Abstract
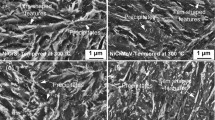
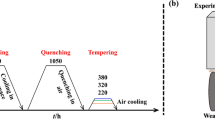
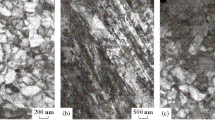
The effect of intense warm deformation on the structure and mechanical properties of low-carbon 12GBA steel was investigated. A submicrocrystalline (SMC) structure with an average element size of 0.3 μm was formed in the steel by isothermal overall forging. The formation of the SMC structure resulted in a sharp increase in strength by a factor of two to three in relation to the initial coarse-grained state while retaining a sufficient level of plasticity and impact toughness. After further annealing, steels exhibit an improved set of properties; i.e., as the strength decreases slightly, the plasticity increases sharply. Impact tests at low temperatures have shown the significant advantage of the SMC state of the steel over the coarse-grained state in the impact toughness. It is established that the cold resistance in the SMC state increases because the crack propagation prevails in the overall sample fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. I. Matrosov, D. A. Litvinenko, and S. A. Golovanenko, Steel for Main Pipelines (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1989) [in Russian].
N. I. Noskova and R. R. Mulyukov, Submicrocrystalline and Nanocrystalline Metals and Alloys (Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ekaterinburg, 2003) [in Russian].
R. R. Mulyukov, R. M. Imayev, and A. A. Nazarov, “Production, Properties and Application Prospects of Bulk Nanostructured Materials,” J. Mater. Sci., 43, 7257–7263 (2008).
M. Georgiev, Crack Resistance of Metals under Shock Loading (BULVEST, Sofia, 2007) [in Bulgarian].
A. V. Korznikov, I. M. Safarov, A. A. Nazarov, and R. Z. Valiev, “High Strength in Low Carbon Steel with Submicron Fibrous Structure,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A 206, 39–44 (1996).
A. V. Korznikov, I. M. Safarov, R. Z. Valiev, B. M. Bronfin, and A. A. Emel’yanov, “Effect of Submicrocrystalline Structure on Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Steels,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2, 27–30 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.M. Safarov, A.V. Korznikov, S.N. Sergeev, S.V. Gladkovskii, E.M. Borodin, 2012, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2012, Vol. 113, No. 10, pp. 1055–1060.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safarov, I.M., Korznikov, A.V., Sergeev, S.N. et al. Effect of submicrocrystalline state on strength and impact toughness of low-carbon 12GBA steel. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 113, 1001–1006 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X12100109
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X12100109