Abstract
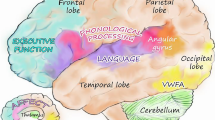
The aim of the present study was to investigate the reading mechanisms in adults (27 subjects; mean age, 19.5 ± 0.8 [SD] years) with different levels of written text comprehension using fMRI. The main objective was to analyze the basic brain mechanisms of verbal stimuli perception with and without semantic component during reading discrimination tasks. The BOLD signal changes during WORD and PSEUDOWORD reading comparing to GAZE FIXATION state were estimated using both analysis of whole brain activation and ROIs (structures connected with the brain system providing reading) in two groups of subjects, “good” and “poor” readers. It was revealed that activations were higher in “poor” readers in lingual gyrus, SMG, STG compared to “good” readers during PSEUDOWORD reading. It was supposed, that the strategies of words and pseudowords recognition differed in two groups of readers: “good” readers identified words or pseudowords already at the stage of visual analysis of “word” structure and demonstrated attempts to decode pseudowords (i.e., language lexical zones were not activated); “poor” readers, apparently, tried to read pseudowords using the same strategy as for the words reading referring to the lexicon, and after failure identified pseudowords as meaningless concepts. In that case, activations of both lexical “language” zones and visual word form area (VWFA) were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Storch, S.A. and Whitehurst, G.J., Oral language and code-related precursors to reading: evidence from a longitudinal structural model, Dev. Psychol., 2002, vol. 38, no. 6, p. 934.
Oakhill, J.V., Cain, K., and Bryant, P.E., The dissociation of word reading and text comprehension: evidence from component skills, Lang. Cognit. Process., 2003, vol. 18, no. 4, p. 443.
Ouellette, G.P., What’s meaning got to do with it: The role of vocabulary in word reading and reading comprehension, J. Educ. Psychol., 2006, vol. 98, no. 3, p. 554.
Bierwisch, M., How on-line is language processing? in The Process of Language Understanding, d’Arcais, G.B.F. and Jarvella, R.J., Eds., New York: Wiley, 1983, pp. 113–168.
Kornev, A.N., Narusheniya chteniya i pis’ma u detei (Disorder of Reading and Writing in Children), St. Petersburg: Karo, 2003.
Egorov, T.G., Psikhologiya ovladeniya navykom chteniya (Psychology of Reading Skilling), St. Petersburg: Karo, 2006.
Price, C.J., A review and synthesis of the first 20 years of PET and fMRI studies of heard speech, spoken language and reading, Neuroimage, 2012, vol. 62, no. 2, p. 816.
Luo, C.R., Johnson, C.R., and Callo, C.R., Automatic activation of phonological information in reading evidence from the semantic relatedness decision task, Mem. Cognit., 1998, vol. 26, p. 833.
Daneman, M. and Reingold, E., What eye fixations tell us about phonological recoding during reading, Can. J. Exp. Psychol., 1993, vol. 47, p. 153.
Forster, K.I. and Chambers, S., Lexical access and naming time, J. Verbal Learn. Verbal Behav., 1973, vol. 12, p. 627.
Marshall, J.C. and Newcombe, F., Patterns of paralexia: a psycholinguistic approach, J. Psycholing. Res., 1973, vol. 2, p. 175.
Coltheart, M., Modeling reading: the dual-route approach, in The Science of Reading: A Handbook, Snowling, M.J. and Hulme, Ch., Eds., Oxford: Blackwell, 2005, p. 6.
Levelt, W.J.M., Models of word production, Trends Cognit. Sci., 1999, vol. 3, p. 223.
Landi, N., Frost, S.J., Menc, W.E., et al., Neurobiological bases of reading comprehension: Insights from neuroimaging studies of word-level and text-level processing in skilled and impaired readers, Reading Writing Quart., 2013, vol. 29, no. 2, p. 145.
Black, S.E. and Behrmann, M., Localization in alexia, in Localization and Neuroimaging in Neuropsychology, Kertesz, A., Ed., New York: Academic, 1994, p. 331.
Fiebach, C.J., Friederici, A.D., Mueller, K., et al., fMRI Evidence for dual routes to the mental lexicon in visual word recognition, J. Cognit. Neurosci., 2002, vol. 14, p. 11.
Simos, P.G., Fletcher, J.M., Bergman, E., et al., Dyslexia- specific brain activation profile becomes normal following successful remedial training, Neurology, 2002, vol. 58, p. 1203.
Poldrack, R.A., Wagner, A.D., Prull, M.W., et al., Functional specialization for semantic and phonological processing in the left inferior prefrontal cortex, Neuroimage, 1999, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 15.
