Abstract
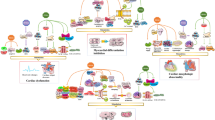
It is known that long-term space flights lead to dysregulation of the cardiovascular system, and the endothelium is the most important functional element of such dysregulation. In order to find the signs of endothelial dysfunction in cosmonauts who have been in long-term space flights, we collected urine samples from 21 cosmonauts before the flight and on the first and seventh days after landing. The urine samples were investigated by chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis. Proteins were identified using the MaxQuant software and the SwissProt database. The software package Perseus was used for semi-quantitative analysis. The reconstruction of associative molecular networks was performed using the ANDSystem software. We identified 200 different proteins in urine samples of 21 Russian cosmonauts. The ANDSystem software made it possible to determine seven processes related to endothelium functioning. These processes had direct relations to 17 urine proteins, which were functionally associated with the endothelium. At the same time, eight proteins (such as serotransferrin, prostate-specific antigen, fibrinogen gamma chain, UFO tyrosine kinase receptor, aminopeptidase N, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, osteopontin, and syndecan-4) were significantly changed (p < 0.01) at different points of the recovery period (the first and seventh days). Thus, we performed the first study of the urine protein composition in cosmonauts for the evaluation of signs of endothelial dysfunction after space flight using proteomics methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogomolov, V.V. and Samarin, G.I., Improvement of the medical support system for the health and work efficiency of the crews of the International Space Station, Kosmonavtika Raketostr., 2007, no. 4 (49), p. 48.
Kotovskaya, A.R. and Fomina, G.A., Characteristics of adaptation and maladaptation of human cardiovascular system under space flight conditions, Hum. Physiol., 2010, vol. 36, no. 2, p. 190.
Rudimov, E.G., Secretory and adhesive properties of human endothelial cells in modeling effects of microgravity in vitro, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow, 2015, p. 27.
Sofronova, S.I., Tarasova, O.S., Gaynullina, D., et al., Spaceflight on the Bion-M1 biosatellite alters cerebral artery vasomotor and mechanical properties in mice, J. Appl. Physiol., 2015, vol. 118, no. 7, p. 830.
Delp, M.D., Charvat, J.M., Limoli, C.L., et al., Apollo lunar astronauts show higher cardiovascular disease mortality: possible deep space radiation effects on the vascular endothelium, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 28, no. 6, p. 29901. doi 10.1038/srep29901
Kashirina, D., Pastushkova, L., Custaud, M.A., et al., Effect of 21-day head down bed rest on urine proteins related to endothelium: correlations with changes in carbohydrate metabolism, Acta Astronaut., 2017, vol. 137, p. 122.
Pretnar-Oblak, J., Cerebral endothelial function determined by cerebrovascular reactivity to L-arginine, Biomed. Res. Int., 2014, vol. 2014, p. 601515. doi 10.1155/2014/601515
Romanov, Yu.A., Kabaeva, N.V., and Buravkova, L.B., Gravitation sensitivity of human endothelium, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2000, vol. 34, no. 4, p. 23.
Michiels, C., Endothelial cell functions, J. Cell Physiol., 2003, vol. 196, no. 3, p. 430.
Gamboa, A., Abraham, R., Diedrich, A., et al., Role of adenosine and nitric oxide on the mechanisms of action of dipyridamole, Stroke, 2005, vol. 36, no. 10, p. 2170.
Verigo, Ya.I., Demko, I.V., Petrova, M.M., et al., The von Willebrand factor and its role in endothelial dysfunction in ischemic heart disease, Sib. Med. Obozr., 2014, no. 5 (89), p. 23.
Boerma, M., Nelson, G.A., Sridharan, V., et al., Space radiation and cardiovascular disease risk, World J. Cardiol., 2015, vol. 7, no. 12, p. 882. doi 10.4330/ wjc.v7.i12.882
Mischak, H., Thongboonkerd, V., Schanstra, J.P., and Vlahou, A., Renal and urinary proteomics, Proteomics Clin. Appl., 2011, vol. 5, nos. 5–6, p. 211. doi 10.1002/prca.201190031
Metzger, J., Negm, A.A., Plentz, R.R., et al., Urine proteomic analysis differentiates cholangiocarcinoma from primary sclerosing cholangitis and other benign biliary disorders, Gut, 2013, vol. 62, no. 1, p. 122. doi 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302047
Valeeva, O.A., Pastushkova, L.Kh., Pakharukova, N.A., Dobrokhotov, I.V., and Larina, I.M., Variability of urine proteome in healthy humans during a 105-day isolation in a pressurized compartment, Hum. Physiol., 2011, vol. 37, no. 3, p. 351.
