Abstract
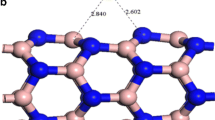
In this study, the isolated boron nitride nanotube has been characterized using the B3LYP exchange-correlation functional of theory by electron paramagnetic resonance of EPR3 basis set. Then the effect of metals such as Li, Na, K, Be, Mg, and Ca inside BN–nanotube has been investigated. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) parameters such as, isotropic chemical shielding, anisotropic chemical shielding, asymmetry, chemical shift anisotropy and total atomic charges of BN–nanotube including of metal systems have been calculated with GIAO approximation. It has been shown that the behavior of chemical shift tensor components (isotropic and anisotropic), chemical shift anisotropy, asymmetry and devotion depending on the metal that locating at the center of BN–nanotube that some of periodic transformations. Also, Atomic charge have considered to full alternation B, N and metal atoms in BN–nanotube determined the active sites of structures. Thermo chemical functions of relative enthalpy (ΔH), entropy (ΔS) and free Gibbs energy (ΔG) have been calculated. Our investigation exhibited that some metal atoms can strongly bind to the BN–nanotube to enhance the potential electronic molecular effects of these compounds for various applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Y. Tian, B. Xu, D. Yu, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 493, 385 (2013).
A. Rubio et al., Phys. Rev. B 49, 5081 (1994).
N. G. Chopra et al., Science (Washington, DC, U.S.) 269 (5226), 966 (1995).
H. Wu, X. Xu, H. Jiao, F. Zhang, and J. Jia, Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1102 (2003).
E. Durgun, S. Dag, V. M. K. Bagci, et al., Phys. Rev. B 67, 201401 (2003).
Y. Yagi, T. M. Briere, M. H. F. Sluiter, et al., Phys. Rev. B 69, 75414 (2004).
X. Wu and X. C. Zeng, Chem. Phys. 125, 044711 (2006).
R. Saito, M. Fujita, G. Dresselhaus, and M. S. Dresselhaus, Phys. Rev. B 46, 1804 (1992).
M. Monajjemi and J. Khaleghian, Clust. Sci. 22, 673 (2011).
A. Srivastava, S. Jain, and A. K. Nagawat, Quantum Matter 2, 469 (2013).
H. Mohan Rai, N. K. Jaiswal, P. Srivastava, and R. Kurchania, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 368 (2013).
M. Monajjemi and M. Seyed Hosseini, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 2473 (2013).
G. H. Cocoletzi and N. Takeuchi, Quantum Matter 2, 382 (2013).
W. Q. Han, P. Redlich, F. Ernst, and M. Rühle, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 1875 (1999).
J.-Y. Guo, C.-X. Xu, F.-Y. Sheng, et al., Quantum Matter 2, 181 (2013).
C. C. Tang, Y. Bo, D. Golberg, et al., Phys. Chem. B 107, 6539 (2003).
I. Will, A. Ding, and Y. Xu, Quantum Matter 2, 17 (2013).
M. Monajjemi, V. S. Lee, M. Khaleghian, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 15315 (2010).
Z. Zhou, J. Zhao, Z. F. Chen, and P. R. Schleyer, Phys. Chem. B 110, 25678 (2006).
N. G. Chopra, R. J. Luyken, K. Cherrey, et al., Science, New Ser. 269 (5226), 966 (1995).
D. Golberg, Y. Bo, M. Eremets, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 2045 (1996).
M. Monajjemi, L. Mahdavian, F. Mollaamin, and M. Khaleghian, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 54, 1465 (2010).
M. Monajjemi, Struct. Chem. 23, 551 (2012).
J. C. Charlier, A. de Vita, X. Blase, and R. Car, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 275 (5300), 647 (1997).
A. Srivastava, N. Saraf, and A. K. Nagawat, Quantum Matter 2, 401 (2013).
C. Tang and Y. Bando, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 659 (2003).
A. M. Ilyin, Quantum Matter 2, 205 (2013).
N. Grobert, Mater. Today 10, 28 (2007).
A. Srivastava, N. Jain, and A. K. Nagawat, Quantum Matter 2, 307 (2013).
H. Yahyaei, M. Monajjemi, H. Aghaie, and K. Zare, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 2332 (2013).
S. Celasun, Rev. Theor. Sci. 1, 319 (2013).
J. Kaur and N. Goel, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 48 (2013).
M. J. Frisch et al., Gaussian 98, Revision A.7 (Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, 1998).
P. Pyykkö, Mol. Phys. 99, 1617 (2001).
J. R. Cheeseman, M. J. Frisch, F. J. Devlin, and P. J. Stephens, Chem. Phys. Lett. 252, 211 (1996).
C. Pisani, S. Casassa, and P. Ugliengo, Chem. Phys. Lett. 253, 201 (1996).
V. Subramanian, K. Venkatesh, D. Mary Prabha, and T. Ramasami, Chem. Phys. Lett. 276, 9 (1997).
R. Poirer, R. Kari, and I. G. Csizmadia, Handbook of Gaussian Basis Sets: A Compendium for Ab-initio Molecular Orbital Calculations (Elsevier Science, New York, 1985)
S. Olszewski, Quantum Matter 2, 102 (2013).
G. Leichtfried et al., in Lolt-Börnstein–Group VIII Advanced Materials and Technologies: Powder Metallurgy Data. Refractory, Hard, and Intermetallic Materials, Ed. by P. Beiss et al. (Springer, Berlin, 2002), Vol. 2A2.
X. Blase et al., Europhys. Lett. 28, 335 (1994).
Wei-Qiang Han et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1110 (2002).
S. N. Bhattacharyya and A. Mukherjee, J. Phys. Chem. 72, 56 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mollaamin, F., Shahriari, S. & Monajjemi, M. Induced Metals on BN–Nanotube by DFT/EPR Methods. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 95 (Suppl 2), S331–S337 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602442115019X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602442115019X