Abstract
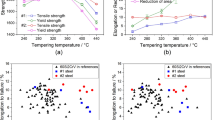
An ultrafine-grained (UFG) structure of equiaxed and fiber types in the low-carbon structural steel 05G2MFBT (Fe–2Mn–Mo–V–Nb–Ti) has been formed with various techniques of deformation-heat treatment. This steel with a UFG structure has been found to exhibit higher strength properties. Different deformation techniques have been shown to produce either a fibrous or an equiaxed UFG structure with carbide particles of a wide range of sizes. The brittle fracture resistance of the fibrous UFG steel has been found to be higher than that of the fine-grained steel after controlled rolling and subsequent accelerated cooling. Standard bending-impact tests have shown that the steel with a fibrous UFG structure is characterized by higher impact strength characteristics and a lower ductile–brittle transition temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
O. A. Sofrygina, S. Yu. Zhukova, S. M. Bityukov, and I. Yu. Pyshmintsev, “Economical steels for the manufacture of high-strength oil pipe (according to the API SPEC5CT standard)” Steel Transl. 40, No. 7, 616–621 (2010).
L. M. Kleiner, K. A. Kobelev, S. K. Greben’kov, and D. M. Larinin, “A new class of structural steels in mechanical engineering,” Metallurg. Mashinost., No. 5, 39–40 (2011).
V. A. Pavlov, Physical Basics of Cold Deformation of BCC Metals (Nauka, Moscow, 1978).
V. M. Chernov, B. K. Kardashev, and K. A. Moroz, “Cold brittleness and fracture of metals with various crystal lattices: dislocation mechanisms,” Tech. Phys. 61, 1015–1022 (2016).
R. Z. Valiev, G Klevtsov, N. A. Klevtsova, M. V. Fasenyuk, M. R. Kashapov, A. G. Raab, M. V. Karavaeva, and A Ganeev, “The influence of the modes of equal channel angular pressing and subsequent heating on the strength and the mechanism of failure of steel 10,” Deformatsiya i Razrusheniya Materialov, No. 1, 21–25 (2013).
I. M. Safarov, A Korznikov, R. M. Galeev, S. N. Sergeev, S. V. Gladkovskii, and I. Yu. Pyshmintsev, “An anomaly of the temperature dependence of the impact strength of low-carbon steel with an ultrafine-grain structure,” Dokl. Phys. 61, 15–18 (2017).
V. M. Schastlivtsev, D. A. Mirzaev, I. L. Yakovleva, N. A. Tereshchenko, and T. I. Tabatchikova, “Effect of increasing impact toughness on the formation of a layered structure upon hot rolling of a ferritic steel,” Dokl. Phys. 55, 334–337 (2010).
D. A. Mirzaev, D Shaburov, I. L. Yakovleva, A Panov, L Elokhina, Factors responsible for increasing ductility of the ferritic steel 08Kh1ST1 In the course of repeated hot rolling,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 98, No. 3, 317–325 (2004).
Dolzhenko A., Z. Yanushkevich, S. A. Nikulin, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, “Impact toughness of an S700MC-type steel: Tempforming vs ausforming,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 723, 259–268 (2018).
T. Inoue, F. Yin, Y. Kimura, K. Tsuzaki, and S. Ochial, “Delamination effect on impact properties of ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel processed by warm caliber rolling,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41, 341–355 (2010).
S. N. Sergeev, I. M. Safarov, A. V. Korznikov, R. M. Galeev, S Gladkovskii, and D. A. Dvoinikov, “Effect of warm rolling on the structure and mechanical properties of low carbon tube steel,” Pis’ma Mater. 5, No. 1, 51–54 (2015).
I. M. Safarov, A. V. Korznikov, R. M. Galeev, S. N. Sergeev, S. V. Gladkovskii, E. M. Borodin, and I. Yu. Pyshmintsev, “Strength and impact toughness of low-carbon steel with fibrous ultrafine-grained structure,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 115, No. 3, 315–323 (2014).
Y. Kimura, T. Inoue, and K. Tsuzaki, “Tempforming in medium-carbon low-alloy steel,” J. Alloys Compd. 577, 538–542 (2013).
Y. Kimura, T. Inoue, F. Yin, and K. Tsuzaki, “Delamination toughening of ultrafine grain structure steels processed through tempforming at elevated temperatures,” ISIJ Int. 50, No. 1, 152–161 (2010).
Y. Kimura and T. Inoue, “Influence of warm tempforming on microstructure and mechanical properties in an ultrahigh-strength medium-carbon low-alloy steel, “Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 560—576 (2013).
V. N. Danilenko, S. Yu. Mironov, A. N. Belyakov, and A. P. Zhilyaev, “Application of EBSD analysis in physical materials science (Review),” Zavod. Lab., Diagn. Mater. 78, No. 2, 28–46 (2012).
J. D. Embury, N. J. Petch, A. E. Wraith, and E. S. Wright, “The fracture of mild steel laminates,” Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 239, 114–118 (1967).
L. R. Botvina, Failure: Kinetics, Mechanisms, General Relations (Nauka, Moscow, 2008) [in Russian].
L. I. Efron, Metal Science in “Large” Metallurgy. Pipe Steels (Metallurgizdat, Moscow, 2012) [in Russian].
I. L. Yakovleva, N. A. Tereshchenko, and N Urtsev, “Observation of the martensitic-austenitic component in the structure of low-carbon low-alloy pipe steel,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 121, No. 4, 352–358 (2020).
M. L. Lobanov, I. Yu. Pyshmintsev, V. N. Urtsev, S. V. Danilov, N Urtsev, and A. A. Redikul’tsev, “Texture inheritance in the ferrito-martensite structure of low-alloy steel after thermomechanical controlled processing,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 120, No. 12, 1180–1186 (2019).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The scientific research was carried out at the Structural and Physical-Mechanical Studies of Materials Center of the Collaborative Use of the Institute for Problems of Metal Superplasticity of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Funding
This work was performed within the state assignment of Institute for Problems of Metal Superplasticity of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Institute of Engineering Science, Ural Branch of the RAS for 2019–2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by T. Gapontseva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sergeev, S.N., Safarov, I.M., Zhilyaev, A.P. et al. Effect of Deformation-Thermal Processing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Structural Steel. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 122, 621–627 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21060090
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21060090