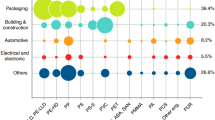
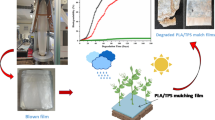
Abstract—
The degradation properties of high-density polyethylene composites filled with amylose and amylopectin polysaccharides were studied. At low dosages of the polysaccharides (0.5% wt/wt), no change in viscosity, molecular weight and physical and mechanical characteristics of HDPE samples were observed, while an increase in the proportion of the natural filler (starch) to 1 and 5% resulted in a decrease in mechanical properties, although the values of deformation and strength parameters satisfied the minimum necessary requirements for film packaging. After incubation in soil for one year, the sample of HDPE film with a corn starch content of 5% (wt/wt) was found to undergo the greatest changes in its properties. The study of ability of aerobic microorganisms to carry out the surface transformation of the studied film composites revealed that bacteria of the genus Bacillus efficiently colonized the polyethylene-starch composites. Among the identified microorganisms, micromycetes of the genus Penicillium and Trichoderma caused the most pronounced changes in the structure of the studied polymer composites, and the greatest effect was achieved in the case of synergistic action of different micromycetes genera.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aamer, A.S., Biological degradation of plastics: a comprehensive review, Biotechnol. Adv., 2006, vol. 26, pp. 246‒265.
Agzamov, R.Z., Russkov, D.V., Min, T.T., Sirotkin, A.S., and Spiridonova, R.R., On the biological degradation of polymer compositions based on polyethylene, Bull. Kazan Technol. Univ., 2012, vol. 15, no. 18, pp. 155‒158.
Barantsevich, E.P. and Barantsevich, N.E., Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical microbiology, Translyatsionnaya Meditsina, 2014, no. 6, pp. 23‒28.
Bensch, K., Groenewald, J.D., Dijksterhuis, J., Starink-Willemse, M., Andersen, B., Summerell, B.A., Shin, H.-D., Dugan, F.M., Schoroers, H.-J., Braun, U., and Grous, R.W., Species and ecological diversity within the Cladosporium cladosporioides complex (Davidiellaceae, Capnodiales), Stud. Mycol., 2010, vol. 67, pp. 1–94. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2010.67.01
Berseneva, O.A. and Kulemina, O.A., New generation polymers, modern chemistry: successes and achievements, Proc. 2nd Int. Sci. Conf., Chita, 2016, pp. 27‒29.
Bio-Damage of Hospital Buildings and Their Impact on Human Health, Shcherbo, A.P. and Antonova, V.B., Eds., S.‑Pb.: S.-Pb. Med. Acad. Postgrad. Educ., 2008, р. 232.
Blumenthal, K. and Bochaton, L., Archive: Waste indicators on generation and landfilling—monitoring sustainable development. Access mode: Archive: Waste indicators on generation and landfilling—monitoring sustainable development. Statistics Explained (europa.eu) / Waste_indicators on generation and landfilling—monitoring sustainable development 2004‒2010‒2013.
Dildi, A.K.F, Linear low density polyethylene —biodegradability using bacteria from marine benthic environment and photodegradability using ultraviolet light, Ph. D. Thesis, Kerala, India, 2011.
Encalada, K., Aldás, M.B., Proaño, E., and Valle, V., An overview of starch-based biopolymers and their biodegradability, Revista Ciencia e Ingeniería, 2018, vol. 39, pp. 245‒258.
https://takiedela.ru/news/2020/10/14/grinpis-plastikvot-ching-2/.
Kotova, I.B. Taktarova, Yu.V., Tsavkelova, E.A., and Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A., Microbial degradation of plastics and approaches to make it more efficient, Microbiology (Moscow), 2021, vol. 90, pp. 671‒701.
Koutny, M., Sancelme, M., Dabin, C., Pichon, N., Delort, A.-M., and Lemaire, J., Acquired biodegradability of polyethylenes containing pro-oxidant additives, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, vol. 91, pp. 1495–1503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.10.007
Litvinov, M.A., Metody izucheniya pochvennykh mikroskopicheskikh gribov (Methods for Investigation of Soil Microscopic Fungi), Moscow: Nauka, 1969.
