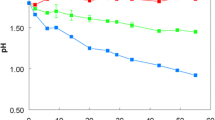
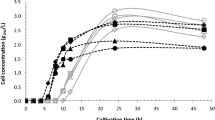
Abstract
Brevibacteria able to decrease phosphate concentration in the medium are of interest for the study of the role of bacteria in the phosphorus cycle and for development of biotechnology of phosphate removal from waste. Brevibacterium casei, Brevibacterium linens, and Brevibacterium epidermidis grown in media with initial phosphorus concentrations of 1–11 mM were shown to decrease its concentration by 90%. The composition of the incubation medium required for B. casei to carry out this process was established. This process occurs in the absence of glucose but requires the presence of Mg2+, NH +4 , and α-ketoglutarate. The latter two components may be replaced by amino acids metabolized to NH +4 and α-ketoglutarate: histidine, arginine, glutamine, proline, or glutamic acid. No formation of insoluble phosphate salts was observed when the media were incubated under the same conditions with heat-inactivated cells or without cells at pH 7–8.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schink, B., Biological Cycling of Phosphorus, Met. Ions Biol. Syst., 2005, vol. 43, pp. 131–151.
McGrath, J.W. and Quinn, J.P., Microbial Phosphate Removal and Polyphosphate Production from Waste Waters, Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 2003, vol. T. 52, pp. 75–100.
Seviour, R.G., Mino, T., and Onuki, M., The Microbiology of Biological Phosphorus Removal in Activated Sludge, FEMS. Microbiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 27, pp. 99–127.
Kortstee, G.J.J., Appeldoorn, K.J., Bonting, C.F.C., van Nil, E.W.J., and van Veen, H.W., Recent Developments in the Biochemistry and Ecology of Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal, Biochemistry (Moscow) (Engl. Transl.), 2000, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 332–340.
Mino, T., Microbial Selection of Phosphatase-Accumulating Bacteria in Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment Processes for Enhanced Biological Phosphate Removal, Biochemistry (Moscow) (Engl. Transl.), 2000, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 341–348.
Keasling, J.D., van Daien, S.J., Trelstad, P., Renninger, N., and McMahon, K., Application of Polyphosphate Metabolism to Environmental and Biotechnological Problems, Biochemistry (Moscow) (Engl. Transl.), 2000, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 324–331.
Van Niel, E.W.J., De Best, J.H., Kets, E.P.W., Bonting, C.F.C., and Kortstee, G.J.J., Polyphosphate Formation by Acinetobacter johnsonii 210A: Effect of Cellular Energy Status and Phosphate-Specific Transport System, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1999, vol. 51, pp. 639–646.
Santos, M.M., Lemos, P.C., Reis, M.A.M., and Santos, H., Glucose Metabolism and Kinetics of Phosphorus Removal by the Fermentative Bacterium Microlunatus phosphovorus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 65, no. 9, pp. 3920–3928.
Zilles, J.L., Peccia, J., Kim, M.W., Hung, C.H., and Noguera, D.R., Involvement of Rhodocyclus-Related Organisms in Phosphorus Removal in Full Scall Wastewater Treatment Plants, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 68, pp. 2763–2769.
Goncharova, I.V. and Gerasimenko, L.M., Dynamics of Inorganic Phosphate Consumption by Microcoleus chthonoplastes Cells, Mikrobiologiya, 1993, vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 1048–1055.
Smirnov, A.V., Suzina, N.E., Kulakovskaya, T.V., and Kulaev, I.S., Magnesium Orthophosphate, a New Form of Reserve Phosphate in the Halophilic Archaeon Halobacterium salinarium, Mikrobiologiya, 2002, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 786–793 [Microbiology (Engl. Transl.), vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 677–683].
Smirnov, A., Suzina, N., Chudinova, N., Kulakovskaya, T., and Kulaev, I., Formation of Insoluble Magnesium Phosphates During Growth of the Archaea Halorubrum distributum and Halobacterium salinarium and the Bacterium Brevibacterium antiquum, FEMS Microb. Ecol., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 129–137.
Kulakovskaya, T.V., Andreeva, N.A., Karpov, A.V., Sidorov, I.S., and Kulaev, I.S., Hydrolysis of Tripolyphosphate by Purified Exopolyphosphatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cytosol: Kinetic Model, Biokhimiya, 1999, vol. 64, no. 9, pp. 1180–1184 [Biochemistry (Moscow) (Engl. Transl.), vol. 64, no. 9, pp. 990–993.
Lehninger, A.L., Osnovy biokhimii (Principles of Biochemistry), Worth, 1982 [Russ. Transl. Moscow: Mir, 1985].
Wu, O., Bishop, P.L., and Keener, T.C., Biological Phosphate Uptake and Release: Effect of pH and Magnesium Ions, Water Environ. Res., 2006, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 196–201.
Van Veen, H.W., Abee, T., Kortstee, G.J.J., Konings, W.N., and Zehnder, A.J.B., Characterization of Two Phosphate Transport Systems in Acinetobacter johnsonii Strain 210A, J. Bacteriol., 1993, vol. 175, pp. 200–206.
Schornborn, C., Bauer, H.D., and Roske, I., Stability of Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal and Composition of Polyphosphate Granules, Water Res., 2001, vol. 35, pp. 3190–3196.
Javelle, A., Thomas, G., Marini, A.-M., Kramer, R., and Merrick, M., In Vivo Functional Characterization of the Escherihia coli Ammonium Channel AmtB: Evidence for Metabolic Coupling of AmtB To Glutamine Synthetase, Biochem. J., 2005, vol. 390, pp. 215–222.
Tynecka, Z., Korona-Glowniak, I., and Los, R. 2-Oxoglutarate Transport System in Staphylococcus aureus, Arch. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 176, pp. 143–150.
Magasanik, B., The Regulation of Nitrogen Utilization in Enteric Bacteria, J. Cell. Biochem., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 34–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.P. Ryazanova, A.V. Smirnov, T.V. Kulakovskaya, I.S. Kulaev, 2007, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2007, Vol. 76, No. 6, pp. 752–758.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryazanova, L.P., Smirnov, A.V., Kulakovskaya, T.V. et al. Decrease of phosphate concentration in the medium by Brevibacterium casei cells. Microbiology 76, 663–668 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261707060033
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261707060033