Abstract
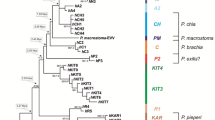
Lizards of the sunwatcher toad-headed agama species complex Phrynocephalus superspecies helioscopus, mostly distributed in Central Asia and Middle East, were examined using analysis of variation at the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase c subunit I gene fragment and fingerprint analysis of nuclear DNA (inter-SINE PCR technique). A total of 86 individual tissue samples from 53 populations, to the full extent representing different parts of the species complex range, were subjected to molecular genetic examination, and surprisingly deep differentiation was revealed. The populations analyzed split into 12 isolated phylogroups, many of which were characterized by a narrow range and genetic isolation. Monophyly of sunwatcher (Ph. helioscopus) and Persian (Ph. persicus) toad-headed agamas was confirmed. However, both of these species probably represent the species complexes. Zoogeography of Central Asiais discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannikov, A.G., Darevsky, I.S., Ishchenko, V.G., et al., Opredelitel’ zemnovodnykh i presmykayushchikhsya fauny SSSR (Key to the Fauna of the Soviet Union: Amphibians and Reptiles), Moscow: Prosveshchenie, 1977.
Sokolovskii, V.V., Comparative Karyological Study of Lizards of the Family Agamidae: I. Chromosome Complements of 8 Species of the Genus Phrynocephalus, Tsitologiya, 1974, vol. 16, no. 7, pp. 920–925.
Manilo, V.V., Golubev, M.L., and Sattorov, T., Karyotype of Phrynocephalus helioscopus saidalievi (Sauria, Agamidae) from Fergana Valley, Vestn. Zool., 1991, no. 2, pp. 79–81.
Manilo, V.V. and Golubev, M.L., Karyotype Information on Some Toad Agamas of the Phrynocephalus guttatus Species Group (Sauria, Agamidae) of the Former USSR, Asiatic Herpetol. Res., 1993, vol. 5, pp. 105–108.
Eremchenko, V.K. and Panfilov, A.M., Some Methodological Questions on Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Toad-Headed Agamas by Example of Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Pallas, 1771) (Sauria: Agamidae), Nauka Novye Technol., 1999, no. 3, pp. 116–122.
Ushakov, B.P., Cytophysiological Analysis of Intraspecies Differentiation of Takyr Toad-Headed Lizards, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1962, vol. 144, no. 5, pp. 1178–1180.
Melville, J., Hale, J., Mantziou, G., et al., Historical Biogeography, Phylogenetic Relationships and Intraspecific Diversity of Agamid Lizards in the Central Asian Deserts of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2009, vol. 53, pp. 99–112.
Melnikov, D.A., On Systematics and Phylogeography of Sun Watcher Toad Agamas Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Pallas, 1771), in Otchetnaya nauchnaya sessiya po itogam rabot 2007 g (Scientific Session Reporting Research Results of 2007), (Proc. Conf.), St. Petersburg, 2008, pp. 32–34.
Melnikov, D.A., Ananjeva, N.B., Rajabizadeh, M., and Milto, K.D., On Systematics and Phylogeography of Sun Watcher Toad Headed Agamas Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Pallas, 1771), De Agamis, (Proc. Int. Symp. Agamis Lizards), Bonn, 2008, pp. 21–22.
Solovyeva, E.N. and Poyarkov, N.A., Specificity of Systematics and Phylogeography of Sun Watcher Toad Headed Agamas (Phrynocephalus helioscopus) (Reptilia: Agamidae) Species Complex, in Tezisy XVI konferentsii studentov, aspirantov i molodykh uchenykh “Lomonosov-2009”, sektsiya Biologiya (Abstracts 16th Conference of Students, Postgraduates, and Young Scientists “Lomonosov-2009”, Section Biology), Moscow, 2009, pp. 10–11.
Solovyeva, E.N. and Poyarkov, N.A., Analysis of Sun Watcher Toad Headed Agamas (Phrynocephalus helioscopus) (Reptilia: Agamidae) Species Complex Distribution Using GIS-Mapping, in Tezisy XVI konferentsii studentov, aspirantov i molodykh uchenykh “Lomonosov-2010”, sektsiya Biologiya (Abstracts 16th Conference of Students, Postgraduates, and Young Scientists “Lomonosov-2010”, Section Biology), Moscow, 2010, p. 142.
Solovyeva, E.N., Poyarkov, N.A., Dunayev, E.A., et al., Taxonomy and Phylogeography of the Sunwatcher Toad-Headed Agama Species Complex (Phrynocephalus helioscopus and Phrynocephalus persicus; Reptilia: Agamidae), in SEH 15th OGM, Programs and Abstracts, Kusadasi: Aydin, 2009, pp. 77–78.
