Abstract
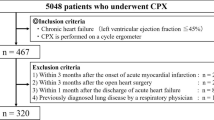
The relationship between the carbon dioxide ventilatory equivalent and hemodynamic parameters during exercise was studied in healthy subjects and coronary heart disease (CHD) patients. Gas exchange, ventilatory control, and central hemodynamics during graded exercise were analyzed in 85 subjects, including 32 healthy subjects and 53 CHD patients. Twenty-seven CHD patients had coronary insufficiency but not heart failure and had a left ventricle ejection fraction of ≥50%; 26 patients had chronic heart failure and an ejection fraction of <40%. A high carbon dioxide ventilatory equivalent and its disturbed response (a decrease below 20%) with an increase in physical load, which reflects an imbalance of ventilatory control with decreased parameters of maximum oxygen consumption and hemodynamics, allows the ventilatory equivalent to be used as a marker for stratifying CHD patients with chronic heart failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohn, J.N., Johnson, G.R., Shebetai, R., et al., Ejection Fraction, Peak Exercise Consumption, Cardiothoracic Ratio, Ventricular Arrhythmias, and Plasma Norepinephrine as Determinants of Prognosis in Heart failure, Circulation, 1993, vol. 87, suppl. VI, p. 5.
Vanhees, L., Fagard, R., Thijs, L., et al., Prognostic Significance of Peak Exercise Capacity in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 1994, vol. 23, p. 358.
Wilson, J.R. and Mancini, D.M., Factors Contributing to the Exercise Limitation of Heart Failure, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 1993, vol. 22, suppl. A, p. 93.
Wilson, J.R., Mancini, D.M., and Dukman, W.B., Exertional Fatigue Due to Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure, Circulation, 1993, vol. 87, p. 470.
Massic, B.M., Conway, M., Yonge, R., et al., Skeletal Muscle Metabolism in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure: Relation to Clinical Severity and Blood Flow, Circulation, 1987, vol. 76, p. 1009.
Sullivan, M.J., Green, H.J., and Cobb, F.R., Skeletal Muscle Biochemistry and Histology in Ambulatory Patients with Long-Term Heart Failure, Circulation, 1990, vol. 81, p. 518.
Gitt, A.T., Wasserman, K., Kilkowski, C., et al., Exercise Anaerobic Threshold and Ventilatory Efficiency Identify Heart Failure Patients for High Risk of Early Death, Circulation, 2002, vol. 106, p. 3079.
Tabet, J.Y., Thabut, G., Hainaut, P., et al., Critical Appraisal of the Prognostic Value of the VE/VCO2 Slope in Chronic Heart Rate Failure, Eur. J. Heart Fail., 2003, vol. 2, p. 67.
Banning, A.D., Lewis, N.P., Northridge, D.B., et al., Perfusion/Ventilation Mismatch during Exercise in Chronic Heart Failure: An Investigation of Circulatory Determinants, Br. Heart J., 1995, vol. 74, p. 27.
Milani, R.V., Mehra, M.R., Reddy, T.K., et al., Ventilation/Carbon Dioxide Production Ratio in Early Exercise Predicts Poor Functional Capacity in Congestive Heart Failure, Heart, 1996, vol. 76, no. 5, p. 393.
The Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association, Boston, 1994.
Cohen-Solal, A., Zannad, F., Kayanakis, J.G., et al., Multicenter Study of Determination of Peak Oxygen Uptake and Ventilatory Threshold during Bicycle Exercise in Chronic Heart Failure, Eur. Heart J., 1991, vol. 12, p. 1055.
Ponikowski, P., Francis, D.F., Piepoli, M., et al., Enhanced Ventilatory Response to Exercise in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Preserved Exercise Tolerance: Marker of Abnormal Cardiorespiratory Reflex Control and Predictor of Poor Prognosis, Circulation, 2001, vol. 103, p. 967.
Zemaityte, D., Varoneckas, G., Ozeraitis, E., et al., Evaluation of Automatic Heart Rate Control and Hemodynamic Responses to Different Tests Using Computerized Rhythmography and Impedance Cardiography, in Proc. IX Int. Conference on Electrical Bio-Impedance, Gersing, E. and Schaefer, M., Eds., Heidelberg, 1995, p. 192.
Andreas, S., Morguet, A.J., Werner, G.S., and Kreuzer, H., Ventilatory Response to Exercise and to Carbon Dioxide in Patients with Heart Failure, Eur. Heart J., 1996, vol. 17, p. 750.
Brozhaitene, J., Jakumaite, V., and Žemaityte, D., Relationships of Oxygen Consumption, Hemodynamics, and Heart Rate Variability with the Functional Class of Coronary Artery Disease Patients, Hum. Physiol., 2004, vol. 30, no. 6, p. 662.
Wasserman, K., Zhang, Y.Y., Gitt, A., et al., Lung Function and Exercise Gas Exchange in Chronic Heart Failure, Circulation, 1997, vol. 96, p. 2221.
Andreas, S., Morguet, A.J., Werner, G.S., and Kreuzer, H., Ventilatory Response to Exercise and to Carbon Dioxide in Patients with Heart Failure, Eur. Heart J., 1996, vol. 17, p. 750.
Kleber, F.X., Vietzke, G., Wernecke, K.D., et al., Impairment of Ventilatory Efficiency in Heart Failure: Prognostic Impact, Circulation, 2000, vol. 101, p. 2803.
Davey, P., Meyer, T., Coats, A., et al., Ventilation in Chronic Heart Failure: Effects of Physical Training, Br. Heart J., 1992, vol. 71, p. 473.
Johnson, R.L., Gas Exchange Efficiency in Congestive Heart Failure, Circulation, 2001, vol. 103, p. 916.
Ehrman, J., Keteyian, S., Fedel, F., et al., Ventilatory Threshold after Exercise Training in Orthotopic Heart Transplant Patients, J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil., 1992, vol. 12, p. 126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © J. Brozhaitene, G. Žiliukas, 2006, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2006, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 24–28.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brozhaitene, J., Žiliukas, G. Characteristics of ventilatory control during exercise in coronary heart disease patients. Hum Physiol 32, 394–397 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119706040037
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119706040037