Abstract
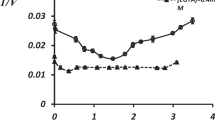
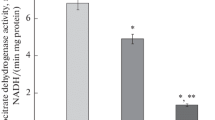
Na+/K+-ATPase (sodium, potassium adenosine triphosphatase, EC 3.6.3.9) activity has been studied in whole erythrocytes from rats over time of total food deprivation for 1, 3, 5, 7–8, and 10–12 days with free access to water. Changes in Na+/K+-ATPase activity have been found to be phase-specific, i.e., associated with periods of certain metabolism level. After the hunger state and accommodation to endogenous nutrition (phases 0-I), from the 3rd to the 7th–8th day a period of compensated accommodation begins (phase II characterized by a stable euglycemic state, while the level of plateau of protein losses and hormonal stimulation are achieved). The Na+/K+-ATPase activity changes during the phase II were insignificant (p > 0.05), but potassium loss was observed in erythrocytes and blood plasma from the 5th day of starvation onwards. The phase III (the 10th–12th days) is an onset of the terminal period characterized by the lower activities of Na+/K+-ATPase (ouabain-sensitive activity) and Mg2+-ATPase (ouabain-independent activity) and by reduced sodium plasma levels that previously had remained virtually unchanged. There are considered possible causes of the observed decrease in the Na+/K+-ATPase activity during prolonged starvation, such as aging of the circulating erythrocyte population (the absence of reticulocytes and young erythrocytes), depletion of cell energy resources (hypoglycemia and glycopenia), effect of endogenous ouabain, and endotoxemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ataullakhanov, F.I., Vitvitskii, V.M., and Komarova, S.V., Energy-Dependent Processes and Adenylate Metabolism in Human Erythrocytes, Biokhimiya, 1996, vol. 61, pp. 266–274.
Jorgensen, P.L., Hakansson, K.O., and Karlish, S.J.D., Structure and Mechanism of Na,KATPase: Functional Sites and Their Interactions, Ann. Rev. Physiol., 2003, vol. 65, pp. 817–849
Zhao, M.J. and Willis, J.S., Reduced Ion Transport in Erythrocytes of Male Sprague-Dawley Rats during Starvation, J. Nutrit., 1988, vol. 118, pp. 1120–1127.
Caloin, M., Modeling of Lipid and Protein Depletion during Total Starvation, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2004, vol. 287, pp. E790–E798.
Young, R., and Ruderman, N.B., Starvation in the Rat. II. Effect of Age and Obesity on Protein Sparing and Fuel Metabolism, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrin. Metab., 1980, vol. 239, pp. E277–E286.
Al-Qarawi, A.A. and Mousa, H.M., Lipid Concentrations in Erythrocyte Membranes in Normal, Starved, Dehydrated and Rehydrated Camels (Camelus dromedarius), and in Normal Sheep (Ovis aries) and Goats (Capra hircus), J. Arid. Environ., 2004, vol. 59, pp. 675–683.
Romero, P.J. and Romero, E.A., Differences in Ca2+-Pump Activity between Sub-Populations of Human Red Cells, Cell Calcium, 1997, vol. 21, pp. 353–358.
Kazennov, A.M., Maslova, M.N., and Shalabodov, A.D., A study of Na,K-ATPase Activity in Mammal Erythrocytes, Biokhimiya, 1984, vol. 49, no. 7, pp. 1089–1094.
Malakhova, M.Ya., Metod registratsii endogennoi intoksikatsii. Metodich. rekomendatsii (A Method of Recording of Endogenous Intoxication. Methodical Recommendations), St. Petersburg, 1995, 33 p.
Kerimov, B.F., Glutathione-Deficient State of Nervous Tissues in Starved Animals Intensifies Lipid Peroxidation and Oxidation of Protein SH-Groups, Ukr. Biokhim. Zh., 2004, vol. 76, no. 1, pp. 108–113.
Lang, K.S., Lang, P.A., Bauer, C., Duranton, C., Wieder, T., Huber, S.M., and Lang, F., Mechanisms of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death, Cell Physiol. Biochem., 2005, vol. 15, pp. 195–202.
Mindukshev, I.V., Krivoshlyk, V.V., Dobrylko, I.A., Goncharov, N.V., Vivulanets, E.V., Kuznetsov, S.S., and Krivchenko, A.I., Abnormalities of Elastic and Transporting Properties of Red Blood Cells under Development of Their Apoptosis, Biol. Membrany, 2010, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 28–38.
Vasić, V., Momić, T., Petković, M., and Krstić, D., Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds (Review), Sensors, 2008, vol. 8, pp. 8321–8360.
Tomoyuki, M., Shigeharu, T., Takashi, O., Satoko, N., Hisataka, I., Hiroki, S., Masayuki, T., Keiji, S., and Masaru, N., Effects of Reduced Food Intake on Toxicity Study Parameters in Rats, J. Toxicol. Sci., 2008, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 537–547.
Dudzinska, W. and Hlynczak, A.J., Purine Nucleotides and Their Metabolites in Erythrocytes of Streptozotocin Diabetes Rats, Diabetes Metab., 2004, vol. 30, pp. 557–567.
McCue, M.D., Starvation Physiology: Reviewing the Different Strategies Animals Use to Survive a Common Challenge, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol., 2010, vol. 156/1, pp. 1–18.
Schoner, W. and Scheiner-Bobis, G., Endogenous and Exogenous Cardiac Glycosides: Their Roles in Hypertension, Salt Metabolism, and Cell Growth, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 2007, vol. 293, pp. C509–C536.
Karaman, Yu.K., Novgorodtseva, T.P., and Zhukova, N.V., Phospholipid Composition of Erythrocytes and Glutathione Redox System in Rats during Adaptation to Cholesterol Load, Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 2010, vol. 150, no. 9, pp. 291–294.
Yaffe, S., Gold, A., and Sampugna, J., Effects of Prolonged Starvation on Plasma Free Fatty Acid Levels and Fatty Acid Composition of Myocardial Total Lipids in the Rat, J. Nutr., 1980, vol. 110, pp. 2490–2496.
Katyukhin, L.N., Skverchinskaya, E.A., Ganelina, I.E., and Stepanova, T.A., Rheological Parameters of Blood in Acute Myocardical Infarction, Kardiologiya, 1999, vol. 2. pp. 41–44.
Skverchinskaya, E.A., Endocrine-Metabolic State in Healthy Humans and in Asthmatics under Total Food Deprivation, Candidate Sci. Dissertation, Leningrad, 1995.
Davydovsky, A.G., The Problem of “Molecular Aging and Deterioration” of Erythron under Antitumor Chemotherapy (Mechanisms, Hypothesis of “Erythrocyte Bystander Effect”, Experience of Mathematical Simulation, Perspectives), Onkol. Zh., 2007, no. 2, http:,omr.med.by/index.php?option=com-content&view=article&id=94&Itemid=107&lang=ru
Fedorova, O.V., Korostovtseva, L.S., Shapiro, J.I., and Bagrov, A.Y., Endogenous Cardiotonic Steroids: Clinical Perspectives, Arterialnaya gipertenziya, 2008, vol. 14. no. 3. pp. 220–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.A. Skverchinskaya, T.V. Tavrovskaya, A.V. Novozhilov, 2013, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2013, Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 144–152.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skverchinskaya, E.A., Tavrovskaya, T.V. & Novozhilov, A.V. Na+/K+-ATPase activity in rat erythrocytes after prolonged starvation. J Evol Biochem Phys 49, 183–192 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093013020072
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093013020072