Abstract
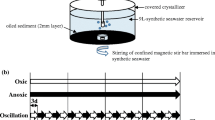
Degradation of oil hydrocarbons artificially introduced into bottom sediments in a bioelectrochemical system of a membrane-free (silt) type was studied. Passive bioelectrochemical stimulation by means of electrodes connected by an external circuit with a resistance of 1 kΩ, with an average electric current of ~85 µA was found to cause an increase in degradation during two months from 23.0 to 57.9%. Contamination of bottom sediments with oil (1.32 g/kg) slightly decreased the current in the external circuit of the bioelectrochemical system. The relationship was revealed between the degree of oil degradation and predominant utilization of the lighter n-alkanes in the C14H30–C30H62 series, compared with both the original oil and the residual hydrocarbons of the control. An increase in the representation of the alkB alkane monooxygenase genes relative to the 16S rRNA gene in the total DNA isolated from the sediments was induced by the introduction of hexadecane, both in the case of electrochemical stimulation and in the control. The results may be of interest for the development of new methods of bioelectrochemical removal of organic pollutants from anaerobic environments.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bose, S., Hochell, M.F., Jr., Gorby, Y.A., Kennedy, D.W., McCready, D.E., Madden, A.S., and Lower, B.H., Bioreduction of hematite nanoparticles by the dissimilatory iron reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2009, vol. 73, no. 4, pp. 962–976.
Bukliarevich, H.A., Gurinovich, A.S., Filonov, A.E., and Titok, M.A., Molecular genetic and functional analysis of the genes encoding alkane 1-monooxygenase synthesis in members of the genus Rhodococcus, Microbiology (Moscow), 2023, vol. 92, no. 2, pp. 242–255.
Bustin, S.A., Benes, V., Garson, J.A., Hellemans, J., Huggett, J., Kubista, M., Mueller, R., Nolan, T., Pfaffl, M.W., Shipley, G.L., Vandesompele, J., and Wittwer C.T., The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments, Clin. Chem., 2009, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 611–622.
Cabrera, J., Irfan, M., Dai, Y., Zhang, P., Zong, Y., and Liu, X., Bioelectrochemical system as an innovative technology for treatment of produced water from oil and gas industry‒a review, Chemosphere, 2021, vol. 285, p. 131428.
Chandrasekhar, K. and Venkata Mohan, S., Bio-electrochemical remediation of real field petroleum sludge as an electron donor with simultaneous power generation facilitates biotransformation of PAH: effect of substrate concentration, Bioresour. Technol., 2012, vol. 110, pp. 517–525.
Idris, M.O., Kim, H.-C., Yaqoob, A.A., and Ibrahim, M.N.M., Exploring the effectiveness of microbial fuel cell for the degradation of organic pollutants coupled with bio-energy generation, Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess., 2022, vol. 52, p. 102183.
Khmelevtsova, L.E., Sazykin, I.S., Sazykina, M.A., and Seliverstova, E.Y., Prokaryotic cytochromes p450 (review), Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 401–409.
Kondaveeti, S., Govindarajan, D., Mohanakrishna, G., Thatikayala, D., Abu-Reesh, I.M., Min, B., Nambi, I.M., Al-Raoush, R.I., and Aminabhavi, T.M., Sustainable bioelectrochemical systems for bioenergy generation via waste treatment from petroleum industries, Fuel, 2023, vol. 331, p. 125632.
Lan, J., Wen, F., Ren, Y., Liu, G., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., and Zhu, X., An overview of bioelectrokinetic and bioelectrochemical remediation of petroleum-contaminated soils, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2023, vol. 16, p. 100278.
Liang, R., Davidova, I.A., Teske, A., and Suflita, J.M., Evidence for the anaerobic biodegradation of higher molecular weight hydrocarbons in the Guaymas Basin, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2023, vol. 181, p. 105621.
Li, W.-W. and Yu, H.-Q., Stimulating sediment bioremediation with benthic microbial fuel cells, Biotechnol. Adv., 2015, vol. 33, pp. 1–12.
Lovley, D.R., Electrically conductive pili‒Biological function and potential applications in electronics, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 4, pp. 190–198.
Marzocchi, U., Palma, E., Rossetti, S., Aulenta, F., and Scoma, A., Parallel artificial and biological electric circuits power petroleum decontamination‒the case of snorkel and cable bacteria, Water Res., 2020, vol. 173, p. 115520.
Mbadinga, S.M., Wang, L.-Y., Zhou, L., Liu, J.-F., Gu, J.-D., and Mu, B.-Z., Microbial communities involved in anaerobic degradation of alkanes, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 1‒13.
Mohanakrishna, G., Al-Raoush, R.I., and Abu-Reesh, I.M., Sewage enhanced bioelectrochemical degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil environment through bioelectro-stimulation, Biotechnol. Rep., 2020, vol. 27, p. e00478.
Nozhevnikova, A.N., Russkova, Y.I., Litti, Y.V., Parshina, S.N., Zhuravleva, E.A., and Nikitina, A.A., Syntrophy and interspecies electron transfer in methanogenic microbial communities, Microbiology (Moscow), 2020, vol. 89, no. 2, pp. 129–147.
Paisse, S., Duran, R., Coulon, F., and Goni-Urriza, M., Are alkane hydroxylase genes (alkB) relevant to assess petroleum bioremediation processes in chronically polluted coastal sediments?, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 92, pp. 835–844.
Powell, S.M., Ferguson, S.H., Bowman, J.P., and Snape, I., Using real-time PCR to assess changes in the hydrocarbon-degrading microbial community in antarctic soil during bioremediation, Microb. Ecol., 2006, vol. 52, pp. 523–532.
