Abstract
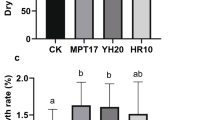
Kengyilia thoroldiana is a nutritionally rich grass species of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Here, to improve its quality and biomass via biological fertilization, we sought out plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. Our screening found one Bacillus species capable of nitrogen fixation, indole-3-acetic acid production, and tolerating the extreme saline-alkali soil of Qinghai Province. We determined the strain’s growth performance and antagonistic effects with pathogens (Fusarium graminearum, F. acuminatum) and evaluated its impact on K. thoroldiana. The test strain KKLW1 was identified as Bacillusamyloliquefaciens by morphology, adversity culture, and 16S rDNA and gyrB partial sequence analyses. KKLW1 strongly tolerates saline conditions (11% salt, pH 11), and showed stable nitrogen fixation activity and IAA production capacity; its Phl gene, which we amplified, was significant antagonistic to pathogenic pasture fungi. Furthermore, compared with the control, the strain showed clear germination and growth-promoting activity after soaking grass seeds and root-irrigating with the Bacillus suspension, increasing each by 8 and 10–12%, respectively. In sum, the strain KKLW1 has excellent biological properties and stable physiological characteristics in this extreme environment of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. We propose KKLW1 for use as a functional strain of microbial fertilizer to increase production and restore vegetation coverage of the Plateau’s grassland.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ali, R.M., Houghton, P.J., and Hoo, T.S., Antifungal activity of some bignoniaceae found in malaysia, Phytother. Res., 2015, vol. 12, pp. 331‒334.
Bhadury, P. and Austen, M.C., Barcoding marine nematodes: an improved set of nematode 18S rRNA primers to overcome eukaryotic co-interference, Hydrobiologia, 2010, vol. 641, pp. 245‒251.
Chen, L., Liu, Y., Wu, G., Veronican, Njeri. K., Shen, Q., Zhang, N., and Zhang, R., Induced maize salt tolerance by rhizosphere inoculation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9, Physiol. Plant., 2016, vol. 158, pp. 34‒44.
Das, K., and Mukherjee, A.K., Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from north-east India, Bioresour. Technol., 2007, vol. 98, pp. 1339‒1345.
Dong, Q., Zhao, X., Wu, G., Shi, J., and Ren, G., A review of formation mechanism and restoration measures of “black-soil-type” degraded grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Environ. Earth Sci., 2013, vol. 70, pp. 2359‒2370.
Dong, Q.M., Zhao, X.Q., Wu, G.L., and Chang, X.F., Optimization yak grazing stocking rate in an alpine grassland of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci., 2015, vol. 73, pp. 2497‒2503.
Dong, S.K., Wen, L., Li, Y.Y., Wang, X.X., Zhu, L., and Li, X.Y., Soil-quality effects of grassland degradation and restoration on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2012, vol. 76, pp. 2256‒2264.
Duarte, G.R.M., Price, C.W., Augustine, B.H., Carrilho, E., and Landers, J.P., Dynamic solid phase DNA extraction and PCR amplification in polyester-toner based microchip, Anal. Chem., 2011, vol. 83, pp. 5182‒5189.
Eriksen, J., Pedersen, L., and Jorgensen, J.R., Nitrate leaching and bread-making quality of spring wheat following cultivation of different grasslands, Agric., Ecosyst. Environ., 2006, vol. 116, pp. 165‒175.
Fan, B., Chen, X.H., Budiharjo, A., Bleiss, W., Vater, J., and Borriss, R., Efficient colonization of plant roots by the plant growth promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, engineered to express green fluorescent protein, J. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 151, pp. 303‒311.
Fang, X.Z., Deng, W., Yuan, Y.W., and Zhao, C.H., The impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland productivity in Qinghai Province, China, Front. Earth Sci., 2014, vol. 8, pp. 93‒103.
Gaiero, J.R., and Dunfield, K.E., Inside the root microbiome: bacterial root endophytes and plant growth promotion, Am. J. Bot., 2013, vol. 100, pp. 1738‒1750.
Gong, G., Kim, S., Lee, S.M., Woo, H.M., Park, T.H., and Um, Y., Complete genome sequence of Bacillus sp. 275, producing extracellular cellulolytic, xylanolytic and ligninolytic enzymes, J. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 254, pp. 59‒62.
Idris,E.E., Iglesias, D.J., Talon, M., and Borriss, R., Tryptophan-dependent production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2007, vol. 20, pp. 619‒626.
Karlidag, H., Esitken, A., Turan, M., and Sahin, F., Effects of root inoculation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on yield, growth and nutrient element contents of leaves of apple, Sci. Hortic., 2007, vol. 114, pp. 16‒20.
Kayalvizhi, N. and Gunasekaran, P., Production and characterization of a low-molecular-weight bacteriocin from Bacillus licheniformis, MKU3, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 47, pp. 600‒607.
Kizilkaya, R., Nitrogen fixation capacity of Azotobacter spp. strains isolated from soils in different ecosystems and relationship between them and the microbiological properties of soils, J. Environ. Biol., 2009, vol. 30, pp. 73‒82.
