Abstract
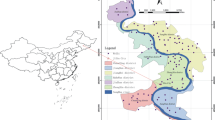
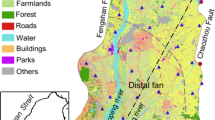
Groundwater is one of most important available water resources in Chengdu Plain. It is sole drinking water in some rural areas, while the concentration of some areas could not meet the drinking water standards. Thus, it is significant to investigate the relationship between the concentration of Cr(VI) and land use types. The concentration of Cr(VI) in 102 groundwater sampling wells were obtained, and the spatial distribution of hexavalent chromium in groundwater was interpolated by Kriging interpolation method. Then, the land use types were analyzed by ENVI. Contributing area surrogate models were employed to investigate the influence of land use type on the concentration of Cr(VI). The following results were obtained, (1) the hexavalent chromium concentrated in crop land, flower-plant/forest land and greenhouse land. (2) The “contributing area surrogate” for the hexavalent chromium pollution region is circular area with a radius of 1750 m. And the pollutant of hexavalent chromium in region groundwater has a good correlation with greenhouse and crop land.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
An, Y.J., Kampbell, D.H., and Jeong, SW., Impact of geochemical stressors on shallow groundwater quality, Sci. Total Environ., 2005, vol. 348, pp. 257–266.
Barron, O.V., Barr, A.D., and Donn, M.J., Evolution of nutrient export under urban development in areas affected by shallow water table, Sci. Total Environ., 2013, vol. 443, pp. 491–504.
Bawa, R. and Dwivedi, P., Impact of land cover on groundwater quality in the Upper Floridan Aquifer in Florida, United States, Environ. Pollut., 2019, vol. 252, pp. 1828–1840.
Bhattacharya, M., Shriwastav, A., Bhole, S., Silori, R., Mansfeldt, T., Kretzschmar, R. and Singh, A., Processes governing chromium contamination of groundwater and soil from a chromium waste source, ACS Earth Space Chem., 2020, vol. 4, pp. 35–49.
Brink, C.V.D., Zaadnoordijk, W.J., Grift, B.V.D., Ruiter, P.C., and Griffioen, J., Using a groundwater quality negotiation support system to change land-use management near a drinking-water abstraction in the Netherlands, J Hydrol., 2008, vol. 350, pp. 339–356.
Chouhan, S. and Flora, S., Arsenic and fluoride: two major ground water pollutants, Indian J. Exp. Biol., 2010, vol. 48, pp. 666–678.
Dong, D., Zhao, X., Hua, X., Liu, X.Y., and Gao M., Investigation of the potential mobility of Pb, Cd and Cr(VI) from moderately contaminated farmland soil to groundwater in Northeast, China, J. Hazard Mater., 2009, vol.162, pp. 1261–1268.
Fatemi, A., Strategies and policies for water quality management of Gharasou River, Kermanshah, Iran: a review, Environ. Earth Sci., 2020, vol. 79, p. 254.
Foster, S. and Chilton, P.J., Groundwater: the processes and global significance of aquifer degradation, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci., 2003, vol. 358, pp. 1957–1972.
Foster, S., Is UN Sustainable Development Goal 15 relevant to governing the intimate land-use/groundwater linkage? Hydrogeol. J., 2018, vol. 26, pp. 979–982.
Giordano, M., Global Groundwater? Issues and Solutions, Annu Rev. Environ. Resour., 2010, vol. 34, pp. 153–178.
Janniche, G.S., Spliid, H., and Albrechtsen, H.J., Microbial Community-Level Physiological Profiles (CLPP) and herbicide mineralization potential in groundwater affected by agricultural land use, J. Contam. Hydrol., 2012, vol. 140, pp. 45–55.
Jia, Z., Bian, J.M., and Wang, Y., Impacts of urban land use on the spatial distribution of groundwater pollution, Harbin City, Northeast China, J. Contam. Hydrol., 2018, vol. 215, pp. 29–38.
Johnson, T.D. and Belitz, K., Assigning land use to supply wells for the statistical characterization of regional groundwater quality: Correlating urban land use and VOC occurrence, J. Hydrol., 2009, vol. 370, pp. 100–108.
Kellner, E. and Hubbart, J., Agricultural and forested land use impacts on floodplain shallow groundwater temperature regime, Hydrol. Process., 2016, vol. 30, pp. 625–636.
Koh, E.H., Lee, S.H., Kaown., Dugin., Moon., Sun, H., Eunhee, and Kang-Kun., Impacts of land use change and groundwater management on long-term nitrate-nitrogen and chloride trends in groundwater of Jeju Island, Korea, Environ. Earth Sci., 2017, vol. 76, p. 176.