Paulesu, E., Goldacre, B., Scifo, P., et al., Functional heterogeneity of left inferior frontal cortex as revealed by fMRI, Neuroreport, 1997, vol. 8, p. 2011.
Roskies, A.L., Fiez, J.A., Balota, D.A., et al., Taskdependent modulation of regions in the left inferior frontal cortex during semantic processing, J. Cognit. Neurosci., 2001, vol. 13, p. 829.
Fiez, J.A. and Petersen, S.E., Neuroimaging studies of word reading, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1998, vol. 95, no. 3, p. 914.
Katz, L., Lee, C.H., Tabor, W., et al., Effects of printed word repetition in lexical decision and naming on behavior and brain Activation, Neuropsychologia, 2005, vol. 43, no. 14, p. 2068.
Shaywitz, B.A., Shaywitz, S.E., Pugh, K.R., et al., Disruption of posterior brain systems for reading in children with developmental dyslexia, Biol. Psychol., 2002, vol. 52, p. 101.
Turkeltaub, P.E., Gareau, L., Flowers, D.L., et al., Development of neural mechanisms for reading, Nat. Neurosci., 2003, vol. 6, no. 7, p. 767.
Pugh, K.R., Mencl, W.E., Jenner, A.R., et al., Functional neuroimaging studies of reading and reading disability (developmental dyslexia), Ment. Retard. Dev. Disab. Res. Rev., 2000, vol. 6, p. 207.
Sarkari, S., Simos, P.G., Fletcher, J.M., et al., The emergence and treatment of developmental reading disability: contributions of functional brain imaging, Semin. Pediatr. Neurol., 2002, vol. 9, p. 227.
Oldfield, R.C., The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory, Neuropsychologia, 1971, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 97.
Kornev, A.N. and Oganov, S.R., Variability of strategies for processing written text: analysis of eye movements in 2–4 courses students reading descriptive texts, in Aitreking v psikhologicheskoi nauke i praktike (Eye Tracking in Psychological Science and Practice), Barabanshchikov, V.A., Ed., Moscow: Kogito-Tsentr, 2015, p. 279.
Friston, K., Ashburner, J., Kiebel, S., et al., Statistical Parametric Mapping: The Analysis of Functional Brain Images, London: Academic, 2007, p. 656.
Jobard, G., Crivello, F., and Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Evaluation of the dual route theory of reading: a metaanalysis of 35 neuroimaging studies, Neuroimage, 2003, vol. 20, no. 2, p. 693.
Richardson, F.M., Seghier, M.L., Leff, A.P., et al., Multiple routes from occipital to temporal cortices during reading, J. Neurosci., 2011, vol. 31, p. 8239.
Choi, W, Desai, R.H., and Henderson, J.M., The neural substrates of natural reading: a comparison of normal and nonword text using eyetracking and fMRI, Front. Hum. Neurosci., 2014, vol. 8, p. 1024.
Mechelli, A., Gorno-Tempini, M.L., and Price, C.J., Neuroimaging studies of word and pseudoword reading: consistencies, inconsistencies, and limitations, J. Cognit. Neurosci., 2003, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 260.
Price, C.J., Noppeney, U., Phillips, J., and Devlin, J.T., How is the fusiform gyrus related to category- specificity? Cognit. Neuropsychol., 2003, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 561.
Levy, J., Pernet, C., Treserras, S., et al., Piecemeal recruitment of left-lateralized brain areas during reading: a spatio-functional account, Neuroimage, 2008, vol. 43, p. 581.
Levy, J., Pernet, C., Treserras, S., et al., Testing for the dual-route cascade-reading model in the brain: an fMRI effective connectivity account of an efficient reading style, PLoS One, 2009, vol. 4, no. 8, p. e6675.
Price, C.J., The anatomy of language: contributions from functional neuroimaging, J. Anat., 2000, vol. 197, no. 3, p. 335.
Cohen, L., Dehaene, S., Naccache, L., et al., The visual word form area: spatial and temporal characterization of an initial stage of reading in normal subjects and posterior split-brain patients, Brain, 2000, vol. 123, no. 2, p. 291.
Cohen, L., Lehéricy, S., Chochon, F., et al., Language- specific tuning of visual cortex? Functional properties of the Visual Word Form Area, Brain, 2002, vol. 125, no. 5, p. 1054.
Price, C.J., Wise, R.J., and Frackowiak, R.S., Demonstrating the implicit processing of visually presented words and pseudowords, Cereb. Cortex, 1996, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 62.
Damasio, A.R. and Geschwind, N., The neural basis of language, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 1984, vol. 7, p. 127.