Kloepper, J.W., Ryu, C.M., and Zhang, S., Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp., Phytopathology, 2004, vol. 94, pp. 1259‒1266.
Li, C.H., Li, S.J., Lei, Y.S., Hu, K., Wang, P.Y., and Sun, H.Q., Study on drought resistance of four native grass species, Pratacul. Sci., 2013, vol. 9, pp. 1386‒1393.
Li, C.H., Li, S.J., Zhang, J., and Sun, H.Q., Observations on spike differentiation of Kengyilia thoroldiana, Pratacul. Sci., 2013, vol. 8, pp. 1189‒1193.
Li, S.J., Li, C.H., and Sun, H.Q., Research progress and development prospect on Kengyilia thoroldiana, Pratacul. Sci., 2009, vol. 1, pp. 64‒68.
Lin, D., Xu, Q., Liu, Y., Wei, J., Qu, L., Gu, H., and Chen, Z.L., The antibacterial effect of the secreted peptide from Bacillus subtilis SO113 and separation and purification of the antibacterial peptides, Chin. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2001, vol. 9, pp. 77‒80.
Lulai, E.C., Suttle, J.C., Olson, L.L., Neubauer, J.D., Campbell, L.G., and Campbell, M.A., Wounding induces changes in cytokinin and auxin content in potato tuber, but does not induce formation of gibberellins, J. Plant Physiol., 2015, vol. 192, pp. 22‒28.
Mena-Violante, H.G. and Olalde-Portugal, V., Alteration of tomato fruit quality by root inoculation with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Bacillus subtilis, BEB-13BS, Sci. Hortic., 2007, vol. 113, pp. 103‒106.
Mizuguchi, Y., Fukunaga, M., and Taniguchi, H., Plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid and translucent-to-opaque variation in mycobacterium intracellulare 103, J. Bacteriol., 1981, vol. 146, pp. 656–659.
Nahi, A., Othman, R., and Omar, D., Effects of SB16 bacterial strain and herbicides on endophytic bacterial populations and growth of aerobic rice, Plant, Soil Environ., 2016, vol. 62, pp. 453‒459.
Ping, X., Jiang, Z., and Li, C., Status and future perspectives of energy consumption and its ecological impacts in the Qinghai–Tibet region, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2011, vol. 15, pp. 514‒523.
Poopathi, S., and Kumar, K.A., Novel fermentation media for production of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis., J. Econ. Entomol., 2003, vol. 96, pp. 1039‒1044.
Rehman, H.U., Siddique, N.N., Aman, A., Nawaz, M.A., Baloch, A.H., and Qader, S.A.U., Morphological and molecular based identification of pectinase producing Bacillus licheniformis, from rotten vegetable, J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 13, pp. 139‒144.
Ruizherrera, J., Leónramírez, C., Veranuñez, A., Sánchezarreguín, A., Ruizmedrano, R., and Salgadolugo, H., A novel intracellular nitrogen-fixing symbiosis made by ustilago maydis and Bacillus spp., New Phytol., 2015, vol. 207, pp. 769‒777.
Santoyo, G., Moreno-Hagelsieb, G., Del, C.O.M., and Glick, B.R., Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes, Microbiol. Res., 2016, vol. 183, pp. 92‒99.
Shao, J., Xu, Z., Zhang, N., Shen, Q., and Zhang, R., Contribution of indole-3-acetic acid in the plant growth promotion by the rhizospheric strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, SQR9, Biol. Fertil. Soils, 2015, vol. 51, pp. 321‒330.
Shiau, Y.J. and Chu, C.Y., Comparative effects of ultrasonic transducers on medium chemical content in a nutrient mist plant bioreactor, Sci. Hortic., 2010, vol. 123, pp. 514‒520.
Stoof, C.R., Richards, B.K., Woodbury, P.B., Fabio, E.S., Brumbach, A.R., and Cherney, J., Untapped potential: opportunities and challenges for sustainable bioenergy production from marginal lands in the northeast USA, BioEnergy Res., 2015, vol. 8, pp. 482‒501.
Strauss, M.L.A., Jolly, N.P., Lambrechts, M.G., and Rensburg, P.V., Screening for the production of extracellular hydrolytic enzymes by non-saccharomyces wine yeasts, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 91, pp. 182‒190.
Voort, M.V.D., Meijer, H.J.G., Schmidt, Y., Watrous, J., Dekkers, E., Mendes, R., Dorrestein, P.C., Gross, H., and Raaijmakers, J.M., Genome mining and metabolic profiling of the rhizosphere bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SHC 52 for antimicrobial compounds, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 6, p. 693.
Xie, S., Wu, H., Zhang, H., Wu, L., Zhu, Q., and Gao, X., Plant growth promotion by spermidine-producing Bacillus subtilis OKB105, Mol. Plant Microbe Interact., 2014, vol. 27, pp. 655‒663.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors are grateful to the authorities of respective departments for support in doing this research. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31660543) and International Sci-Technology Cooperation Project of Qinghai Provincial Science and Technology Department (2018-HZ-813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Xie, Y., Qiao, J. et al. Rhizobacteria Strain from a Hypersaline Environment Promotes Plant Growth of Kengyilia thoroldiana. Microbiology 88, 220–231 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020127
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020127