Abstract
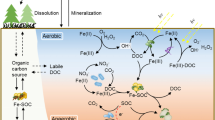
A relationship is established between within-year variations in Fetot/Ptot ratio in pore solution and the concentration of organic P compounds in solid phase. The passage of the FeOOH-P system in the silts of the Mozhaisk Reservoir from the aerobic conditions to aerobic is generally accompanied by dissolution of FeOOH and desorption of phosphates. The change from anaerobic conditions to aerobic during the spring and autumn seasons exhibits hysteresis in oxidation of Fe compounds in silts, such that variations in Fe/P ratio in the solid phase of silt do not agree with those in the pore solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arinushkina, E.V., Rukovodstvo po khimicheskomu analizu pochv (Guide on Chemical Analysis of Soils), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1961.
Brekhovskikh, V.F., Kazmiruk, V.D., and Vishnevskaya, G.N., Biota v protsessakh massoperenosa v vodnykh ob“ektakh (Biota in Mass Transport Processes in Water Bodies), Moscow: Nauka, 2008.
Bugaenko, A.L. and Kuznetsov, D.A., Nuclear-Magnetic Control of Energy Carriers in Living Organisms, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2008, vol. 78, no. 6, pp. 579–583.
Vinogradova N.N., Suspended Matter and Bottom Sediments, Kompleksnye issledovaniya vodokhranilishch (Multidisciplinary Studies of Reservoirs), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1979, iss. II, pp. 231–261.
Martynova M.V., Samplers for Studying Bottom Water, Voprosy gidrologicheskogo priborostroeniya (Issues of Hydrological Instrumentation), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1977.
Martynova, M.V., Azot i fosfor v donnykh otlozheniyakh ozer i vodokhranilishch (Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Bottom Sediments of Lakes and Reservoirs), Moscow: Nauka, 1984.
Martynova, M.V., Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Phosphorus Compounds in the Bottom Water of a Small Reservoir, Vodn. Resur., 2004, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 315–324 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 315–324].
Martynova, M.V., Impact of the Chemical Composition of Bottom Sediments on Internal Phosphorus Load, Vodn. Resur., 2008, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 358–363 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 339–345].
Martynova, M.V., Fe(II)/Fe(III) Ratio in Silt Pore Solution in the Mozhaisk Reservoir, Vodn. Resur., 2009, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 705–710 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 683–688].
Martynova, M.V., and Kozlova, E.I., Phosphorus in Deposits of Two High-Trophicity Lakes, Vodn. Resur., 1987, no. 2, pp. 103–112.
Martynova, M.V., and Shmideberg, N.A. On Methods for Determining Different Phosphorus Forms in Bottom Sediments, Gidrokhim. Mater., 1983, vol. 85, pp. 49–55.
Modelirovanie rezhima fosfora v dolinnom vodokhranilishche (Modeling Phosphorus Regime in a Valley Reservoir), Edel’shtein, K.K., Ed., Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1995.
Pivovarov, S.A., Physicochemical Modeling of Behavior of Heavy Metals (Cu, Zn, Cd) in Natural Waters: Complexes in Solution, Adsorpion, Ionic Exchange, Transport Phenomena, Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation, Moscow: IGEM, 2003.
Savenko, A.V., Phosphorus within the Mixing Zone of Sea and River Waters, Vodn. Resur., 1998, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 330–334 [Water Resour. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 293–301].
Sapozhnikov, V.V., and Nosova, V.V., Methodology and Some Preliminary Results of Determining Different Phosphorys Forms in Mozhaisk Reservoir Water, Gidrokhimicheskie issledovaniya poverkhnostnykh i podzemnykh vod raiona Mozhaiskogo vodokhranilishcha (Hydrochemical Studies of Surface and Subsurface Water in Mozhaisk Reservoir Area), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1977, pp. 23–34.
Unifitsirovannye metody analiza vod (Unified Methods of Water Analysis), Moscow: Khimiya, 1973.
Fatchikhina, O.E., Dynamics of Phosphorus Concentration in Black Lake, Gidrokhim. mater., 1948, vol. 15, pp. 180–204.
Kheifets, D.M., Methods for Determining Phosphorus in Soil, Agrokhimicheskie metody issledovaniya pochv (Agrochemical Methods for Soil Studies), Moscow: Sel’khozgiz, 1965.
Baccini, P., Phosphate Interactions at the Sediment-Water Interface, Chemical Processes in Lakes, Stumm. W., Ed., New York: Wiley, 1985, pp. 189–205.
Borovek, Ja., Chemical Composition and Phosphorus Fractionation of Sediments in the Bohemian Forest Lakes, Silva Gabreta, 2000, vol. 4, pp. 179–184.
Buffle, J., De Vitre, R.R., Perret, D., and Leppard, G.G., Physico-Chemical Characteristics of a Colloidal Iron Phosphate Species Formed at the Oxic-Anoxic Interface of a Eutrophic Lake, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 1989, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 399–408.
Edzwald, J.K., Toensing, D.C., and Leung, M., Phosphate adsorption reactions with clay minerals, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1976, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 485–490.
Einsele, W., Über die Beziehungen des Eisenkreislaufs zum Phosphatkreislauf im eutrophen See, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1936, vol. 29, no. 6. pp. 664–686.
Elrod, V.A., Berelson, W.M., Coale, K.H., and Johnson, K.S., The Flux of Iron from Continenetal Shelf Sediments: A Missing Source of Global Budgets, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2004, vol. 31, P. L 12307/1–L12307/4.
