Abstract
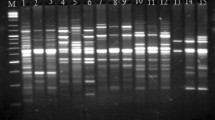
Genetic similarity and diversity of cultured catfishSilurus asotus populations collected from two areas in western Korea were examined using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-polymerase chain reaction (RAPD-PCR). Out of 20 random primers tested, 5 produced 1344 RAPD bands ranging from 8.2 to 13.6 polymorphic bands per primer. The polymorphic bands in these populations ranged from 56.4% to 59.6%. Polymorphic bands per lane within populations ranged from 4.9% to 5.3%. The similarity within the Kunsan population varied from 0.39 to 0.82 with a mean (± SD) of 0.56 ± 0.08. The level of bandsharing values was 0.59 ± 007 within the catfish population from Yesan. The genetic similarity in cultured catfish populations may have been caused because individuals from two populations were reared in the same environmental conditions or by inbreeding during several generations. However, in view of bandsharing values, polymorphic bands and also the specific major bands that were inter-population-specific, significant genetic differentiation between these populations were present even if bandsharing (BS) values were somewhat numerically different. Therefore, the number of RAPD polymorphisms identified in this study may be sufficient to permit estimating genetic similarity and diversity. However, in future, additional populations, sampling sites and individuals will be necessary to make up for these weak points.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BS:
-
bandsharing
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RAPD:
-
randomly amplified polymorphic DNA
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
References
Bartish I V, Garkava L P, Rumpunen K and Nybom H 2000 Phylogenetic relationships and differentiation among and within populations ofChaenomeles Lindl. (Rosaceae) estimated with RAPDs and isozymes;Theor. Appl. Genet. 101 554–561
Begg G A, Keenan C P and Sellin M J 1998 Genetic variation and stock structure of school mackerel and spotted mackerel in northern Australian waters;J. Fish Biol. 53 543–559
Bernardi G and Talley D 2000 Genetic evidence for limited dispersal in the coastal California killifish,Fundulus parvipinnis;J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 255 187–199
Brutovská R, Cellárová E and Schubert I 2000 Cytogenetic characterization of threeHypericum species byin situ hybridization;Theor. Appl. Genet. 101 46–50
Cagigas M E, Vazquez E, Blanco G and Sánchez J A 1999 Combined assessment of genetic variability in populations of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) based on allozymes, microsatellites and RAPD markers;Mar. Biotechnol. 1 286–296
Fischer M, Husi R, Prati D, Peintinger M, Kleunen M V and Schmid B 2000 RAPD variation among and within small and large populations of the rare clonal plantRanunculus reptans (Ranunculaceae);Am. J. Bot. 87 1128–1137
Garcia-Mas J, Oliver M, Gomez-Paniagua H and Vicente M C 2000 Comparing AFLP, RAPD and RFLP markers for measuring genetic diversity in melon;Theor. Appl. Genet. 101 860–864
Hallerman E M and Beckmann J S 1988 DNA-level polymorphism as a tool in fisheries science;Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 45 1075–1087
Jeffreys A J and Morton D B 1987 DNA fingerprints of dogs and cats;Anim. Genet. 18 1–15
Jensen S R 2000 Chemical relationships ofPolypremum procumbens, Tetrachondra hamiltonii andPeltanthera floribunda;Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 28 45–51
Klinbunga S, Ampayup P, Tassanakajon A, Jarayabhand P and Yoosukh W 2000 Development of species-specific markers of the tropical oyster (Crassostrea belcheri) in Thailand;Mar. Biotechnol. 2 476–484
Lehmann D, Hettwer H and Taraschewski H 2000 RAPD-PCR investigations of systematic relationships among four species of eels (Teleostei: Anguillidae), particularly Anguilla anguilla and A. rostrata;Mar. Biol. 137 195–204
Levin I, Crittenden L B and Dodgson J B 1993 Genetic map the chicken Z-chromosome using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers;Genomics 16 224–230
Li X, Li K, Fan B, Gong Y, Zhao S, Peng Z and Liu B 2000 The genetic diversity of seven pig breeds in China, estimated by means of microsatellites;Asian-Aus. J. Anim. Sci. 13 1193–1195
Liu Z, Li P, Argue B J and Dunham R A 1998 Inheritance RAPD markers in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus), blue catfish (I. furcatus) and their F1, F2 and backcross hybrids;Anim. Genet. 29 58–62
Menke M, Fuchs J and Schubert I 1998 A comparison sequence resolution on plant chromosomes: PRINS versus FISH;Theor. Appl. Genet. 97 1314–1320
Mohd-Azmi M, Ali A S and Kheng W K 2000 DNA fingerprinting of red jungle fowl, village chicken and broilers;Asian-Aus. J. Anim. Sci. 13 1040–1043
Smith P J, Benson P G and McVeagh S M 1997 A comparison of three genetic methods used for stock discrimination orange roughy, Hoplostethus atlanticus: allozymes, mitochondrial DNA, and random amplified polymorphic DNA;Fish. Bull. 95 800–811
Taggart J B and Ferguson A 1990 Minisatellite DNA fingerprints of salmonid fishes;Anim. Genet. 21 377–389
Vierling R A, Xiang Z, Joshi C P, Gilbert M L and Nguyen H 1994 Genetic diversity among elite Sorghum lines revealed by restriction fragment length polymorphisms and random amplified polymorphic DNAs;Theor. Appl. Genet. 87 816–820
Welsh J, Petersen C and McClelland M 1991 Polymorphisms generated by arbitrarily primed PCR in the mouse: application to strain identification and genetic mapping;Nucleic Acids Res. 19 303–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, JM., Kim, GW. Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-polymerase chain reaction analysis of two different populations of cultured Korean catfishSilurus asotus . J. Biosci. 26, 641–647 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704762
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704762