Abstract
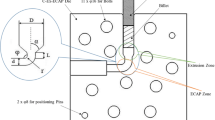
In this paper, We investigate the effects of one pass severe deformation, obtained by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) process, using dies with channel angles of 90° and 120°, on hardness, texture, and corrosion behavior, of AA1370 aluminum alloy wire. A severe deformation, by ECAP process, leads to athinning of several diffraction peaks and an increase of their angular values; modifies the texture of material from pseudo-texture to mix texture; reduces the microhardness; modifies a part of localized corrosion towards generalized one; shifts the corrosion potential to negative values; and increases the values of open circuit potential (OCP). The deformation by ECAP process induces fragmentation of parts of intermetallic particles, and reduction of grains size. The imprisoned air, between the channel wall of the die and the wire, creates microporosities in the deformed samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. Zazi, “Effect of heat treatments on the microstructure, hardness and corrosion behavior of nondendritic AlSi9Cu3(Fe) cast alloy,” Mater. Sci. 19, No. 3, 258–263 (2013).
R. Gravina, C. Josse, B. Viguier, A. Laurino, J. Alexis, A. E. Hughes, and C. Blanc, “Corrosion behaviour of AA 1370 strands for wires: Identification of the critical metallurgical parameters,” Corros. Sci. 134, 112–121 (2018).
G. Nurislamova, X. Sauvage, M-Y. Murashkin, R. Islamgaliev, and R. Valiev, “Nanostructure and related mechanical properties of an Al–Mg–Si alloy processed by severe plastic deformation,” Philos. Mag. Lett. 88, No. 6, 459–466 (2008).
A. S. Khan and C. S. Meredith, “Thermo-mechanical response of Al 6061 with and without equal channel angular pressing (ECAP),” Int. J. Plast. 26, No. 2, 189–203 (2010).
S. N. Lezhnev, I. E. Vokitina, and D. V. Kuis, “Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of composite aluminum-based alloy during ECAP,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 119, No. 8, 810–815 (2018).
A. P. Zhilyaev, I. Shakhova, A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, and T. G. Langdon, “Wear resistance and electroconductivity in copper processed by severe plastic deformation,” Wear 305, Nos. 1–2, 89–99 (2013).
C. Xu and T. G. Langdon, “Influence of a round corner die on flow homogeneity in ECA pressing,” Scr. Mater. 48, No. 1, 1–4 (2003).
M. Yu., Murashkin, E. V. Bobruk, A. R. Kil’mametov, and R. Z. Valiev, “Structure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 6061 subjected to equal-channel angular pressing in parallel channels,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 108, No. 4, 415–423 (2009).
K. Hajizadeh, S. Ejtemaei, B. Eghbali, and K. J. Kurzydlowski, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of 1050 aluminum after the combined processes of constrained groove pressing and cold rolling,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 121, No. 1, 72–77 (2020).
M. Š. Musa and Z. Schauperl, “ECAP–New consolidation method for production of aluminium matrix composites with ceramic reinforcement,” Process. Appl. Ceram. 7, No. 2, 63–68 (2013).
J. R. Davis, Corrosion of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys (ASM International, Ohio, 1999).
D. Song, A-b. Ma., J-H. Jiang, P-H. Lin, and D.‑H. Yang, “Corrosion behavior of ultra-fine grained industrial pure Al fabricated by ECAP,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 19, No. 5, 1065–1070 (2009).
K. Gopala Krishna, K. Sivaprasad, T. S. N. Sankara Narayanan, and K. C. Hari Kumar, “Localized corrosion of an ultrafine grained Al–4Zn–2Mg alloy produced by cryorolling,” Corros. Sci. 60, 82–89 (2012).
K. D. Ralston, N. Birbilis, and C. H. J. Davies, “Revealing the relationship between grain size and corrosion rate of metals,” Scr. Mater. 63, No. 12, 1201–1204 (2010).
Z. Horita, T. Fujinami, M. Nemoto, and T. G. Langdon, “Equal-channel angular pressing of commercial aluminum alloys: grain refinement, thermal stability and tensile properties,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31, No. 3, 691–701 (2000).
J.G. Brunner, N. Birbilis, K. D. Ralston, and S. C. Virtanen, “Impact of ultrafine-grained microstructure on the corrosion of aluminium alloy AA2024,” Corros. Sci. 57, 209–214 (2012).
I-J. Son, H. Nakano, S. Oue, S. Kobayashi, H. Fukushima, and Z. Horita, “Effect of equal-channel angular pressing on pitting corrosion resistance of anodized aluminum-copper alloy,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 19, No. 4, 904–908 (2009).
