Abstract
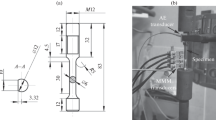
This work is focused on an experimental study of E26-2 pipeline steel tearing by mode III. The crack propagation length is obtained as a function of the applied force magnitude for specimens of different thicknesses and widths. The critical stress intensity factor and the essential work needed for crack propagation are determined by the energy balance method. It is demonstrated that these variables depend on the pipeline thickness and specimen geometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. R. Irwin, “Fracture Testing of High-Strength Sheet Materials under Conditions Appropriate for Stress Analysis,” Report No. 5486 (U.S. Naval Res. Lab., 1960).
G. C. Sih, “Stress Distribution near Internal Crack Tips for Longitudinal Shear Problems,” J. Appl. Mech. 32, 51–58 (1965).
P. K. Poulose, D. L. Jones, and H. Liebowitz, “Determination of Nonlinear Energy Toughness Values for Cyclic Loading Applications,” Eng. Fracture Mech. 8 (1), 293–299 (1976).
R. J. A. Ehart, S. E. Stanzl-Tschegg, and E. K. Tschegg, “Crack Face Interaction and Mixed Mode Fracture of Wood Composites during Mode III Loading,” Eng. Fracture Mech. 61, 253–278 (1998).
A. Szekrenyes, “Improved Analysis of the Modified Split-Antilever Beam for Mode-III Fracture,” Int. J. Mech. Sci. 51, 682–693 (2009).
V. Lazarus and J.-B. Leblond, “Crack Paths under Mixed Mode (I+III) or (I+II+III) Loadings,” C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Ser. 2b 326, 171–177 (1998).
M. F. S. F. de Moura, M. V. C. Fernandez, A. B. de Morais, and R. D. S. G. Campilho, “Numerical Analysis of the Edge Crack Torsion Test for Mode III Interlaminar Fracture of Composite Laminates,” Eng. Fracture Mech. 76, 469–478 (2009).
M. Meriem-Benziane and B. Bou-Said, “Determination of Friction Factor of Algerian Crude Oil during Flow in Pipe-Lines,” Flow Measur. Instrum. 33, 28–35 (2013).
A. A. Carvalho, J. M. A. Rebello, M. P. V. Souza, et al., “Reliability of Non-Destructive Test Techniques in the Inspection of Pipelines Used in the Oil Industry,” Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping 85, 745–751 (2008).
F. S. Ribeiro, P. R. Souza Mendes, and S. L. Braga, “Obstruction of Pipelines Due to Paraffin Deposition during the Flow of Crude Oils,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 40 (18), 4319–4328 (1997).
S. Frimpong, J. Szymanski, and R. M. M. Changirwa, “Oil Sands Slurry and Waste Recycling Mechanics in a Flexible Pipeline System,” Resources, Conservat. Recycling 39, 33–50 (2003).
S. Cravero and C. Ruggieri, “Correlation of Fracture Behavior in High Pressure Pipelines with Axial Flaws Using Constraint Designed Test Specimens. Pt 1. Plane-Strain Analyses,” Eng. Fracture Mech. 72, 1344–1360 (2005).
R. Banki, H. Hoteit, and A. Firoozabadi, “Mathematical Formulation and Numerical Modeling of Wax Deposition in Pipelines from Enthalpy-Porosity Approach and Irreversible Ihermodynamics,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 51, 3387–3398 (2008).
P. Tang, J. Yang, J. Zheng, et al., “Failure Analysis and Prediction of Pipes Due to the Interaction between Multiphase Flow and Structure,” Eng. Failure Anal. 16, 1749–1756 (2009).
F. Dotta and C. Ruggieri, “Structural Integrity Assessments of High Pressure Pipelines with Axial Flaws Using a Micromechanics Model,” Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping 81, 761–770 (2004).
V. T. Sapounov, E. M. Morozov, Z. Azari, and G. Pluvinage, “Déchirement Ductile en Statique des Alliages D’aluminium,” Rev. Franc. Mec., No. 3, 239–244 (1994).
A. R. Shahani, M. Rastegar, M. Botshekanan Dehkordi, and H. Moayeri Kashani, “Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Thickness Effect on Ductile Fracture Toughness of Steel Alloy Sheets,” Eng. Fracture Mech. 77, 646–659 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M. Meriem-Benziane, H. Zahloul.
Translated from Prikladnaya Mekhanika i Tekhnicheskaya Fizika, Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. 182–189, May–June, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meriem-Benziane, M., Zahloul, H. Experimental study of pipelines steel. J Appl Mech Tech Phy 56, 502–509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894415030219
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894415030219