Abstract
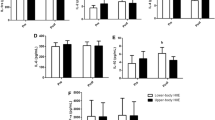
Inflammatory activity, heart rate variability (HRV), and biochemical and functional indices were assessed in young ski racers during the preparation, competition, and recovery periods of an annual training cycle. During the preparation period, autohemodilution (decreased red blood cell count (RBC) and hematocrit (Ht) levels) and a decrease in the systemic inflammatory activity (C-reactive protein) occurred, without significant differences in the HRV or serum protein and lipid profile. During the competition period, the systemic inflammatory activity increased by 50% (p = 0.047), eliminating differences from the control group, and the HRV indices (SDNN, HF, TP, and IT) decreased (p ≤ 0.013), indicating an increase in the sympathetic effects on the HRV. During the recovery period, hematological indices (Ht and RBC), inflammatory activity, and fibrinogen levels decreased, and the parasympathetic effects on the heart increased. These findings allowed us to conclude that mental and physical activation led to a moderate increase in the systemic inflammatory activity and a shift in the sympathovagal balance towards increased sympathetic activity, providing a nonspecific contribution to the physiological regulation of biochemical (lipoproteins and immunoglobulins) and hematological indices in the athletes. However, similar changes in many biochemical and hematological indices in both groups during the year indicated the important role of a common, probably seasonal, factor in the regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Platonov, V.N., Sistema podgotovki sportsmenov v olimpiiskom sporte. Obshchaya teoriya i ee prakticheskie prilozheniya. Uchebnik trenera vysshei kvalifikatsii (Athletic Training System in Olympic Sports. General Theory and Its Practical Applications. High Performance Coach Textbook), Kiev: Olimp. Lit., 2004.
Clauss, A., Measure of Fibrinogen, Acta Haematol., 1957, vol. 17, p. 237.
Imai, K., Sato, H., Hori, M., et al., Vagally Mediated Heart Rate Recovery after Exercise is Accelerated in Athletes but Blunted in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 1994, vol. 24, p. 1529.
Goldberger, J., Sympathovagal Balance: How Should We Measure It, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 1999, vol. 276, p. H1273.
Baevskii, R.M., Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Space Medicine, Fiziol. Chel., 2002, vol. 28, no. 2, p. 70 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), 2002, vol. 28, no. 2, p. 202].
Eckberg, D.L., Sympathovagal Balance. A Critical Appraisal, Circulation, 1997, vol. 96, p. 3224.
Biem, J., Koehncke, N., and Classen, D., Out of the Cold: Management of Hypothermia and Frostbite, Can. Med. Assoc. J., 2003, vol. 168, p. 305.
Goldberger, J.J., Le, F. K., Lahiri, M., and Kannankeril, P.J., Assessment of Parasympathetic Reactivation after Exercise, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 2006, vol. 290, p. H2446.
Goldsmith, R.L., Bigger, J.J., Steinman, R.C., et al., Comparison of 24-h Parasympathetic Activity in Endurance-Trained and Untrained Young Men, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 1992, vol. 20, p. 552.
Tulppo, M.P., Hautala, A.J., Mäkikallio, T.H., et al., Effects of Aerobic Training on Heart Rate Dynamics in Sedentary Subjects, J. Appl. Physiol., 2003, vol. 95, p. 364.
Iellamo, F., Legramante, J.M., Pigozzi, F., et al., Conversion from Vagal to Sympathetic Predominance with Strenuous Training in High Performance World Class Athletes, Circulation, 2002, vol. 105, p. 2719.
Kinugasa, H. and Hirayanagi, K., Effects of Skin Surface Cooling and Heating on Autonomic Nervous Activity and Baroreflex Sensitivity in Humans, Exp. Physiol., 1999, vol. 84, p. 369.
Kristal-Boneh, E., Froom, P., Harari, G., et al., Summer-Winter Differences in 24 h Variability of Heart Rate, J. Cardiovasc. Risk, 2000, vol. 7, p. 141.
Pagani, M., Montano, N., Porta, A., et al., Relationship between Spectral Components of Cardiovascular Variabilities and Direct Measures of Muscle Sympathetic Nerve Activity in Humans, Circulation, 1997, vol. 95, p. 1441.
Petersen, A.M. and Pedersen, B.K., The Role of IL-6 in Mediating the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Exercise, J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2006, vol. 57, p. 43.
Fatouros, I.G., Destouni, A., Margonis, K., et al., Cell-Free Plasma DNA as a Novel Marker of Aseptic Inflammation Severity Related to Exercise Overtraining, Clin. Chem., 2006, vol. 52, p. 1820.