Solovyeva, E.N., Poyarkov, N.A., Dunayev, E.A., and Bannikova, A.A., Phylogeny of the Sunwatcher Agama Species Complex, Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Reptilia, Agamidae) Inferred from Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Markers, Molecular Phylogenetics, (Proc. 2nd Moscow Int. Conf. MolPhy-2), Moscow, 2010, p. 71.
Solovyeva, E.N., Molecular Differentiation and Distribution within the Species Complex of Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Reptilia: Agamidae) De Agamis, (Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Agamis Lizards), St. Petersburg, 2010, pp. 26–27.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 1989.
Ivanova, N.V. and Hebert, P.D.N., An Inexpensive, Automation-Friendly Protocol for Recovering High-Quality DNA, Mol. Ecol. Notes, 2006, vol. 6, pp. 998–1002.
Bannikova, A.A., Bulatova, N.Sh., and Kramerov, D.A., Molecular Variability in the Commom Shrew Sorex araneus L. from European Russia and Siberia Inferred from the Length Polymorphism of DNA Regions Flanked by Short Interspersed Elements (Inter-SINE PCR) and the Relationships between the Moscow and Seliger Chromosome Races, Russ. J. Genet., 2006, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 595–604.
Jurka, J., Zietkiewicz, E., and Labuda, D., Ubiquitous Mammalian-Wide Interspersed Repeats (MIRs) Are Molecular Fossils from the Mesozoic Era, Nucl. Acids Res., 1995, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 170–175.
Hall, T.A., BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT, Nucl. Acids Symp., 1999, ser. 41, pp. 95–98.
Swofford, D.L., Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods): Version 4, Sunderland: Sinauer, 1998.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S., MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2007, vol. 24, pp. 1596–1599.
Nei, M. and Li, W.-H., Mathematical Model for Studying Genetic Variation in Terms of Restriction Endonucleases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1979, vol. 76, pp. 5269–5273.
STATISTICA for Windows (Computer Program Manual), Tulsa: StatSoft, 1996.
Excoffier, L., Smouse, P.E., and Quattro, J.M., Analysis of Molecular Variance Inferred from Metric Distances among DNA Haplotypes: Application to Human Mitochondrial DNA Restriction Data, Genetics, 1992, vol. 131, no. 2, pp. 479–491.
Excoffier, L., Laval, G., and Schneider, S., Arlequin ver. 3.5.1.2: An Integrated Software Package for Population Genetics Data Analysis, http://cmpg.unibe.ch/software/arlequin35.
Tajima, F., Evolutionary Relationship of DNA Sequences in Finite Populations, Genetics, 1983, vol. 105, pp. 437–460.
Rogers, A.R. and Harpending, H., Population Growth Makes Waves in the Distribution of Pairwise Genetic Differences, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1992, vol. 9, pp. 552–569.
Aris-Brosou, S. and Excoffier, L., The Impact of Population Expansion and Mutation Rate Heterogeneity on DNA Sequence Polymorphism, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1996, vol. 13, pp. 494–504.
Ray, N., Currat, M., and Excoffier, L., Intra-Deme Molecular Diversity in Spatially Expanding Populations, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2003, vol. 20, pp. 76–86.
Ryabinina, N.L., Bannikova, A.A., Sheremet’eva, V.A., et al., Analysis of DNA of Higher Primates Using Inter-SINE PCR, Russ. J. Genet., 2008, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 266–272.
Ryabinina, N.L., Bannikova, A.A., Kosuchkin, S.A., et al., Estimation of the Subspecific Level of Differentiation in Caucasian Lizards of the Genus Darevskia (Syn. “Lacerta saxicola Complex”, Lacertidae, Sauria) Using Genome DNA Markers, Russ. J. Herpetol., 2002, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 185–194.
Grechko, V.V., Bannikova, A.A., Kosushkin, S.A., et al., Molecular Genetic Diversification of the Lizard Complex Darevskia raddei (Sauria: Lacertidae): Early Stages of Speciation, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2007, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 839–851.
Buntjer, J.B., DNA Repeats in Vertebrate Genome as Probes in Phylogeny and Species Identification, Utrecht: Univ. Utrecht, 1997, pp. 25–38.
Bannikova, A.A., Matveev, V.A., and Kramerov, D.A., Using Inter-SINE-PCR to Study Mammalian Phylogeny, Russ. J. Genet., 2002, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 704–715.
Pang, J., Wang, Y., Zhong, Y., et al., A Phylogeny of Chinese Species in the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae) Inferred from Mitochondrial DNA Sequences, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2003, vol. 27, pp. 398–409.