Gächter, R., Meyer, J.S., and Mares, A., Contribution of Bacteria to Release and Fixation of Phosphorus in Lake Sediments, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1988, vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 1542–1558.
Gächter, R., and Müller, B., Why the Phosphorus Retention of Lakes Does Not Necesserily Depend on the Oxygen Supply to Their Sediment Surface, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2003, vol. 48, no. 7, pp. 929–933.
Golterman, H.L., The Labyrinth of Nutrient Cycles and Buffers in Wetlands: Results Based on Research in the Camarague (Southern France), Hydrobiologia, 1995, vol. 315, no. 1, pp. 39–58.
Golterman, H.L., and Glumo, R.S., Methods for Chemical Analysis of Fresh Water, Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publ., 1969.
Hansen, H.C.B., Guldberg, S., Erbs, M., and Koch, C.B., Kinetics of Nitrate Reduction by Green Rusts-Effects of Interlayer Anion and Fe(II): Fe(III) Ratio, Appl. Clay Sci., 2001, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 81–91.
Holdren, G.C., and Armstrong, D.E., Interstitial Ion Concentrations as an Indicator of Phosphorus Release and Mineral Formation in Lake Sediments, Sediments and Water Interactions, Sly, P.G, Ed., New York: Springer, 1986.
Hongve, D., Chemical Stratification and Stability of Meromectic Lakes in the Upper Romerike District, Schweiz. Z. Hydrol., 1981, vol. 42. no. 2, pp. 171–195.
Jensen, H.S., Kristensen, P., Jeppen, E., and Skytthe, A., Iron: Phosphorus Ratio in Surface Sediment as an Indicator of Phosphate Release from Aerobic Sediments in Shallow Lakes, Hydrobiola, 1992, vol. 235/236, pp. 731–743.
Lehtoranta, J., and Heiskanen, A.-S., Dissolved Iron: Phosphate Ratio as an Indicator of Phosphate Release to Oxic Water of the Inner and Outher Coastal Baltic Sea, Hydrobiologia, 2003, vol. 492,Pt 1, pp. 69–84.
Lijklema, L., Interaction of Ortophosphate with Iron (III) and Aluminium Hydroxides, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1980, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 537–541.
Löfgren, S., Boström, B., Interstitial Water Concentration of Phosporus, Iron and Manganese in a Shallow Eutrophic Swedish Lake—Implications for Phosphorus Cycling, Water Res., 1989, vol. 23, no. 9, pp. 1115–1125.
Manning, P. G., Birchall, T., and Jones, W., The Partitioning of Non-Apatite Inorganic Phosporus in Sediments from Lakes Erie and Ontario, Can. Mineral., 1984, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 357–365.
Mortimer, C. H., The Exchange of Dissolved Substances between Mud and Water in Lakes, J. Ecol., 1941, no. 2, pp. 280–329.
Ostrofsky, M.L., Phosphorus Species in the Surficial Sediments of Lakes of Eastern North America, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1987, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 960–966.
Petersson, K., The Fractional Composition of Phosphorus in Lake Sediments of Different Characteristics, Sediment and Water Interactions, Ed. Sly, P.G., N. Y.: Springer, 1986, pp. 149–155.
Schindler, D.W., The Coupling of Elemental Cycles by Organisms: Evidence from Whole-Lake Chemical Perturbations, Chemical Pprocesses in Lakes, Stumm, W., Ed. N. Y.: John Wiley & Sons, 1985, pp. 225–250.
Schwertmann, U., Carlson, L., and Fechter, H., Iron Oxide Formation in Artifical Ground Waters, Schweiz. Z. Hydrol., 1984, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 185–191.
Stauffer, R.E., and Armstrong, D.E., Cycling of Iron, Manganese, Silica, Phosphorus, Calcium and, Potassium in Two Stratified Basins of Shagawa Lake, Minnesota, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1986, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 215–229.
Tessenow, U., Lösungs-, Diffusions- and Sorptions Processe in Der Oberschicht Von Seesedimenten, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1974, Suppl. 47, pp. 1–79.
Tipping, E., Woof, C., and Cooke, D., Iron Oxide from Seasonally Anoxic Lake, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1981, vol. 45, no. 12, pp. 1411–1419.
Von Gunten, U., and Schneider, W., Primary Products of the Oxygenation of Iron (II) at an Oxic-Anoxic Boundary: Nucleation, Aggregation, and Aging, J. Coll. Interf. Sci., 1991, vol. 145, no. 1, pp. 127–139.
Weber, K.A., Urrutia, M.M., Churchill, P.F., et al., Anaerobic Redox Cycling of Iron by Freshwater Sediment Microorganisms, Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 100–113.
Williams, J. D.H., Syers, J.K., Armstrong, D.E., and Harris, R.F., Levels of Inorganic and Total Phosphorus in Lake Sediments as Related to Other Sediments Parameter, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1971, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1113–1120.
Zhu, G.-W., Qin, B.-Q., Zhang, L., and Luo L.-C., Geochemical Forms of Phosphorus in Sediments of Three Large, Shallow Lakes of China, Pedosphere, 2006, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 726–734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.V. Martynova, 2011, published in Vodnye Resursy, 2011, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 205–213.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynova, M.V. Fe/P concentration ratio in Mozhaisk reservoir deposits as an indicator of phosphate sorption. Water Resour 38, 211–219 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807810061053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807810061053