Abstract
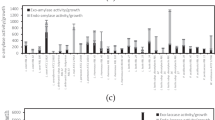
Genetic certification of commercial strains of bacteria antagonistic to phytopathogenic microorganisms guarantees their unequivocal identification and confirmation of safety. In Russia, unlike EU countries, genetic certification of Bacillus subtilis strains is not used. Based on the previously proposed double digestion selective label (DDSL) fingerprinting, a method for genetic identification and certification of B. subtilis strains was proposed. The method was tested on several strains differing in their physiological and biochemical properties and in the composition of secondary metabolites responsible for the spectrum of antibiotic activity. High resolving power of this approach was shown. Optimal restriction endonucleases (SgsI and Eco32I) were determined and validated. A detailed protocol for genetic certification of this bacterial species was developed. DDSL is a universal method, which may be adapted for genetic identification and certification of other bacterial species. Keywords: genotyping, restriction
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bais, H.P., Fall, R., and Vivanco, J.M., Biocontrol of Bacillus subtilis against infection of Arabidopsis roots by Pseudomonas syringae is facilitated by biofilm formation and surfactin production, Plant Physiol., 2004, vol. 134, no. 1, pp. 307–319.
Barbosa, T.M., Serra, C.R., La Ragione, R.M., Woodward, M.J., and Henriques A.O., Screening for Bacillus isolates in the broiler gastrointestinal tract, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 968–978.
Bikandi, J., San Millan, R., Rementeria, A., and Garaizar, J., In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR and endonuclease restriction, Bioinformatics, 2004, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 798–799.
Botina, S.G., Molecular genetic identification, DNA genotyping, and certification of lactic acid bacteria of the genus Lactobacillus, in V S’ezd genetikov i selektsionerov (5th Congress of Geneticists and Breeders), Moscow, 2009, p. 49.
Cazorla, F.M., Romero, D., Pérez-García, A., Lugtenberg, B.J., Vicente, A.D., and Bloemberg, G., Isolation and characterization of antagonistic Bacillus subtilis strains from the avocado rhizoplane displaying biocontrol activity, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 103, no. 5, pp. 1950–1959.
El-Hamshary, O.I.M., Abo-Aba, S.E.M., Awad, N., and Gomaa, A.M., Genetic profile of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis indigenous isolates and their performance as Bio-control agent against the plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum, Res. J. Cell Mol. Biol., 2008, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 30–38.
Fakhr, M.K., Nolan, L.K., and Logue, C.M., Multilocus sequence typing lacks the discriminatory ability of pulsedfield gel electrophoresis for typing Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 2215–2219.
Hosoi, T., Strain typing of Bacillus subtilis (natto) using a modified randomly amplified polymorphic DNA method, Bull. Tokyo Metropol. Agr. For. Res. Cent., 2010, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 45–48.
Leser, T.D., Knarreborg, A., and Worm, J., Germination and outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis spores in the gastrointestinal tract of pigs, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 104, no. 4, pp. 1025–1033.
Marten, P., Smalla, K., and Berg, G. Genotypic and phenotypic differentiation of an antifungal biocontrol strain belonging to Bacillus subtilis, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 89, no. 3, pp. 463–471.
Mitani, N., Koizumi, A., Sano, R., Masutani, T., Murakawa, K., Mikasa, K., and Okamoto, Y., Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by PCR-RFLP and its usefulness in an epidemiological study of an outbreak, Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 2005, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 250–252.
Novikova, I.I., Polyfunctional biopreparations for plant protection against diseases, Zashchita i Karantin Rastenii, 2005, no. 2, pp. 22–26.
Novikova, I.I. and Shenin, Yu.D., Isolation, identification and antifungi activity of metabolites of Gamair complex generated by Bacillus subtilis strain M-22, producer of biopreparation for plant protection against mycosis and bacteriosis, Biotechnology (Moscow), 2011, no. 2, pp. 45–48.
Shenin, Yu.D., Novikova, I.I., Kruglikova, L.F., and Kaljko, G.V., Characterization of Alirin B, major component of fungicide preparation produced by Bacillus subtilis-10-VIZR strain, Antibiot. Chemother., 1995, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 3–7.
Tapaljskiy, D.V., Osipov, V.A., and Zhavoronok, S.V., Phenotypic and molecular genetic typing of Salmonella: actual state and prospects, J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol., 2005, no. 6, pp. 88–93.
Terletski, V., Schwarz, S., Carnwath, J., and Niemann, H., Typing of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovars Choleraesuis, Typhimurium, Dublin and laboratory strains of Escherichia coli using subtracted restriction fingerprinting (SRF), Microbiol. Res., 2003, vol. 158, no. 2, pp. 135–142.
Terletskiy, V., Kuhn, G., Francioli, P., and Blanc, D., Application and evaluation of double digest selective label (DDSL) typing technique for Pseudomonas aeruginosa hospital isolates, J. Microbiol. Methods, 2008, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 283–287.
Terletskii, V.P., Tyshchenko, V.I., Novikova, O.B., Borisenkova, A.N., Belash, D.E., and Yakovlev, A.F., An efficient molecular genetic method for identification of Salmonella and Proteus strains, Doklady RASKhN, 2013, no. 5, pp. 60–63.
Willse, A., Straub, T.M., Wunschel, S.C., Small, J.A., Call, D.R., Daly, D.S., and Chandler, D.P., Quantitative oligonucleotide microarray fingerprinting of Salmonella enterica isolates, Nucl. Acids Res., 2004, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 1848–1856.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Terletsky, V.I. Tyshchenko, I.I. Novikova, I.V. Boikova, S.D. Tyulebaev, I.Ya. Shakhtamirov, 2016, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2016, Vol. 85, No. 1, pp. 50–55.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terletsky, V.P., Tyshchenko, V.I., Novikova, I.I. et al. An efficient method for genetic certification of Bacillus subtilis strains, prospective producers of biopreparations. Microbiology 85, 71–76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716010136
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716010136