7651, pp. 427—433.
Luo, M.C., Gu, Y.Q., Puiu, D., et al., Genome sequence of the progenitor of the wheat D genome Aegilops tauschii, Nature, 2017, vol. 551, no. 7681, p. 498.
Murray, M. and Thompson, F., Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 1980, vol. 8, no. 19, pp. 4321—4325.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., et al., MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2013, vol. 30, no. 12, pp. 2725—2729.
Hu, B., Jin, J., Guo, A., et al., GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server, Bioinformatics, 2014, vol. 31, no. 8, p. 1296.
Letunic, I., Doerks, T. and Bork, P., SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2015, Nucleic Acids Res., 2015, vol. 43, pp. 257—260.
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., et al., PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences, Nucleic Acids Res., 2002, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 325—327.
Xia, L., Zou, D., Sang, J., et al., Rice Expression Database (RED): an integrated RNA-Seq-derived gene expression database for rice, J. Genet. Genomics, 2017, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 235—241.
Borrill, P., Ramirez-Gonzalez, R., and Uauy, C., expVIP: a customisable RNA-seq data analysis and visualisation platform opens up gene expression analysis, Plant Physiol., 2016, vol. 170, no. 4, p. 2172.
Pearce, S., Vazquezgross, H., Herin, S., et al., WheatExp: an RNA-seq expression database for polyploid wheat, BMC Plant Biol., 2015, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 299.
Zadoks, J., Chang, T., and Konzak, F., A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals, Weed Res., 2010, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 415—421.
Zhai, H., Feng, Z., Du, X., et al., A novel allele of TaGW2-A1, is located in a finely mapped QTL that increases grain weight but decreases grain number in wheat (Triticum aestivum, L.), Theor. Appl. Genet., 2018, vol. 131, no. 3, pp. 539—553.
Klein, J., Saedler, H. and Huijser, P., A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA, Mol. Gen. Genet., 1996, vol. 250, no. 1, pp. 7—16.
Rushton, J., Torres, J., Parniske, M., et al., Interaction of elicitor-induced DNA-binding proteins with elicitor response elements in the promoters of parsley PR1 genes, Embo J., 1996, vol. 15, no. 20, pp. 5690—5700.
Messenguy, F. and Dubois, E., Role of MADS box proteins and their cofactors in combinatorial control of gene expression and cell development, Gene, 2003, vol. 316, no. 1, pp. 1—21.
Gao, S., Gao, J., Zhu, X., et al., ABF2, ABF3, and ABF4 promote ABA-mediated chlorophyll degradation and leaf senescence by transcriptional activation of chlorophyll catabolic genes and senescence-associated genes in Arabidopsis, Mol. Plant, 2016, vol. 9, no. 9, pp. 1272—1285.
Cai, C., Guo, W., and Zhang, B., Genome-wide identification and characterization of SPL transcription factor family and their evolution and expression profiling analysis in cotton, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 762.
Lee, S., Kang, J., Park, H., et al., DREB2C interacts with ABF2, a bZIP protein regulating abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and its overexpression affects abscisic acid sensitivity, Plant Physiol., 2010, vol. 153, no. 2, pp. 716—727.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Cristobal Uauy and Dr. Philippa Borrill for providing the wheat transcriptome data. We appreciate the anonymous referees for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C.C., Ma, J., Li, T. et al. Structural Organization and Functional Activity of the Orthologous TaGLW7 Genes in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Russ J Genet 55, 571–579 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795419050168
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795419050168