Ivanisenko, V.A., Saik, O.V., Ivanisenko, N.V., et al., ANDSystem: an associative network discovery system for automated literature mining in the field of biology, BMC Syst. Biol., 2015, vol. 9, no. 2, p. S2. doi 10.1186/1752-0509.9
Berendeeva, T.A., The analysis of the level of cytokines in a healthy person during space flight factors and their ground modeling, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Med.) Dissertation, Moscow, 2010, p. 22.
Morukov, B.V., Rykova, M.P., Antropova, E.N., Berendeeva, T.A., Ponomaryov, S.A., and Larina, I.M., Parameters of the innate and adaptive immunity in cosmonauts after long-term space flight on board the international space station, Hum. Physiol., 2010, vol. 36, no. 3, p. 264.
Gustafsson, A., Martuszewska, D., Johansson, M., et al., Differential expression of Axl and Gas6 in renal cell carcinoma reflecting tumor advancement and survival, Clin Cancer Res., 2009, vol. 15, no. 14, p. 4742. doi 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2514
Cook-Mills, J.M., Johnson, J.D., Deem, T.L., et al., Calcium mobilization and Rac1 activation are required for VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) stimulation of NADPH oxidase activity, Biochem J., 2004, vol. 378, no. 2, p. 539.
Gershovich, P.M., Gershovich, Yu.G., and Buravkova, L.B., Cytoskeleton structure and adhesion properties of human stromal precursors under conditions of simulated microgravity, Cell Tissue Biol., 2009, vol. 3, p. 423.
Romanov, Y.A., Buravkova, L.B., Rikova, M.P., et al., Expression of cell adhesion molecules and lymphocyte- endothelium interaction under simulated hypogravity in vitro, J. Gravitational Physiol., 2001, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 5.
Buravkova, L., Romanov, Y., Rykova, M., et al., Cellto- cell interactions in changed gravity: Ground-based and flight experiments, Acta Astronaut., 2005, vol. 57, p. 67.
Muid, S., Froemming, G.R.A., Manaf, A., et al., Changes in protein and gene expression of adhesion molecules and cytokines of endothelial cells immediately following short-term spaceflight travel, Gravitational Space Biol., 2010, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 1.
Liu, H., Wang, Z.C., Yue, Y., et al., Simulated microgravity induces an inflammatory response in the common carotid artery of rats, Can J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2014, vol. 92, no. 8, p. 661.
Gasanov, A.G. and Bershova, T.V., The role of changes of the extracellular matrix in the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases, Biomed. Khim., 2009, vol. 55, no. 2, p. 155.
Du, P., Suhaeri, M., Subbiah, R., et al., Elasticity modulation of fibroblast-derived matrix for endothelial cell vascular morphogenesis and mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, Tissue Eng., Part A, 2016, vol. 22, nos. 5–6, p. 415. doi 10.1089/ten.TEA.2015.0503
Tamura, A., Shingai, M., Aso, N., et al., Osteopontin is released from the heart into the coronary circulation in patients with a previous anterior wall myocardial infarction, Circ. J., 2003, vol. 67, no. 9, p. 742.
Satoh, M., Nakamura, M., Akatsu, T., et al., Myocardial osteopontin expression is associated with collagen fibrillogenesis in human dilated cardiomyopathy, Eur. J. Heart Failure, 2005, vol. 7, no. 5, p. 755.
Teng, Y.H.-F., Aquino, R.S., and Park, P.W., Molecular functions of syndecan-1 in disease, Matrix Biol., 2012, vol. 31, p. 3.
Jakobsson, L., Kreuger, J., Holmborn, K., et al., Heparan sulfate in trans potentiates VEGFR-mediated angiogenesis, Dev. Cell, 2006, vol. 10, p. 625.
Multhaupt, H.A., Yoneda, A., Whiteford, J.R., et al., Syndecan signaling: when, where and why? J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2009, vol. 60, suppl 4, p. 31.
Vuong, T.T., Reine, T.M., Sudworth, A., et al., Syndecan- 4 is a major syndecan in primary human endothelial cells in vitro, modulated by inflammatory stimuli and involved in wound healing, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 2015, vol. 63, no. 4, p. 280.
Kumar, S., Sharma, P., Bansal, A., et al., Hypobaric hypoxia-mediated protein expression in plasma of susceptible & tolerant rats, Indian J. Med. Res., 2014, vol. 140, p. 756.
Orlov, Yu.P., Lukach, V.N., Dolgikh, V.T., et al., Pathogenetic significance of the failured iron metabolism in the development of microcirculatory disorders during reperfusion: experimental study, Sib. Med. Zh., 2012, no. 5, p. 71.