Litvinov, M.A., Opredelitel’ mikroskopicheskikh pochven-nykh gribov (Manual for Identification of Microscopic Soil Fungi), Leningrad: Nauka, 1967.
Mazitova, A.K., Aminova, G.K., Zaripov, I.I., and Vikhareva, I.N., Biodegradable polymer materials and modifying additives: present state. Part 2, Nanotekhnol v Proizvodstve. Razrabotka novykh polimernykh materialov (Nanotechnologies in Industry. Development of New Polymer Materials), 2021, vol. 13, pp. 32‒38. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2021-13-1-32-38
Nafchi, A.M. Moradpour, M., Saeidi, M., and Alias, A.K., Thermoplastic starches: properties, challenges, and prospects, Starch, 2013, vol. 65, pp. 61–72.
Nagarkar, R. and Patel, J., Polyvinyl alcohol: a comprehensive study, Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci., 2019, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 34‒44.
Nowak, B., Pajak, J., Drozd-Bratkowicz, M., and Rymarz, G., Microorganisms participating in the biodegradation of modified polyethylene films in different soils under laboratory conditions, Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 757–767.
Podkorytova, A.V., Marine plant biopolymers, Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Biotechnology and Life Quality,” Moscow, 2014, pp. 498‒499.
Rajandas, H., Parimannan, S., Sathasivam, K., Ravichandran, M., and Yin, L.S., A novel FTIR-ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation, Polymer Testing, 2012, vol. 31, pp. 1094–1099.
Raziyafatima, M., Microbial degradation of plastic waste: a review, J. Pharma Chem. Biol. Sci., 2016, vol. 4, pp. 231‒242.
RF Patent no. 2669865C1, Composition for obtaining biodegradable polymer material and biodegradable polymer material on it is basis, 2016.
Roy, P.K., Titus, S, Surekha, P., Tulsi, E., Deshmukh, C., and Rajagopal, C., Degradation of abiotically aged LDPE films containing pro-oxidant by bacterial consortium, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2008, vol. 93, pp. 1917–1922.
Santo, M., Weitsman, R., and Sivan, A., The role of the copper-binding enzyme—laccase—in the biodegradation of polyethylene by the actinomycete Rhodococcus ruber, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr., 2013, vol. 84, pp. 204–210.
Shah, A.A., Biodergadation of natural and synthetic rubbers: a review, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr., 2013, vol. 83, pp. 145‒157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.05.004
Shah, A.A., Hasan, F., Hameed, A., and Ahmed, S., Biological degradation of plastics: a comprehensive review, Biotechnol. Adv., 2008, vol. 26, pp. 246–265.
Sudhakar, M., Doble, M., Murthy, P.S., and Venkatesan, R., Marine microbe-mediated biodegradation of low- and high-density polyethylenes, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr., 2008, vol. 61, pp. 203–212.
Suslova, T.N., Nikonorova, V.N., Sosnovskaya, L.B., Gilaeva, G.V., and Salakhov, I.I., Evaluation of the effectiveness of destruction of compositions based on polyethylene and starch, Bull. Kazan Technol. Univ., 2014, vol. 17, no. 24, pp. 120‒123.
Tasekeev, M.S. and Eremeeva, L.M., Proizvodstvo biopolimerov kak odin iz putei resheniya problem ekologii i APK (Production of Biopolymers as an Approach to Solving the Problems of Ecology and AIC), Almaty: NTs NTI, 2009, р. 7.
Wong, P.K., Preparation and characterization of polymeric biocomposites using plant-based materials, MS Thesis, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by P. Sigalevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suslova, T.N., Salakhov, I.I., Nikonorova, V.N. et al. Biodegradation Features of Composite Materials Based on High-Density Polyethylene and Starch. Microbiology 92, 695–703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723601653
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723601653