Abstract
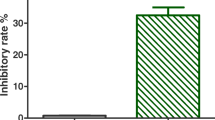
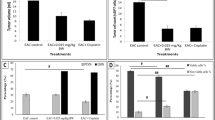
Macrovipera lebetina obtusa (MLO) is a venomous snake endemic to Middle East. Here we describe the therapeutic potential of the MLO snake venom. In S-180 sarcoma-bearing mouse model, we showed that the MLO snake venom inhibits tumour growth by 50%. In human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-D), treatment with the MLO snake venom lead to an increase of expression levels of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), while the level of the expression of caspase 8 did not change. In HMVEC-D cells MLO snake venom induces necroptosis, rather than apoptosis. In the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay, exposure to MLO snake venom inhibited bFGF-induced angiogenesis by 22%. Taken together, these results indicate that the MLO snake venom has a potent cytotoxic activity. Regulated necroptic cell death pathway, which is engaged by MLO snake venom, may become a promising novel target for antitumor therapies.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
WHO. 2002. World Health Organisation Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. Eds. Fletcher C.D.M., Uni K.K., Mertens F. Lyon: IARC Press.
Cormier J.N., Pollock R.E. 2004. Soft tissue sarcomas. CA Cancer J. Clin. 54, 94–109.
Dean B.J.F., Whitwell D. 2009. Epidemiology of bone and soft-tissue sarcomas. Orthop. Trauma. 23, 223–230.
Folkman J. 1971. Tumor angiogenesis theraperutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 285, 1182–1186.
Carmeliet P., Jain R.K. 2000. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407, 249–257.
Hashizume H., Baluk P., Morikawa S., McLean J.W., Thurston G., Roberge S., Jain R.K., McDonald D.M. 2000. Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am. J. Pathol. 156, 1363–1380.
Senger D.R., Perruzzi C.A., Streit M., Koteliansky V.E., De Fougerolles A.R., Detmar M. 2002. The α1β1 and α2β1 integrins provide critical support for vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, endothelial cell migration, and tumor angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 160,195‒204.
Ferrara N. 2002. VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2, 795–803.
Folkman J. 2003. Fundamental concepts of the angiogenic process. Curr. Mol. Med. 3, 643–651.
Naldini A., Carraro F. 2005. Role of inflammatory mediators in angiogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy. 4, 3–8.
Lijnen H.R. 2008. Angiogenesis and obesity. Cardiovasc. Res. 78, 286–293.
Carmeliet P., Jain R.K. 2011. Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10, 417–427.
Benassi M.S., Gamberi G., Magagnoli G., Molendini L., Ragazzini P., Merli M., Chiesa F., Balladelli A., Manfrini M., Bertoni F. 2001. Metalloproteinase expression and prognosis in soft tissue sarcomas. Ann. Oncol. 12, 75–80.
Hedlund E.M., Hosaka K., Zhong Z., Cao R., Cao Y. 2009. Malignant cell-derived PlGF promotes normalization and remodeling of the tumor vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 17505–17510.
Marcinkiewicz C., Rosenthal L.A., Mosser D.M., Kunicki T.J., Niewiarowicz C. 1996. Immunological characterization of erististatin and echistatin binding sites on αIIbβ3 and ανβ3 integrins. Biochem. J. 317, 817–825.
Marcinkiewicz C., Weinreb P.H., Calvete J.J., Kisiel D.G., Mousa S.A., Tuszynski G.P, Lobb R.R. 2003. Obtustatin: A potent selective inhibitor of alpha1beta1 integrin in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 9, 2020–2023.
Marcinkewicz C. 2005. Functional characteristic of snake venom disintegrins: Potential therapeutic implication. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11, 815–827.
Calvete J.J., Mureno-Murciano M.P., Theakston D.G., Kisiel D.G., Marcinkiewicz C. 2003. Snake venom disintegrins: Novel dimeric disintegrins and structural diversification by disulphide bond engineering. Biochem. J. 372, 725–734.
Sanz L., Ayvazyan N., Calvete J.J. 2008. Snake venomics of the Armenian mountain vipers Macrovipera lebetina obtusa and Vipera raddei. J. Proteomics. 71, 198–209.