Smith, L.L., Tissue Trauma: the Underlying Cause of Overtraining Syndrome, J. Strength. Cond. Res., 2004, vol. 18, p. 184.
Malm, C., Sjödin, T.L., Sjöberg, B., et al., Leukocytes, Cytokines, Growth factors, and Hormones in Human Skeletal Muscle and Blood after Uphill or Downhill Running, J. Physiol., 2004, vol. 556, p. 983.
Elenkov, I.J., Wilder, R.L., Chrousos, G.P., et al., The Sympathetic Nerve–An Integrative Interface between two Supersystems: the Brain and the Immune System, Pharmacol. Rev., 2000, vol. 52, p. 595.
Aso, Y., Wakabayashi, S., Nakano, T., et al., High Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Concentrations Are Associated with Realative Cardiac Sympathetic Overactivity during the Early Morning Period in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Metabolic Syndrome, Metabolism, 2006, vol. 55, p. 1014.
Hemingway, H. and Walker, B.R., Adrenocortical, Autonomic, and Inflammatory Causes of the Metabolic Syndrome: Nested Case-Control Study, Circulation, 2002, vol. 106, p. 2659.
Klausen, T., The Feed-Back Regulation of Erythropoietin Production in Healthy Humans, Dan. Med. Bull., 1998, vol. 45, p. 345.
Nemeth, E., Rivera, S., Gabayan, V., Keller, C., IL-6 Mediates Hypoferremia of Inflammation by Inducing the Synthesis of the Iron Regulatory Hormone Hepcidin, J. Clin. Invest., 2004, vol. 113, p. 1251.
Fonseca, R.B., Mohr, A.M., Wang, L., et al., Adrenergic Modulation of Erythropoiesis Following Severe Injury is Mediated through Bone Marrow Stroma, Surg. Infect., 2004, vol. 5, p. 385.
Convertino, V.A., Greenleaf, J.E., and Bernauer, E.M., Role of Thermal and Exercise Factors in the Mechanism of Hypervolemia, J. Appl. Physiol., 1980, vol. 48, p. 657.
Khovidhunkit, W., Kim, M.S., Memon, R.A., et al., Effects of Infection and Inflammation on Lipids and Lipoprotein Metabolism: Mechanisms and Consequences to the Host, J. Lipid Res., 2004, vol. 45, p. 1169.
Roitt, A., Brostoff, J., and Male, D., Immunology, Translated from English, Moscow: Mir, 2000.
McKune, A.J., Smith, L.L., and Semple, S.J., Influence on Ultra-Endurance Exercise on Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Subclasses, Br. J. Sports Med., 2005, vol. 39, p. 665.
McKune, A.J., Smith, L.L., and Semple, S.J., Immunoglobulin Responses to a Repeated Bout of Downhill Running, Br. J. Sports Med., 2006, vol. 40, p. 844.
Smith, T.P., Kennedy, S.L., Fleshner, M., Influence of Age and Physical Activity on the Primary in vivo Antibody and T Cell-Mediated Responses in Men, J. Appl. Physiol., 2004, vol. 97, p. 491.
Pedersen, V.K. and Hoffman-Goetz, L., Exercise and the Immune System: Regulation, Integration, and Adaptation, Physiol. Rev., 2000, vol. 80, p. 1055.
Mackiewicz, A., Speroff, T., ganapathi, M.K., et al., Effects of Cytokine Combinations on Acute Phase Protein Production in Two Human Hepatoma Cell Lines, J. Immunol., 1991, vol. 146, p. 3032.
Zubairov, D.M., Molekulyarnye osnovy svertyvaniya krovi i tromboobrazovaniya (Molecular Bases for Blood Coagulation and Thrombus formation), Kazan: Fan, 2000.
Vasse, M., Paysant, I., Soria, J., et al., Down-Regulation of Fibrinogen Biosynthesis by IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13, Br. J. Haematol., 1996, vol. 93, p. 955.
Brun, J.F. and Varlet-Marie, E., Unresolved Issues in Exercise Hemorheology, Proc. Euro. Summ. School on Biorheology, Varna, 2003, p. 30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Kylosov, A.A. Mel’nikov, A.Yu. Mal’tsev, A.D. Vikulov, O.L. Borisova, 2009, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2009, Vol. 35, No. 4, pp. 82–96.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kylosov, A.A., Mel’nikov, A.A., Mal’tsev, A.Y. et al. Changes in inflammatory activity, heart rate variability, and biochemical indices in young athletes during the annual training cycle. Hum Physiol 35, 465–478 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119709040124
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119709040124