Lee, S.M., Min, K.D., and Woo, N.C., Statistical models for the assessment of nitrate contamination in urban groundwater using GIS, Environ. Geol., 2003, vol. 44, pp. 210–221.
Li, Y., Bi, Y.H., Mi, W.J., Xie, S.L., and Li, J., Land-use change caused by anthropogenic activities increase fluoride and arsenic pollution in groundwater and human health risk, J. Hazard Mater., 2021, vol. 406, p. 124337.
Liu, X.C., Zhang, M.D., Zhou, W.Y., Zhang, J., and Deng, S.H., A path analysis for chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen discharge from industrial sewage in China, Water Resour., 2020, vol. 47, pp. 1012–1019.
Lotfy, S.M. and Mostafa, A.Z., Phytoremediation of contaminated soil with cobalt and chromium, J. Geochem. Explor., 2014, vol. 144, pp. 367–373.
Mukherjee, I. and Singh, U., Groundwater fluoride contamination, probable release, and containment mechanisms: a review on Indian context, Environ. Geochem. Health., 2018, vol. 40, pp. 2259–2301.
Nasrabadi, T. and Maedeh, P.A., Groundwater quality degradation of urban areas (case study: Tehran city, Iran), Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 11, pp. 293–302.
Pal, M. and Foody, GM., Evaluation of SVM., RVM and SMLR for accurate image classification with limited ground data, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens., 2012, vol. 5, pp. 1344–1355.
Pesquer, L., Cortes, A. and Pons, X., Parallel ordinary kriging interpolation incorporating automatic variogram fitting, Comput. Geosci., 2011, vol. 37, pp. 464–473.
Petropoulos, G.P., Kontoes, C.C. and Keramitsoglou, I., Land cover mapping with emphasis to burnt area delineation using co-orbital ALI and Landsat TM imagery, Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf., 2012, vol. 18, pp. 344–355.
Reyes, V., Gutieerez, M., Haro, B.N., Lopez, D.N., and Alarcon-Herrera, M.T., Groundwater quality impacted by land-use/land cover change in a semiarid region of Mexico, Groundw. Sustain Dev., 2017, vol. 5, pp. 160–167.
Sari, M. and Petri, E., Lakes in the Finnish Eurowaternet: status and trends, Sci. Total Environ., 2003, vol. 310, pp. 37–45.
Schroeder, T.A., Cohen, W.B., Song, C.H., Canty, M.J. and Yang, Z.Q., Radiometric correction of multi-temporal Landsat data for characterization of early successional forest patterns in western Oregon, Remote Sens Environ., 2006, vol. 103, pp. 16–26.
Singh S.K., Srivastava P.K., and Pandey A.C., Integrated assessment of groundwater influenced by a Confluence River system: concurrence with remote sensing and geochemical modeling, Water Resour Manag., 2013, vol. 27, pp. 4291–4313.
Worrall, F. and Kolpin, D., Aquifer vulnerability to pesticide contamination- combining soil, land use and aquifer properties with molecular descriptors. J. Hydrol., 2004, vol. 293, pp. 191–204.
Yan, B.Z., Xiao, C.L., Liang, X.J., and Fang, Z., Impacts of urban land use on nitrate contamination in groundwater, Jilin City, Northeast China, Arab. J. Geosci., 2016, vol. 9, p. 105.
Yang, W.L., Zhou, W.Y., Wan, W.X., Gou, S.Z., Zhang, J., Deng, S.H., Shen, F., Wang, Y.J., Yang, G., and Luo, L., Assessing soil environmental capacity on different land uses in a suburban area of Chengdu, China, Environ. Pro Engin., 2019, vol. 45, pp. 55–67.
Zhang, J., Zhang, J.M., Xing, B., Liu, G.D. and Liang, Yue., Study on the effect of municipal solid landfills on groundwater by combining the models of variable leakage rate, leachate concentration, and contaminant solute transport, J. Environ. Manage., 2021, vol. 292, p. 112815.
Zhang, J., Zhang, L Y, Qin, X, Yao, X.P., Deng, S.H., Shen, F., Li, Y.W., Yang, Gang, and Song, C., An empirical method to investigate the spatial and temporal distribution of annual average groundwater recharge intensity-a case study in Grand River, Michigan, USA. Water Resour Manag., 2016, vol. 30, pp. 195–206.
Funding
This study was supported by the Projects of talent introduction fund in Chong Qing Jiao Tong University (2 020 020 036) and Sichuan University, State Key Laboratory of Hydraulics and Mountain River Engineering (SKHL2012). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, Z., Long-Chuang, L., Jing-Gang, Z. et al. Using CAS Models to Investigate the Influence of Land Use on the Concentration of Cr(VI) in Groundwater, Case Study in the Central Region of Chengdu Plain, China. Water Resour 50, 960–968 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807822601455
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807822601455