Brown M.C., Staniszewska I., Del Valle L., Tuszynski G.P., Marcinkiewicz C. 2008. Angiostatic activity of obtustatin as alpha1beta1 integrin inhibitor in experimental melanoma growth. Int. J. Cancer. 123, 2195–2203.
Ghazaryan N., Movsisyan N., Macedo J., Vaz S., Ayvazyan N., Pardo L., Logarinho E. 2019. The antitumor efficacy of monomeric disintegrin obtustatin in S‑180 sarcoma mouse model. Invest. New Drugs. 37, 1044–1051.
Ghazaryan N.A., Ghulikyan L., Kishmiryan A., Kirakosyan G., Nazaryan O., Ghevondyan T., Zakaryan N., Ayvazyan N.M. 2015. Anti-tumor effect investigation of obtustatin and crude Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom in S-180 sarcoma bearing mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 11, 340–345.
Najafov A., Chen H., Yuan J. 2017. Necroptosis and cancer. Trends Cancer. 3, 294–301.
Huang Q., Li F., Liu X., Li W., Shi W., Liu F.F., O’Sullivan B., He Z., Peng Y., Tan A.C. 2011. Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 17, 860–866.
Liu X., He Y., Li F., Huang Q., Kato T.A., Hall R.P., Li C.Y. 2015. Caspase-3 promotes genetic instability and carcinogenesis. Mol. Cell. 58, 284–296.
Mirzayans R., Andrais B., Kumar P., Murray D. 2016. The growing complexity of cancer cell response to DNA-damaging agents: Caspase 3 mediates cell death or survival? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (5), 708.
Wang G.L., Semenza G.L. 1993. Characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and regulation of DNA binding activity by hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 21513–2158.
Pugh C.W., Ratcliffe P.J. 2003. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat. Med. 9, 677–684.
Hirota K., Semenza G.L. 2006. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxiainducible factor 1. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 59, 15–26.
Liang H., Xiao J., Zhou Z., Wu J., Ge F., Li Z., Zhang H., Sun J., Li F., Liu R., Chen C. 2018. Hypoxia induces miR-153 through the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway to fine tune the HIF1α/VEGFA axis in breast cancer angiogenesis. Oncogene. 37, 1961–1975.
Aranda-Souza M., Rossato F., Costa R., Figueira T., Castilho R., Guarniere M., Nunes E., Coelho L., Correia M., Vercesi A.A. 2014. Lectin from Bothrops leucurus snake venom raises cytosolic calcium levels and promotes B16-F10 melanoma necrotic cell death via mitochondrial permeability transition. Toxicon. 2, 97–103.
Ebrahim, K., Shirazi F., Mirakabadi A., Vatanpour H. 2015. Cobra venom cytotoxins: Apoptotic or necrotic agents? Toxicon. 108, 134–140.
Prinholato da Silva C., Costa T.R., Paiva R.M.A., Cintra A.C.O., Menaldo D.L., Antunes L.M.G., Sampaio S.V. 2015. Antitumor potential of the myotoxin BthTX-I from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom: Evaluation of cell cycle alterations and death mechanisms induced in tumor cell lines. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 21, 44.
Stupack D.G., Cheresh D.A. 2002. Get a ligand, get a life: Integrins, signaling and cell survival. J. Cell Sci. 115, 3729–3738.
Mcllwain D., Berger Th., Mak T. 2013. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5, a008656.
D’Amelio M., Cavallucci V., Cecconi F. 2010. Neuronal caspase-3 signaling: Not only cell death. Cell Death Differ. 17, 1104–1114.
Porter A., Jaènicke R. 1999. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6, 99–104.
Funding
This work was made possible by the research grant no. NS-biochem-2218 from the Armenian National Science and Education Fund (ANSEF) based in New York and State Committee of Science from Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sport of the Republic of Armenia no. 19YR-1F012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The text was submitted by the author(s) in English.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghazaryan, N., Movsisyan, N., Macedo, J.C. et al. Macrovipera lebetina obtusa Snake Venom as a Modulator of Antitumor Effect in S-180 Sarcoma Mouse Model. Mol Biol 55, 405–412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020217