Abstract
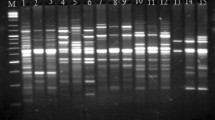
The Giant river catfish, Sperata seenghala (Sykes) is commercially very important fish species of South Asia. Genetic variability between its populations collected from two rivers i.e. river Sutlej and river Beas of Indus river system in India were examined using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Total 38 fish samples were collected from river Sutlej whereas 46 fish samples were collected from river Beas. Total 40 primers were screened, out of these 7 were selected for studying polymorphism which produced a total of 64 RAPD loci in two populations. Percentage polymorphic loci calculated following 95% criterion was 89.06 % for Beas population as compared to 95.31 % for Sutlej population. Moderate level of genetic divergence (genetic distance of 0.0486) between both the populations suggests distinct population substructure of giant river catfish in both the rivers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Froese, R. and Pauly, D., Fish Base: World Wide Web Electronic Publication, www.fishbase.org, version(11/2007).
Jayaram, K.C., The Fresh Water Fishes of the Indian Region, Delhi, India: Narendra publ. House, 2002, pp. 1–13.
Talwar, P.K. and Jhingran, A.G., Inland Fisheries of India and Adjacent Countries, New Delhi, India: Oxford and IBH, 1991, vol. 2.
Tripathi, S.D., Present Status of Breeding and Culture of Catfishes in South Asia, Aquatic Living Res., 1996, vol. 9, pp. 219–228.
Carvalho, G.R., Evolutionary Aspects of Fish Distribution: Genetic Variability and Adaptation, J. Fish Biol., 1993, vol. 43, pp. 53–73.
Schierwater, B., Ender, A., Schwenk, K., et al., Molecular Ecology and Evolution: Approaches and Applications, Schierwater, B., Streit, B., Wagner, G.P., and Desalle, R., Eds., Basel: Birkhouser, 1994, pp. 495–508.
Pogson, G.H., Mesa, K.A., and Boutillier, R.G., Genetic Population Structure and Gene Flow in the Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua a Comparison of Allozyme and Nuclear RFLP Loci, Genetics, 1995, vol. 139, pp. 375–385.
Okazaki, T., Jeon, S., Watanabe, M., and Kitagava, T., Genetic Relationships of Japanese and Korean Bagrid Catfishes from Mitochondrial DNA Analysis, Zool. Sci., 1999, vol. 16, pp. 363–373.
Appleyard, S.A., Grewe, P.M., Innes, B.H., and Ward, R.D., Population Structure of Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacores) in the Western Pacific Ocean Inferred From Microsatellite Loci, Mar. Biol., 2001, vol. 139, pp. 383–393.
Beacham, T.D., McIntosh, B., and MacConnachie, C., Microsatellite Identification of Individual Sockeye Salmon in Barkley Sound British Columbia, J. Fish Biol., 2002, vol. 61, pp. 1021–1032.
Williams, J.K.G., Kubelik, A.R., Livak, K.J., et al., DNA Polymorphism Amplified by Arbitrary Primers Are Useful as Genetic Markers, Nucl. Acids Res., 1990, vol. 18, pp. 6531–6535.
Lehmann, D., Hettwer, H., and Taraschewski, H., RAPD-PCR Investigations of Systematic Relationships among Four Species of Eels (Teleostei: Anguillidae), Particularly Anguilla anguilla and A. rostrata, Mar. Biol., 2000, vol. 137, pp. 195–204.
Bagley, M.J., Anderson, S.L., and May, B., Choice of Methodology for Assessing Genetic Impacts of Environmental Stressors: Polymorphism and Reproducibility of RAPD and AFLP Fingerprints, Ecotoxicology, 2001, vol. 10, pp. 239–244.
Almeida, F.S., Sodre, L.M.K., and Contel, E.P.B., Population Structure Analysis of Pimelodus maculates (Pisces, Siluriformes) from the Tiete and Paranapanema Rivers (Brazil), Genet. Mol. Biol., 2003, vol. 26, pp. 301–305.
Sandoval-Castellanos, E., Uribe-Alcocer, M., Diaz-Jaimes, P., Population Genetic Structure of Jumbo Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Evaluated by RAPD Analysis, Fish. Res., 2007, vol. 83, pp. 113–118.
Chong, L.K., Tan, S.G., Yusoff, K., and Siraj, S.S., Identification and Characterization of Malaysian River Catfish, Mystus nemurus (C. and V.): RAPD and AFLP Analysis, Biochem. Genet., 2000, vol. 38, pp. 63–76.
Yoon, J.M. and Kim, G.W., Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Two Different Populations of Cultured Korean Catfish Silurus asotus, J. Biosci., 2001, vol. 26, pp. 641–647.
Muneer, P.M.A., Gopalakrishnaa, A., Basheer, V.S., and Lakra, W.S., Identification of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Markers in Endemic Yellow Catfish, Horabagrus brachysoma (Gunther 1864), Asian Fish. Sci., 2008, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 293–304.
Ruzzante, D.E., Taggart, C.T., Cook, D., and Goddard, S., Genetic Differentiation between Inshore and Offshore Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) off Newfoundland: Microsatellite DNA Variation and Antifreeze Level, Canad. J. Fish. Aquatic Sci., 1996, vol. 53, pp. 634–645.
Miller, M.P., Tools for Population Genetic Analysis (TFPGA) 1.3: A Windows Program for the Analysis of Allozyme and Molecular Population Genetic Data, Computer Software Distributed by Authors, www.marksgeneticcoftware.net/tfpga.htm, 1997.
Liu, Z., Jarret, R.L., Duncan, R.R., and Kresovich, S., Genetic Relationships and Variation among Ecotypes of Seashore Paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum) Determined by Random Polymorphic DNA Markers, Genome, 1994, vol. 37, pp. 1011–1017.
Nagarajan, M., Haniffa, M.A., Gopalakrishnan, A., et al., Genetic Variability of Channa punctatus Populations Using Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA, Aquaculture Res., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 1151–1155.
Smith, T.B. and SkÚlason, S., Evolutionary Significance of Resource Polymorphism in Fishes, Amphibians, and Birds, Ann. Rev. Ecol. Systematics, 1996, vol. 27, pp. 111–133.
Dieckmann, U. and Doebeli, M., On the Origin of Species by Sympatric Speciation, Nature, 1999, vol. 400, pp. 354–357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A. Saini, A. Dua, V. Mohindra, 2010, published in Genetika, 2010, Vol. 46, No. 8, pp. 1102–1107.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, A., Dua, A. & Mohindra, V. Genetic variability analysis of Giant river cattish (Sperata seenghala) populations from Indus river system by RAPD-PCR. Russ J Genet 46, 982–987 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410080107
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795410080107