Prathiba, S., Kumar, P.S., and Vo, D.-V.N., Recent advancements in microbial fuel cells: A review on its electron transfer mechanisms, microbial community, types of substrates and design for bio-electrochemical treatment, Chemosphere, 2022, vol. 286, p. 131856.
Samkov, A.A., Chugunova, Yu.A., Kruglova, M.N., Moiseeva, E.V., Volchenko, N.N., Khudokormov, A.A., Samkova, S.M., and Karaseva, E.V., Decolorization of dyes in a bioelectrochemical system depending on the immobilization of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 cells on the anode surface and electrical stimulation of an external circuit, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2023, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 198–205.
Samkov, A.A., Dzhimak, S.S., Barishev, M.G., Volchenko, N.N., Khudokormov, A.A., Samkova, S.M., and Karaseva, E.V., The effect of water isotopic composition on Rhodococcus erythropolis biomass production, Biophysics, 2015, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 107‒112.
Shvets, D. and Vinogradova, S., Occurrence and genetic characterization of grapevine pinot gris virus in Russia, Plants, 2022, vol. 11 (8), no. 1061, pp. 1–15.
Solyanikova, I.P. and Golovleva, L.A., Hexadecane and hexadecane-degrading bacteria: mechanisms of interaction, Microbiology (Moscow), 2019, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 15–26.
Tao, L., Song, M., and Jiang, G., Enhanced depolluting capabilities of microbial bioelectrochemical systems by synthetic biology, Synth. Syst. Biotechnol., 2023, vol. 8, pp. 341–348.
Taylor, S., Wakem, M., Dijkman, G., Alsarraj, M., and Nguyen, M., A practical approach to RT-qPCR‒publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines, Methods, 2010, vol. 50, pp. S1–S5.
Tourova, T.P., Sokolova, D.Sh., Semenova, E.M., Poltaraus, A.B., and Nazina, T.N., Diversity of the AlkB genes of n-alkane biodegradation in thermophilic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria of the Geobacillus, Parageobacillus, and Aeribacillus, Microbiology (Moscow), 2018, vol. 87, no. 3, pp. 301–307.
Tucci, M., Viggi, C.C., Núnez, A.E., Schievano, A., Rabaey, K., and Aulenta, F., Empowering electroactive microorganisms for soil remediation—Challenges in the bioelectrochemical removal of petroleum hydrocarbons, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, vol. 419, p. 130008.
Venkidusamy, K., Megharaj, M., Marzorati, M., Lockington, R., and Naidu, R., Enhanced removal of petroleum hydrocarbons using a bioelectrochemical remediation system with pre-cultured anodes, Sci. Total Environ., 2016, vol. 539, pp. 61–69.
Vodyanitskii, Y.N., Trofimov, S.Y., and Shoba, S.A., The influence of Fe(III) on oil biodegradation in excessively moistened soils and sediments, Euras. Soil Sci., 2015, vol. 48, no. 7, pp. 764–772.
Voeikova, T.A., Emel’yanova, L.K., Novikova, L.M., Shakulov, R.S., Sidoruk, K.V., Smirnov, I.A., Il’in, V.K., Soldatov, P.E., Tyurin-Kuz’min, A.Yu., Smolenskaya, T.S., and Debabov, V.G., Intensification of bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cells using Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 mutants with increased reducing activity, Microbiology (Moscow), 2013, vol. 82, no. 4, pp. 410–414.
Wang, H., Lu, L., Mao, D., Huang, Z., Cui, Y., Jin, S., Zuo, Y., and Ren, Z.J., Dominance of electroactive microbiomes in bioelectrochemical remediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils with different textures, Chemosphere, 2019a, vol. 235, pp. 776–784.
Wang, H., Xing, L., Zhang, H., Gui, C., Jin, S., Lin, H., Li, Q., and Cheng, C., Key factors to enhance soil remediation by bioelectrochemical systems (BESs): a review, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, vol. 419, p. 129600.
Wang, X., Wan, G., Shi, L., Gao, X., Zhang, X., Li, X., Zhao, J., Sha, B., and Huang, Z., Direct micro-electric stimulation alters phenanthrene-degrading metabolic activities of Pseudomonas sp. strain DGYH-12 in modified bioelectrochemical system, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2019b, pp. 31449–31462.
Wasmund, K., Burns, K.A., Kurtböke, D.I., and Bourne, D.G., Novel alkane hydroxylase gene (alkB) diversity in sediments associated with hydrocarbon seeps in the Timor Sea, Australia, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 75, pp. 7391–7398.
Yuan, J.S., Reed, A., Chen, F., and Stewart, C.N., Jr., Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data, BMC Bioinformatics, 2006, vol. 7, no. 85, pp. 1‒15.
Zhuravleva, E., Kovalev, A., Kovalev, D., Kotova, I., Shekhurdina, S., Laikova, A., Krasnovsky, A., Pygamov, T., Vivekanand, V., Li, L., He, C., and Litti, Y., Does carbon cloth really improve thermophilic anaerobic digestion performance on a larger scale? Focusing on statistical analysis and microbial community dynamics, J. Environ. Manage., 2023, vol. 341, p. 118124.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Chromatographic studies were carried out at the Ecological Analytical Center for Collective Research, Kuban State University.
The authors are grateful to prof. E.V. Karasev for kindly providing the strain Rhodococcus erythropolis VKM Ac-2017D.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 22-24-00401, https://rscf.ru/project/22-24-00401/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
This work does not contain any studies involving human and animal subjects.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Bulaev
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samkov, A.A., Volchenko, N.N., Musorina, T.N. et al. Biodegradation of n-Alkanes in Oil-Contaminated Bottom Sediments under Bioelectrochemical Stimulation. Microbiology 93, 314–323 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723602804
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723602804