Dunayev, E.A., Ivanova, N.V., Poyarkov, N.A., et al., Molecular Perspective on the Evolution and Barcoding of Toad-Headed Agamas (Genus Phrynocephalus; Agamidae) in Middle Asia, 14th European Congress of Herpetology and SEH Ordinary General Meeting (Porto (Portugal), 2007), Porto, 2007, p. 208.
Avise, J.C., Arnold, J., Ball, R.M., et al., Intraspecific Phylogeography: The Mitochondrial DNA Bridge between Population Genetics and Systematics, Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 1987, vol. 18, pp. 489–522.
Avise, J.C., Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard Univ. Press, 2000.
Ananjeva, N.B. and Tuniev, B.S., Historical Biogeography of the Phrynocephalus Species of the USSR, Asiatic Herpetol. Res., 1992, vol. 4, pp. 76–98.
Melnikov, D.A., Ananjeva, N.B., Agasyan, A.L., and Radzhabizade, M., Historical Background and Taxonomic Status of the Persian Toad Head Agama, Phrynocephalus persicus de Filippi, 1863 and Horvath’s Sun Watcher Toad Head Agama Phrynocephalus helioscopus horvathi Mehely, 1894, in Tretii s“ezd gerpetologicheskogo obshchestva im. A.N. Nikol’skogo (The Problems of Herpetology), (Proc. 3rd Congr. of A.N. Nikol’skiy, Herpetological Society, St-Peterburg, 2008), St-Peterburg, 2008, pp. 286–297.
Darevsky, I.S., Turanian Elements in Herpetofauna of Transcaucasia and Conceivable Ingress Routes from Middle Asia, Izv. Akad. Nauk Armyanskoi SSR, 1957, vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 69–77.
Golubev, M.L. and Mezhzherin, S.V., On the Specific Attribution and the Origin of the Persian Toad-Headed Agama Phrynocephalus persicus (Reptilia, Agamidae) Apsheron Population, Byull. Mosk. O-va. Ispytateley Prirody, Otdel Biol., 1999, vol. 104, no. 1, pp. 59–61.
Barabanov, A.V. and Ananjeva, N.A., Catalogue of the Available Scientific Species-Group Names for Lizards of the Genus Phrynocephalus Kaup, 1825 (Reptilia, Sauria, Agamidae), Zootaxa, 2007, vol. 1399, pp. 1–56.
Nikol’skii, A.M., Presmykayushchiesya (Reptilia): Chelonia and Sauria. Fauna Rossii i sopredel’nykh stran (Reptiles (Reptilia): Chelonia and Sauria. Fauna of Russia and Neighboring Countries), Petrograd, 1915.
Dunaev, E.A., Systematics and Paleogeography: Contseptual Synthesis by Example of Phrynocephalus (Superspecies guttatus) (Reptilia: Agamidae), Sb. Tr. Zool. Muzeya Mosk. Gos. Univ., 2009, vol. 50, pp. 275–298.
Sindaco, R. and Jeremcenko, V.K., The Reptiles of the Western Palearctic, Latina: Edizioni Belvedere, 2008.
Fu, J.-z. and Zeng, X.-m., How Many Species Are in the Genus Batrachuperus? A Phylogeographical Analysis of the Stream Salamanders (Family Hynobiidae) from Southwestern China, Mol. Ecol., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 1469–1488.
Guo, X. and Wang, Y., Partitioned Bayesian Analyses, Dispersal-Vicariance Analysis, and the Biogeography of Chinese Toad-Headed Lizards (Agamidae: Phrynocephalus): A Re-Evaluation, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2007, vol, 45, no. 2, pp. 643–662.
Macey, J.R., Schulte, J.A.., Larson, A., et al., Evaluating Trans-Tethys Migration: An Example Using Acrodont Lizard Phylogenetics, Syst. Biol., 2000, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 233–256.
An Zh.-sh., Kutzbach, J.E., Prell, W.L., and Porter, S.C., Evolution of Asian Monsoons and Phased Uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau Since Late Miocene Times, Nature, 2001, vol. 411, pp. 62–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.N. Solovyeva, N.A. Poyarkov, E.A. Dunaev, T.N. Duysebayeva, A.A. Bannikova, 2011, published in Genetika, 2011, Vol. 47, No. 7, pp. 952–967.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solovyeva, E.N., Poyarkov, N.A., Dunaev, E.A. et al. Molecular differentiation and taxonomy of the sunwatcher toad-headed agama species complex Phrynocephalus superspecies helioscopus (Pallas 1771) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Russ J Genet 47, 842–856 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795411070155
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795411070155