Ivanova, S.M., The blood system during space flight conditions and after, in Orbital’naya stantsiya Mir. Kosmicheskaya biologiya i meditsina. Tom 2. Mediko-biologicheskie eksperimenty (Orbital Station Mir. Space Biology and Medicine, Vol. 2: Medical-Biological Experiments), Moscow: Anikom, 2002, p. 159.
Kapitonova, M.Yu., Kuznetsov, S.L., Froemming, G.R.A., Muid, S., Nor-Ashikin, M.N.K., Otman, S., Shahir, A.R.M., and Nawawi, H., Effects of space mission factors on the morphology and function of endothelial cells, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2013, vol. 154, no. 6, p. 796.
Carlsson, S.I., Bertilaccio, M.T., Ballabio, E., et al., Endothelial stress by gravitational unloading: effects on cell growth and cytoskeletal organization, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2003, vol. 1642, no. 3, p. 173.
Lewis, M.L., Reynolds, J.L., Cubano, L.A., et al., Spaceflight alters microtubules and increases apoptosis in human lymphocytes (Jurkat), FASEB J., 1998, vol. 12, no. 11, p. 1007.
Yarovaya, G.A. and Neshkova, A.E., Past and present research on the kallikrein-kinin system (on the 90th anniversary of the discovery of the system), Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem., 2015, vol. 41, no. 3, p. 245.
Pul’bere, S.A., Diseases of the prostate, differential diagnosis, and prognosis of the outcome, Doctoral (Med.) Dissertation, Moscow, 2015.
Dorofeev, S.D., Kudryavtsev, Yu.V., and Kudryavtseva, L.V., Immunohistochemical aspects of chronic abacterial prostatitis, Eff. Farmakoter., Urol. Nefrol., 2014, no. 2, p. 26.
Alexandrova, S.A. and Pinaev, G.P., Actin cytoskeleton reorganization in bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells at the initial step of transendothelial migration, Biophysics, 2014, vol. 59, no. 5, p. 741.
Subramani, J., Ghosh, M., Rahman, M.M., et al., Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD13 regulates inflammatory cell–cell adhesion and monocyte trafficking, J. Immunol., 2013, vol. 191, no. 7, p. 3905.
Ghosh, M., Jaganathan, S., Rahman, M.M., and Shapiro, L.H., CD13 restricts TLR4 endocytic signal transduction in inflammation, J. Immunol., 2015, vol. 194, no. 9, p. 4466.
Mitrofanov, K.Yu., Zhelankin, A.V., and Sazonova, M.A., Association of nuclear genome mutations with the development of myocardial infarction, Ateroskler. Dislipidemii, 2013, no. 2 (11), p. 56.
Paton, L.N., Mocatta, T.J., Richards, A.M., and Winterbourn, C.C., Increased thrombin-induced polymerization of fibrinogen associated with high protein carbonyl levels in plasma from patients post myocardial infarction, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2010, vol. 48, no. 2, p. 223. doi 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.10.044
Korotkova, N.V., Activity of cathepsins l and n in diseases of the veins of the lower extremities, Cand. Sci. (Med.) Dissertation, Moscow, 2015.
Korchagina, A.A., Shein, S.A., Gurina, O.I., and Chekhonin, V.P., VEGFRS in neoplastic angiogenesis and prospects for therapy of brain tumors, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 2013, vol. 68, no. 11, p. 104.
Arthur, J.S. and Ley, S.C., Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2013, vol. 3, no. 9, p. 679.
Kuzichkin, D.S., Morukov, B.V., Markin, A.A., Juravlyova, O.A., Zabolotskaya, I.V., and Vostrikova, L.V., Hemostasis system indices after short-term space flights and during 7-day “dry” immersion experiment, Hum. Physiol., 2010, vol. 36, no. 4, p. 478.
Gonzales, P.A., Pisitkun, T., Hoffert, J.D., et al., Large-scale proteomics and phosphoproteomics of urinary exosomes, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2009, vol. 20, no. 2, p. 363. doi 10.1681/ASN.2008040406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.Kh. Pastushkova, D.N. Kashirina, A.S. Kononikhin, A.G. Brzhozovsky, V.A. Ivanisenko, E.S. Tiys, A.M. Novosyolova, M.-A. Custaud, E.N. Nikolaev, I.M. Larina, 2018, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2018, Vol. 44, No. 1, pp. 72–81.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastushkova, L.K., Kashirina, D.N., Kononikhin, A.S. et al. The Effect of Long-term Space Flights on Human Urine Proteins Functionally Related to Endothelium. Hum Physiol 44, 60–67 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119718010139
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119718010139