C. Banjongprasert, A. Jak-Ra, C. Domrong, U. Patakham, W. Pongsaksawad, and T. Chairuangsri, “Characterization of an equal channel angular pressed Al–Zn–In alloy,” Arch. Metall. Mater. 60, No. 2, 887–890 (2015).
C. M. Allena, Kaq. O’Reilly, B. Canto, and P. V. Evans, “Intermetallic phase selection in 1XXX Al alloys,” Prog. Mater. Sci. 43, No. 2, 89–170 (1998).
B. Sundman, I. Ohnuma, N. Dupin, U. R. Kattner, and S. G. Fries, “An assessment of the entire Al–Fe system including D03 ordering,” Acta Mater. 57, No. 10, 2896–2908 (2009).
Z. Szklarska-Smialowska, ”Pitting corrosion of aluminum,” Corros. Sci. 41, No. 9, 1743–1767 (1999).
W.R. Osório, L. C. Peixoto, P. R. Goulart, and A. Garcia, “Electrochemical corrosion parameters of as-cast Al–Fe alloys in a NaCl solution,” Corros. Sci. 52, No. 9, 2979–2993 (2010).
I. C. Noyan and J. B. Cohen, “Residual stress–measurement by diffraction and interpretation, Book Review, ” Cryst. Res. Technol. 24, No. 2, K37 (1989).
U. Welzel, J. Ligot, P. Lamparter, A. C. Vermeulen, and E. J. Mittemeijer, “Stress analysis of polycrystalline thin films and surface regions by X-ray diffraction,” J. Appl. Crystallogr. 38, No. 1, 1–29 (2005).
A. Baczmanski, P. Lipinski, A. Tidu, K. Wierzbanowski, and B. Pathiraj, “Quantitative estimation of incompatibility stresses and elastic energy stored in ferritic steel,” J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41, No. 5, 854–867 (2008).
T. H. De Keijser, J. I. Langford, E. J. Mittemeijer, and A. B. P. Vogels, “Use of the Voigt function in a single-line method for the analysis of X-ray diffraction line broadening,” J. Appl. Crystallogr. 15, No. 3, 308–314 (1982).
M. Marciszko, A. Baczmański, K. Wierzbanowski, M. Wrobel, C. Braham, J.-P. Chopart, A. Lodini, J. Bonarski, L. Tarkowski, and N. Zazi, “Application of multireflection grazing incidence method for stress measurements in polished Al–Mg alloy and CrN coating,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 266, 256–267 (2013).
L. Muresan, L. Oniciu, M. Froment, and G. Maurin, “Inhibition of lead electrocrystallization by organic additives,” Electrochim. Acta 37, No. 12, 2249–2254 (1992).
N. Zazi, J. P. Chopart, and A. Bilek, “Corrosion behavior and the weak-magnetic-field effect of aluminum packaging paper,” Mater. Technol. 50, No. 2, 165–173 (2016).
A. Urrutia, S. Tumminello, D. G. Lamas, and S. Sommadossi, “X-Ray Characterization of Intermetallic Phases in Al/Ni Multilayer System,” International Congress of Science and Technology of Metallurgy and Materials, SAM—CONAMET 2013, Procedia Mater. Sci., No. 8, 1150 (2015).
R. Ambat, A. J. Davenport, G. M. Scamans, and A. Afseth, “Effect of iron-containing intermetallic particles on the corrosion behaviour of aluminium,” Corros. Sci. 48, No. 11, 3455–3471 (2006).
J. O. Park, C.-H. Paik, and R. C. Alkire, “Scanning microsensors for measurement of local pH distributions at the microscale,” J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, No. 8, 174 (1996).
O. Seri and M. Imaizumi, “The dissolution of FeAl3 intermetallic compound and deposition on aluminum in AlCl3 solution,” Corros. Sci. 30, No. 11, 1121–1131 (1990).
M. Murayama, Z. Horita, and K. Hono, “Microstructure of two-phase Al–1.7 at % Cu all y deformed by equal-channel angular pressing,” Acta Mater. 49, No. 1, 21–29 (2001).
Z. Horita, K. Oh-ishi, and K. Kaneko, “Microstructure control using severe plastic deformation,” Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 7, No. 7, 649–654 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youcef Hadj Ali, Zazi, N., Durmus, H. et al. Effects of ECAP with One Pass Severe Deformation on Microhardness, Texture, and Corrosion Behavior of AA1370 Aluminum Alloy Wire. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 122, 1382–1390 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X20140021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X20140021