Cohen, L., Martinaud, O., Lemer, C., et al., Visual word recognition in the left and right hemispheres: anatomical and functional correlates of peripheral alexias, Cereb. Cortex, 2003, vol. 12, p. 1313.
Cohen, L., Henry, C., Dehaene, S., et al., The pathophysiology of letter-by-letter reading, Neuropsychologia, 2004, vol. 42, no. 13, p. 1768.
Starrfelt, R., Habekost, T., and Leff, A.P., Too little, too late: reduced visual span and speed characterize pure alexia, Cereb. Cortex, 2009, vol. 19, no. 12, p. 2880.
Taylor, J.S., Rastle, K., and Davis, M.H., Can cognitive models explain brain activation during word and pseudoword reading? A meta-analysis of 36 neuroimaging studies, Psychol. Bull., 2013, vol. 139, no. 4, p. 766.
Cutting, L.E., Clements-Stephens, A., Pugh, K.R., et al., Not all reading disabilities are dyslexia: distinct neurobiology of specific comprehension deficits, Brain Connect., 2013, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 199.
Benjamin, C.F. and Gaab, N., What’s the story? The tale of reading fluency told at speed, Hum. Brain Mapp., 2012, vol. 33, no. 11, p. 2572.
Gabrieli, J.D., Poldrack, R.A., and Desmond, J.E., The role of left prefrontal cortex in language and memory, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1998, vol. 95, p. 906.
Minamoto, T., Yaoi, K., Osaka, M., and Osaka, N., The rostral prefrontal cortex underlies individual differences in working memory capacity: An approach from the hierarchical model of the cognitive control, Cortex, 2015, vol. 71, p. 277.
Daniel, T.A., Katz, J.S., and Robinson, J.L., Delayed match-to-sample in working memory: A BrainMap meta-analysis, Biol. Psychol., 2016, vol. 120, p. 10.
Abdullaev, Y.G. and Bechtereva, N.P., Neuronal correlate of the higher-order semantic code in human prefrontal cortex in language tasks, Int. J. Psychophysiol., 1993, vol. 14, p. 167.
Buckner, R.L., Raichle, M.E., and Petersen, S.E., Dissociation of human prefrontal cortical areas across different speech production tasks and gender groups, J. Neurophysiol., 1995, vol. 74, no. 5, p. 2163.
Borowsky, R., Cummine, J., Owen, W.J., et al., FMRI of ventral and dorsal processing streams in basic reading processes: insular sensitivity to phonology, Brain Topogr., 2006, vol. 18, no. 4, p. 233.
Carreiras, M., Mechelli, A., and Price, C.J., Effect of word and syllable frequency on activation during lexical decision and reading aloud, Hum. Brain Mapp., 2006, vol. 27, no. 12, p. 963.
Pugh, K.R., Frost, S.J., Sandak, R., et al., Effects of stimulus difficulty and repetition on printed word identification: an fMRI comparison of nonimpaired and reading-disabled adolescent cohorts, J. Cognit. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 20, no. 7, p. 1146.
Seghier, M.L., The angular gyrus: multiple functions and multiple subdivisions, Neuroscientist, 2013, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 43.
Bechtereva, N.P., Shemyakina, N.V., Starchenko, M.G., et al., Error detection mechanisms of the brain: background and prospects, Int. J. Psychophysiol., 2005, vol. 58, nos. 2–3, p. 227.
Khani, A. and Rainer, G., Neural and neurochemical basis of reinforcement-guided decision making, J. Neurophysiol., 2016, vol. 116, no. 2, p. 724.
Petersen, S.E., Fox, P.T., Snyder, A.Z., et al., Activation of extrastriate and frontal cortical areas by visual words and word-like stimuli, Science, 1990, vol. 249, p. 1041.
Hagoort, P., Indefrey, P., Brown, C., et al., The neural circuitry involved in the reading of German words and pseudowords: a PET study, J. Cognit. Neurosci., 1999, vol. 11, p. 383.
Wise, R., Chollet, F., Hadar, U., et al., Distribution of cortical neural networks involved in word comprehension and word retrieval, Brain, 1991, vol. 114, no. 4, p. 1803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.V. Shemyakina, V.A. Novikov, Zh.V. Nagornova, E.I. Galperina, A.V. Pozdnjakov, A.N. Kornev, 2018, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2018, Vol. 44, No. 2, pp. 41–51.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shemyakina, N.V., Novikov, V.A., Nagornova, Z.V. et al. Mechanisms of Reading in Persons with Different Levels of Written Text Comprehension. Hum Physiol 44, 152–160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119718020159
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119718020159