Abstract
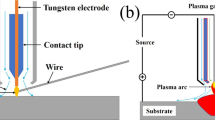
In this work, the aluminum 5356 (Al5356) component was fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) process and subjected to heat treatment at three different temperatures i.e., 450, 525, and 600°C. Detailed mechanical and microstructural characterization was performed on the as-fabricated and heat-treated samples to correlate the change in mechanical properties with its corresponding microstructure. The mechanical properties were estimated using the tensile and Rockwell hardness tester, and the microstructural characterization was performed using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) technique. The samples heat-treated at 450°C show superior strength (i.e. UTS 260 MPa) as compared to as-fabricated, heat-treated at 525 and 600°C due to the beneficial evolution of fine second phase particles after heat treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. A. Rodrigues, V. Duarte, R. M. Miranda, T. G. Santos, and J. P. Oliveira, “Current status and perspectives on wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM),” Materials 12, 1121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071121
M. Köhler, S. Fiebig, J. Hensel, and K. Dilger, “Wire and arc additive manufacturing of aluminum components,” Metals 9, 608 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050608
W. E. Frazier, “Metal additive manufacturing: A review,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 1917–1928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
K. S. Derekar, “A review of wire arc additive manufacturing and advances in wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminium,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 895–916 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2018.1455012
J. R. Davis, “Introduction to aluminum and aluminum alloys,” in Metals Handbook Desk Edition (ASM International, 2001), pp. 417–423. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.mhde2.a0003121
J. G. Kaufman and E. L. Rooy, Aluminum Alloy Castings (ASM International, 2004). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.tb.aacppa.9781627083355
S. Li, L.-J. Zhang, J. Ning, X. Wang, G.-F. Zhang, J.‑X. Zhang, S.-J. Na, and B. Fatemeh, “Comparative study on the microstructures and properties of wire+arc additively manufactured 5356 aluminium alloy with argon and nitrogen as the shielding gas,” Addit. Manuf. 34, 101206 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101206
G. Saad, S. A. Fayek, A. Fawzy, H. N. Soliman, and E. Nassr, “Work hardening characteristics of gamma-ray irradiated Al-5356 alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 607, 132–137 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.03.137
S. Sanamar, H. Brokmeier, and N. Schell, “Phase evolution of Al–Mg metal matrix composites during low temperature annealing at 200°C and 250°C,” Intermetallics 124, 106862 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106862
J. Wang, Q. Shen, X. Kong, and X. Chen, “Arc additively manufactured 5356 aluminum alloy with cable-type welding wire: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 7472–7478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05905-y
C. Li, H. Gu, W. Wang, S. Wang, L. Ren, Z. Wang, Z. Ming, and Yu. Zhai, “Effect of heat input on formability, microstructure, and properties of Al–7Si–0.6Mg alloys deposited by CMT-WAAM process,” Appl. Sci. 10, 70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010070
D. Su, J. Zhang, and B. Wang, “The microstructure and weldability in welded joints for AA 5356 aluminum alloy after adding modified trace amounts of Sc and Zr,” J. Manuf. Processes 57, 488–498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.07.017
C. Ma, Yu. Yan, Z. Yan, Yo. Liu, X. Wu, D. Li, L. Zhao, P. Liu, and H. Jin, “Investigation of bypass-coupled double-pulsed directed energy deposition of Al–Mg alloys,” Addit. Manuf. 58, 103058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.103058
G. Saad, S. A. Fayek, A. Fawzy, H. N. Soliman, and E. Nassr, “Serrated flow and work hardening characteristics of Al-5356 alloy,” J. Alloys Compd. 502, 139–146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.04.119
Ya. Geng, I. Panchenko, X. Chen, Yu. Ivanov, and S. Konovalov, “Wire arc additive manufacturing Al–5.0 Mg alloy: Microstructures and phase composition,” Mater. Charact. 187, 111875 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.111875
M. Köhler, J. Hensel, and K. Dilger, “Effects of thermal cycling on wire and arc additive manufacturing of Al-5356 components,” Metals 10, 952 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070952
ESAB. Aluminium 5356 Wires Autrod.
M/s Kemppi. X8 MIG Welder (2022).
ASTM E8/E8M standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials. Annu. B. ASTM Stand. 4 ASTM E8 (2010).
Standard Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM Int. ASTM E18 (2015).
S. Scudino, G. Liu, M. Sakaliyska, K. B. Surreddi, and J. Eckert, “Powder metallurgy of Al-based metal matrix composites reinforced with β-Al3Mg2 intermetallic particles: Analysis and modeling of mechanical properties,” Acta Mater. 57, 4529–4538 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.06.017
A. Ahmed, S. Akl, and A. S. Hassanien, Int. J. Adv. Res. 2 (11), 1–9 (2014). https://www.journalijar.com/ uploads/838_IJAR-4360.pdf.
J. L. Murray, “The Al−Mg (aluminum−magnesium) system,” J. Phase Equilib. 3, 60–74 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02873413
S. Bannour, K. Abderrazak, S. Mattei, J. E. Masse, M. Autric, and H. Mhiri, “The influence of position in overlap joints of Mg and Al alloys on microstructure and hardness of laser welds,” J. Laser Appl. 25, 032001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4792615
W. Zuo, L. Ma, Yu. Lu, S. Li, Z. Ji, and M. Ding, “Effects of Solution treatment temperatures on microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG–MIG hybrid arc additive manufactured 5356 aluminum alloy,” Met. Mater. Int. 24, 1346–1358 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0142-3
Ch. Su, X. Chen, C. Gao, and Ya. Wang, “Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Mg alloys fabricated by WAAM,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 486, 431–440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.04.255
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRM IST) for their support. We acknowledge the National facility for OIM and Texture IIT Bombay for EBSD measurements. We thank Mr. Manavallan, Metallurgy Lab, SRM IST for the help in optical microscopy.
Funding
This work was supported by ongoing institutional funding. No additional grants to carry out or direct this particular research were obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harshavardhana, N., Sivam, S.P., Savio, R.R. et al. Effect of Heat Treatment on Wire + Arc Additive Manufactured Aluminum 5356 Alloy: Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Correlation. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1845–1855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22601846
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22601846